Introduction
The Roles of Financial Reporting and FSA
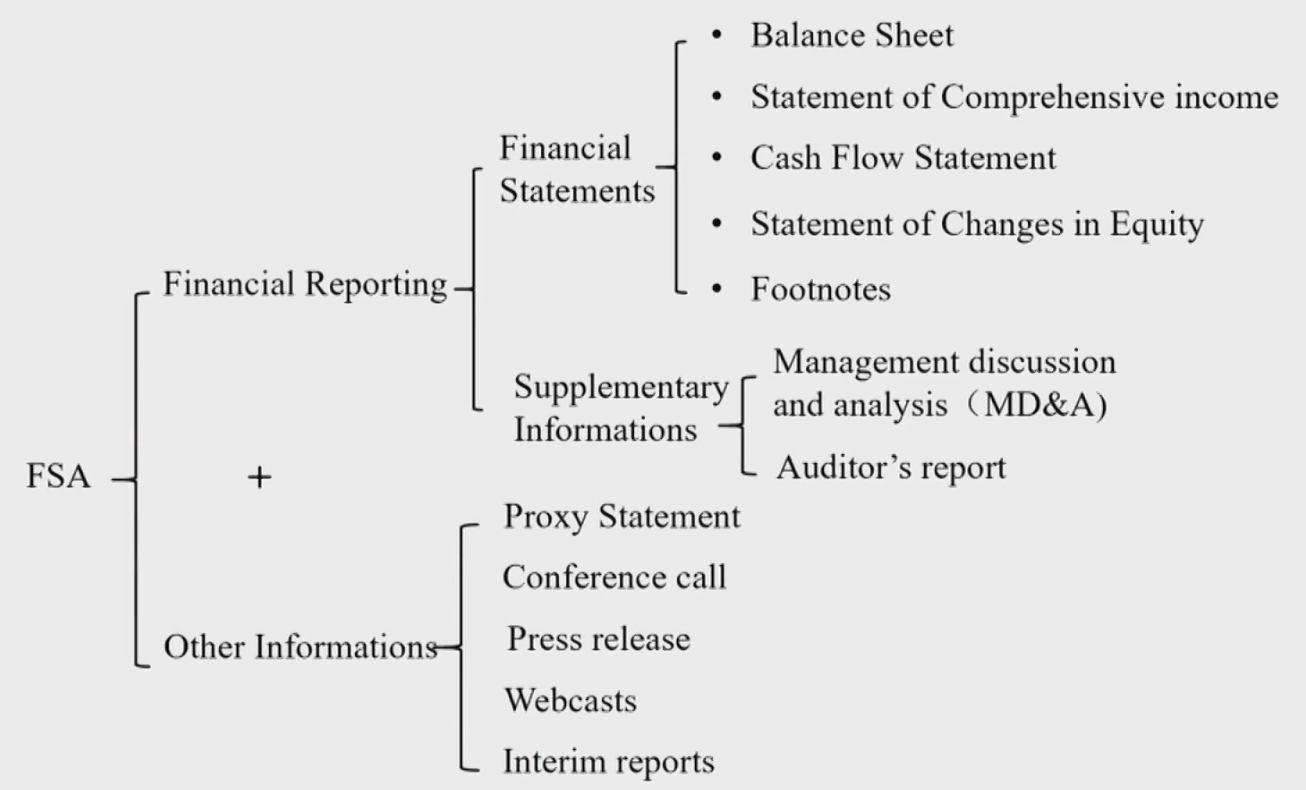
Definition of financial reporting
- The way companies provide information to wide range of users, such as investors, creditors, and other interested parties about:
- Financial position财务状况(时间点)
- Financial performance财务表现(时间段)
- Changes in financial position of an entity财务状况的变动,联系了财务状况和财务表现
The role of financial reporting analysis
- Use financial reports and other information to evaluate company's performance and financial position for the purpose of making economic decisions(内部外部做经济决策).
Key Financial Statements四表
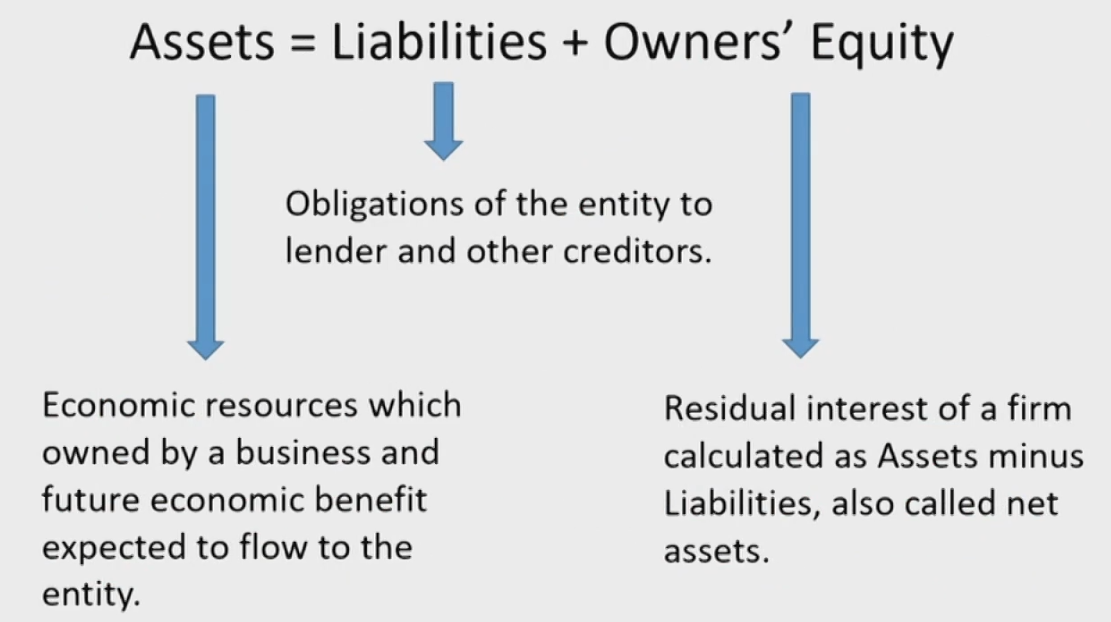
Balance Sheet资产负债表
- Presents a company's current financial position by disclosing the resources the company controls (Assets) and its obligations to lenders or other creditors (Liabilities) at a specific point in time.中国12月31日,国外可以选定
- Elements on Balance sheet:
- Assets are the resources controlled by the firm.为企业所拥有;将来很有可能带来利润;利润是可以可靠计量的
- Liabilities are amounts owed to lenders and other creditors. Debt属于Liabilities
- Owner's equity is the residual interest in the net assets of an entity that remains after deducting its liabilities.也叫净资产
- Related to the measurement of financial position: assets, liabilities, and equity
Income Statement利润表
- Also known as profit and loss (P&L) statement.
- Presents information on the financial results of a company's business activities over a period of time时间段.
- Net income is known as the bottom line利润表的最终结果是净利润.
- Net Income = Income - Expenses
- Income = Revenue + Other Income + Gain
- Revenue、Other Income是收入,与业务相关,其中Revenue是主营业务(Sales);Gain是利得,与业务无关
- Revenue: The amount charged for the goods delivered or service rendered in the ordinary activities of business
- Expenses = Expenses from ordinary activities of business + Other Expense + Loss
- 同样的,前两项和业务相关,后一项无关
- Expense: the outflows and depletion of assets, or incurrence of liabilities in the course of business activities
- Related to the measurement of performance (profit and related measures) are income and expense
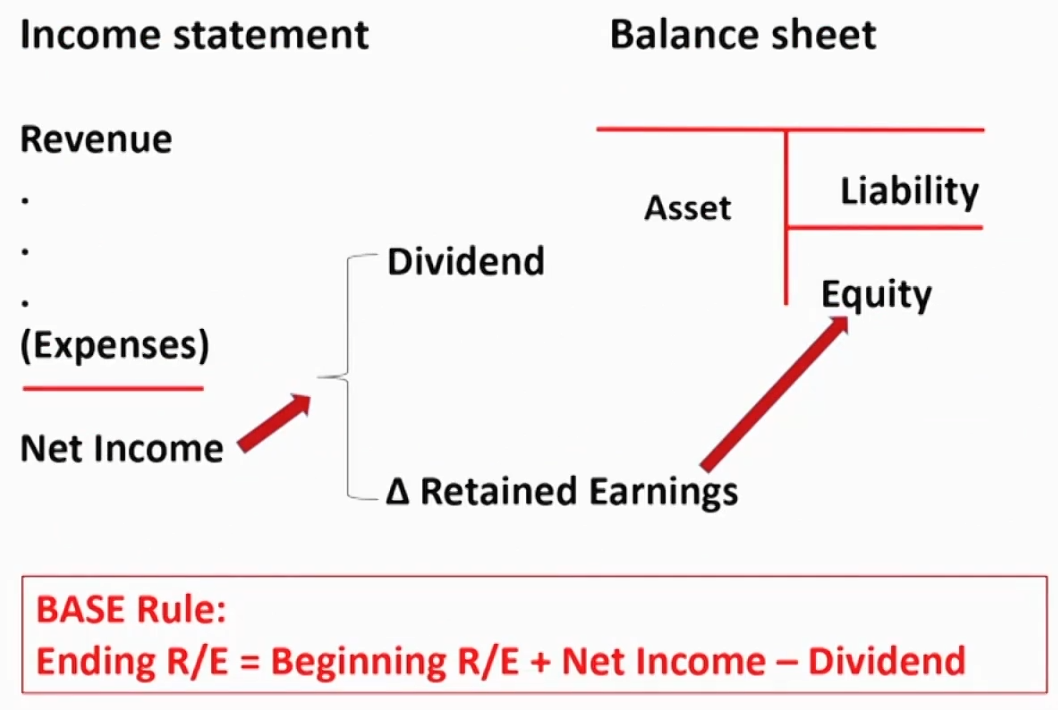
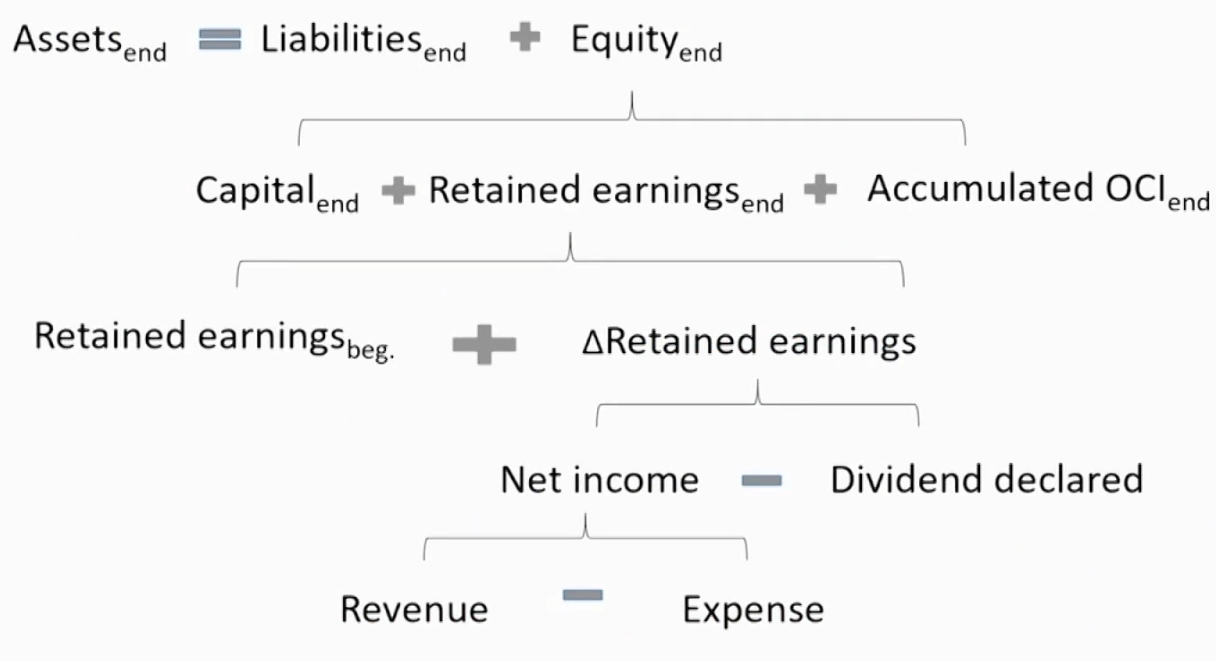
Relationship between Financial Statements-1 利润表与资产负债表的勾稽关系
Cash Flow Statement现金流量表
- Reports the company's sources and uses of cash over a period of time时间段.
- Elements on Cash Flow Statement
- Cashflowsfrom operating activities(CFO经营性现金流)
- Cash flows from investing activities(CFI投资性现金流)
- Cash flows from financing activities(CFF融资性现金流)
- 唯一的收付实现制
Relationship between Financial Statements-2 现金流量表与资产负债表的勾稽关系

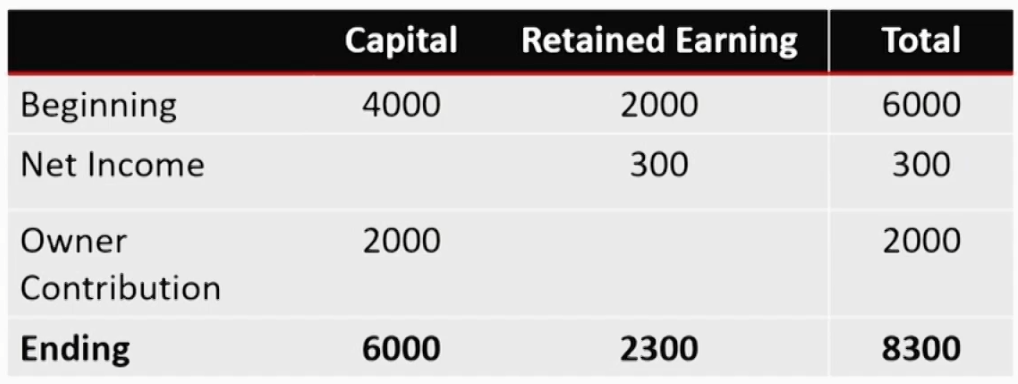
Statement of Changes in Equity股东权益变动表
- Presents each component of equity's beginning balance,any changes during the period, and the ending balance.
- The basic components of owners' equity are paid-in capital资本公积金 and retained earnings留存收益.
T-account
- Asset = Liability + Equity
- ΔAsset = ΔLiability + ΔEquity
- Ending R/E = Beginning R/E + Net Income - Dividend
- Ending Cash = Beginning Cash + Cash Flow In - Cash Flow Out
- Double Entry Accounting复式记账法,对于一个事件,至少在两个科目记账
Other Information Sources附注和补充信息
Footnotes附注
- Provide information that is essential to understanding the primary statements
- Basis of preparation of financial statements编制基础
- Significant accounting policies and methods会计政策、方法
- Significant accounting estimates会计假设
- Explanatory information of statements' line items某些详细解释
- Additional disclosures (financial instruments, contingencies,acquisitions, related parties, segments, etc)
- Footnotes must be audited会被审计.
Supplemental Disclosure补充信息
- MD&A/Management Commentary/management report(ing)/operating and financial review
- Including the nature of business, past performance, and future outlook. (contents other than financial excerpts are typically unaudited)
- Highlight any favorable or unfavorable trends,
- Identify significant events and uncertainties that affect the company's liquidity, capital resources, and results of operations.
- Information about off-balance-sheet obligations表外负债,如不确定的损失 and contractual commitments合同约定.
- Audit财务报表审计
- An independent review of an entity's financial statements
- Reasonably assure合理保证 the statements are fairly presented (free from misstatement and in accordance with accounting principle)
- Must provide opinion on company's internal controls for US listed companies在美国还要对内控发表意见。内控审计则对内控合理保证
- Auditor's opinion审计意见
- Unqualified opinion (clean opinion)无保留意见: Free from material omissions and errors, fairly presented, give a "true and fair view".
- Qualified opinion有保留意见: If statements make some exceptions to the accounting principles.
- Adverse opinion否定意见: If statements materially depart from accounting standards and are not presented fairly.
- Disclaimer of opinion无法表达意见: unable to express an opinion due to scope limitation审计范围受限.
Other Relevant Information
- Interim reports期间报告
- quarterly reports季度报告
- Proxy statement委托代理声明
- Matters to vote in a shareholders' meeting
- Press release媒体公告
- Earnings' announcement
- SEC filling美国证券会表格
- Conference call分析师报告
- Information from other sources regarding economy, industry,the company, and competitors.
Financial Statement Analysis Framework
- Purpose and Context of Analysis
- Collect Data
- Process Data
- Analyze/Interpret Data
- Conclusions and Recommendations
- Update analysis periodically/Follow-up
Financial Report Standards会计准则
Standards-Setting Bodies and Regulatory Authorities
Standard-setting Bodies制定主体
- Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
- Sets U.S.GAAP
- International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
- Sets IFRS
Regulatory Authorities监管机构
- Government agencies have the enforcement power (IASB and FASB don't have)
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC美国证监会) in the U.S.
- Financial Service Authority (FSA英国金融服务管理局) in the U.K.
- Most national authorities are members of the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO国际证监会联盟).
- Protect investors
- Ensure that markets are fair, efficient, and transparent
- Reduce systemic risk
SEC filings required
- Form S-1 (Securities Offerings Registration Statement招股说明书)
- Registration statement filed for issuing new securities.
- Form DEF-14A(proxy statement委托代理声明)
- Proposals need to vote
- Executive compensation
- Details of security ownership
- Form 8-K重大事项公告
- Acquisitions and disposals of major assets.
- Changes in its management.
- Changes in corporate governance.
- Form 10-K年度报告
- Annual financial statements.(Audited)
- Form 10-Q季度报告
- Quarterly financial statements.(Not necessarily audited)
- Form 144限售股解禁
- Notice of the proposed sale of restricted securities or securities held by an affiliate of the issuer in reliance on Rule 144.
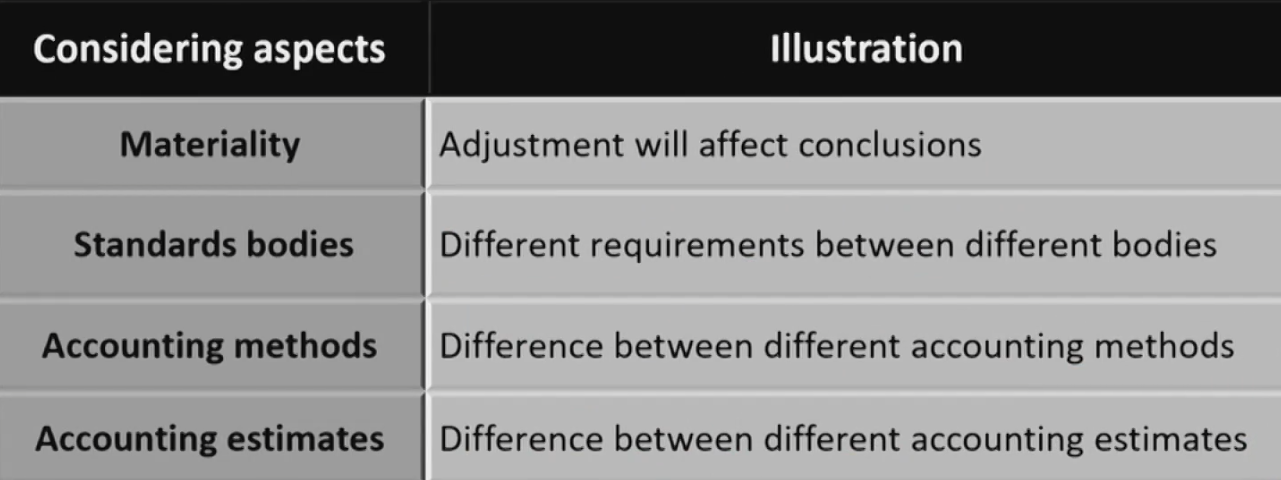
Convergence of Global Financial Reporting Standards会计准则的趋同
- Many aspects of IFRS and U.S. GAAP have converged over the past decade.
- Effective in 2008, the SEC adopted rules to eliminate the reconciliation requirement for foreign private issuers' financial statements prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB.
- Previously, any non-US issuer using accounting standards other than US GAAP was required to provide a reconciliation to US GAAP.
The International Financial Reporting Standards Framework
Qualitative characteristics: two fundamental characteristics
- Relevance相关性
- Information is relevant if it would potentially affect or make a difference in user's decisions. If omission or misstatement of information could influence decisions, it is considered material.
- Faithful representation忠实表述
- Complete (all information necessary is depicted), neutral (without bias), and free from error.
Qualitative characteristics: four enhancement characteristics
- Comparability可比性(横向纵向)
- Financial statements are presented in a consistent manner among firms and over time.
- Verifiability可验证性
- Independent and knowledgeable observers using the same methods can obtain similar results.
- Timeliness及时性
- Information is available to decision makers prior to they make a decision.
- Understandability可理解性
- Can understand the information the statements with a reasonable business and economic knowledge.
Barriers to a Single Coherent Framework矛盾
IASB General Requirements for Financial Statements
Required Reporting Elements会计要素
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
- Revenue
- Expense
Required Financial Statements
- Balance sheet
- Statement of comprehensive income综合收益表,利润表的升级
- Comprehensive income = Net Income + Other comprehensive income
- a single statement of comprehensive income披露一张: Reports all items that impact shareholders' equity but are not the result of transactions with shareholders
- two statements披露两张: an income statement and a statement of comprehensive income that begins with profit or loss from the income statement
- Cash flow statement
- Statement of changes in owners'equity
- Footnotes
General Features of Financial Statements
- Classified balance sheet
- A classified balance sheet should to distinguish between current and non-current assets and liabilities.
- Minimum information
- The minimum line item disclosures on the face of, or in the notes to, the financial statements are required.
- Comparative information
- Comparative information should be provided for prior periods.
- Aggregation
- Aggregation of similar items, separation of dissimilar items.
- No offsetting
- Assets and liabilities, income and expenses, are not offset unless required or permitted by standards.
- Reporting frequency
- Reporting must be prepared at least annually.
General Features of Financial Statements会计假定
- Going concern basis永续经营
- Assume the company will continue in business for the foreseeable future.
- Accrual basis of accounting权责发生
- assumes that financial statements should reflect transactions in the period when they actually occur, not necessarily when cash movements occur.
Change
- Change in accounting estimate会计估计如折旧: prospective未来适用
- Change in accounting policies会计政策如存货计量方式: retrospective追溯调整
- Correction of an error: restatement报表重塑
Accrual Accounting
- Cash movement prior to accounting recognition
- Unearned revenue(deferred revenue):提前收到现金,预收账款U.R.,属于负债
- Prepaid expense(deferred expense):提前支付现金,预付账款P.E.,属于资产
- Cash movement after accounting recognition
- Account receivable/Unbilled revenue(accrued revenue):延迟收到现金,应收账款A.R.,属于资产
- Account payable(accrued expenses):延迟支付现金,应付账款A.P.,属于负债
Understanding the I/S
Components and Format
Components and Format
- Recurring items and non-recurring items/continued operations and discontinued operations
\begin{align} \text{Net income}&=\text{ revenues }+\text{ other income} + \text{gains } \\ &-\text{ordinary expenses} - \text{other expense} -\text{losses} \\ & \pm\text{gain (loss) from unusual or infrequent items} \\ & \pm \text{gain (loss) from discontinued operation} \end{align} - Revenues are the amounts charged for the sale of goods or services in the ordinary activities of a business.
- Revenue adjusted for estimated discounts is net revenue比如打折,保修服务,记为预收账款.
- Expenses reflect outflows, depletions of assets.
- Expenses are grouped together by their nature如折旧、利息和税 or function如COGS和SG&A.
- 关于第一行的收入,有两种编制方法
- 第一行是净收入(Sales、Revenues、Net Sales、Net Revenues),下一行为COGS
- 第一行是毛收入(Sales、Revenues、Gross Sale、Gross Revenues、Total Sale、Total Revenues),然后减去退货(Returns)、消费税(Excise taxes)、降价(Allowances )、折扣(Discounts)等得到净收入、然后下一行为COGS
- 对于寄售(Consignment),Revenue考虑佣金(Commission)而不是收入
Multi-Step I/S Vs.Single-Step I/S
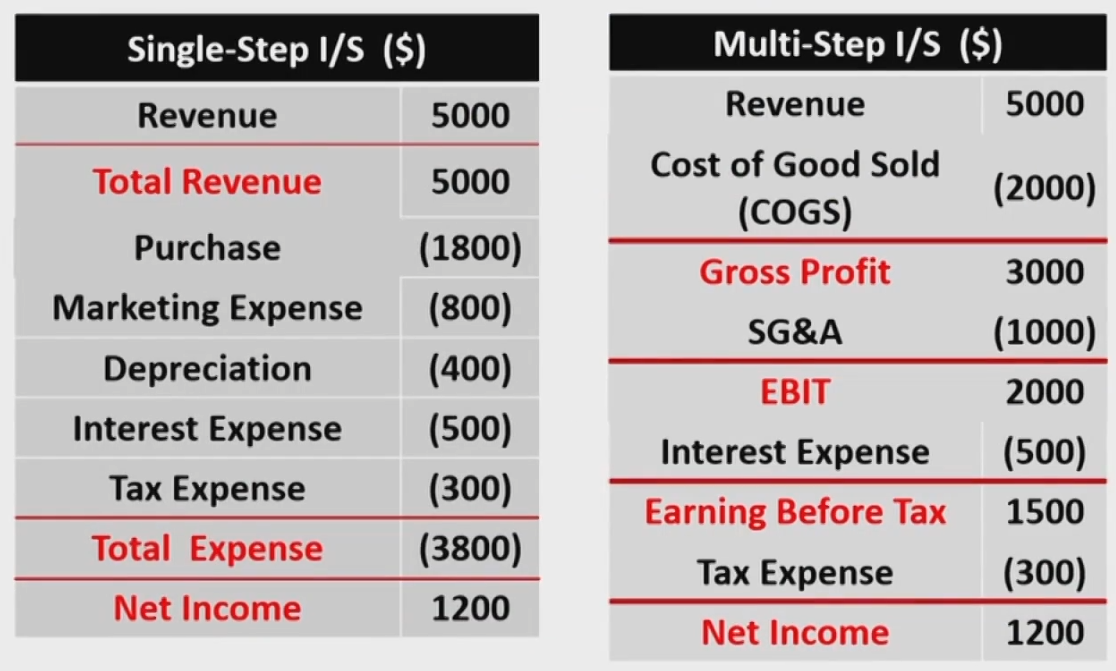
Multi-Step I/S-More Detailed
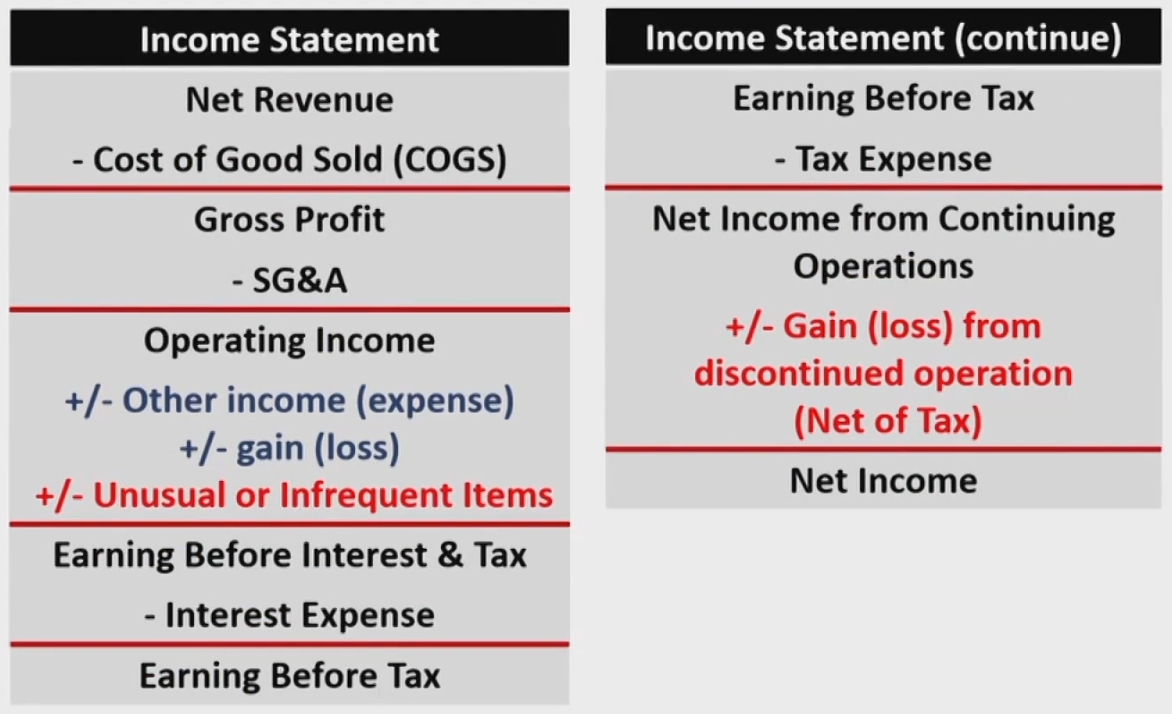
- Other Income其它业务的收入;Gain利得,如投资收益
Non-Recurring Items
- Unusual or infrequent items (continuing operations)
- Reported "above the line" and presented on a pretax税前 basis.
Natural disaster自然灾害
Impairments, write-offs, write-downs资产减值
Restructuring costs资产重组
G/L from the sale of assets资产处置
- Reported "above the line" and presented on a pretax税前 basis.
- Discontinued operations (presented on net of tax税后)
- When a company disposes of or establishes a plan to dispose of one of its component operations and will have no further involvement in the operation:
During the phaseout period: Any loss or gain should be recognized in the discontinued operations处置之前带来的收入和损失
On the actual disposal date: Any loss or gain on the sale of the business should be recognized in the unusual or infrequent items (above the line).买卖本身属于continuing operations
- When a company disposes of or establishes a plan to dispose of one of its component operations and will have no further involvement in the operation:
General Principles of Revenue & Expense Recognition
Revenue Recognition - General Principles
- Revenue is recognized when it is earned and expenses are recognized when it is incurred.
- Accrual accounting does not necessarily coincide with the receipt or payment of cash.
Expense Recognition - General Principles
- A general principle of expense recognition is matching principle匹配性原则,收入产生的同时计算费用
- COGS
- Depreciation and amortization
- Doubtful account如赖账
- Warranties如退款
- Period expenses期间费用: cannot be directly tied to revenue generation,should be expensed in the period incurred.
- Admin cost行政管理费用
Aggressive Accounting & Conservative Accounting
- Aggressive accounting policies means increase the assets, revenue and decrease liabilities and expense.

Five Steps in Recognizing Revenue
- Identify the contract(s) with a customer.
- Identify the performance obligations履约义务 in the contract.
- 区分成多个的前提是买方卖方都能区分
- 细节的修正视为对合同的修正,若差别太大则视为新合同
- Determine the transaction price确认交易价格.
- 确认可能性最大情况的收入
- 可以随时修正
- Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract
- 将交易价格分摊到各个履约义务
- Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
- 完成一项履约义务就确认一次收入,或根据进度
- 进度可以随时修正
- 代理人的业务净额法确认收入
完工百分比法
- 完工进度等于成本消耗进度
- 累计收入等于完工进度乘以预期价格
- 当年收入等于期初期末累计收入的差值
Earnings Per Share
Earnings Per Share每股(普通股)盈利
- EPS is the most commonly used corporate profitability performance measure for publicly-traded firms
- Basic EPS基本
- Diluted EPS稀释后
- A simple capital structure contains no potentially dilutive securities.
- Firm reports only basic EPS.
- A complex capital structure contains potentially dilutive securities.
- Firm must report both basic and diluted EPS.
Basic EPS
\text{Basic EPS} =\frac{\mathrm{NI}-\text { Div preferees stock }}{\text { Weighted average number of common shares outstanding }}- Weighted average number of common share outstanding
- New issue, repurchase is weighted by time (days or months)
- Stock dividend/split is not weighted by time, instead it should adjust the number of common share which exist before the stock dividend or split. (Eg: 3-for-2 split: two shares split to three shares)追溯往前调整,2-for-1就是之前的乘2;10%dividend就是之前的乘1.1;不论发生时间,处理都一样
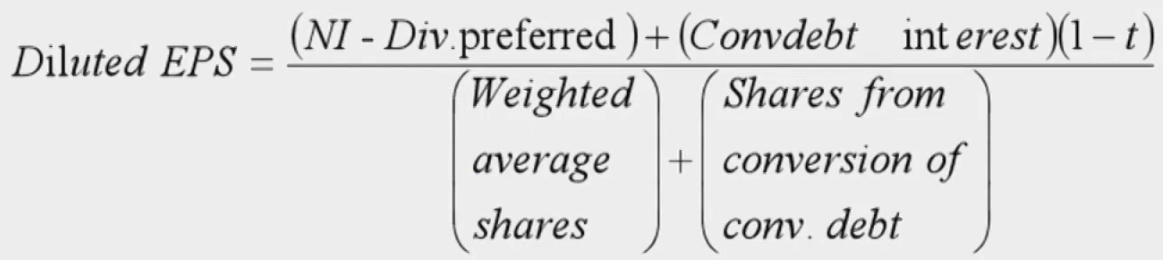
Diluted Earnings Per Share

- Dilutive securities decrease EPS if exercised or converted into new common stock
- Convertible preferred stock可转换优先股
- Convertible debt
- Stock options/ Warrants
- Anti-dilutive securities increase EPS if exercised or converted into common stock. (Don't include such security in the computation of dilutive EPS)
- Diluted EPS can not be higher than Basic EPS
Convertible Preferred Stock
- 对分母的影响:转为普通股的股数
- 对分子的影响:因转换而节省的优先股股利

Convertible Debt
- 对分母的影响:转为普通股的股数,
- 对分子的影响:因转换而节省的税后利息
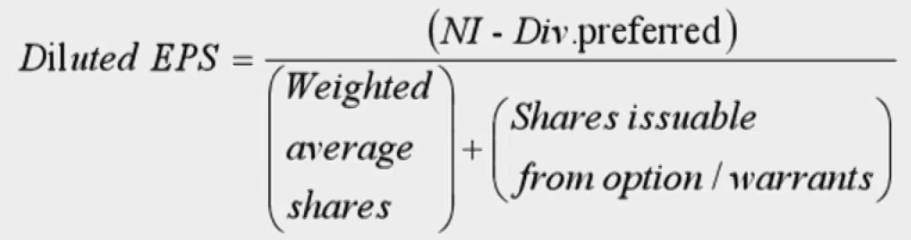
Options and Warrants
- 对分母的影响:库存股法下增加的普通股股数
- 增发股票(执行价格) - 收到的钱回购的股票(全年平均价格,大于执行价格才能稀释)
- 对分子的影响:无
Treasury Stock Method for Options and Warrants
- Funds received from the exercise of the options would be used to hypothetically repurchase shares in the market at the average market price.
- The net increase in the number of shares: the difference between the number of shares issued and the number of shares hypothetically repurchased.
Analysis of Income Statement & Comprehensive Income
Common-Size Income Statement比较百分比
- Express each income statement item as a percentage of sales.
- 同时除以Revenue
- Used to analyze changes in cost structure, profitability and company's strategies.

Comprehensive Income
- Comprehensive income综合收益
- Comprehensive income includes both net income and other comprehensive income.
- Other comprehensive income其他综合收益,不进利润表
- Foreign currency translation这算 gains and losses
transaction属于Net Income - Adjustments for minimum pension liability (DB plan部分的).
DC plan属于Net Income - Unrealized gains and losses from cash flow hedging derivatives现金流量套期保值
fair value hedging属于Net Income
realized属于Net Income - Unrealized gains and losses from available-for-sale securities(FVOCI).
FVPL属于Net Income
realized属于Net Income - Valuation Surplus for long-lived asset (IFRS only)评估增值.

- Foreign currency translation这算 gains and losses
Understanding the B/S
Components and Format - Asset
Components and Format
- Assets
- Provide probable future economic benefits controlled by an entity as a result of previous transactions.
- Current and Non current assets (Long term assets)一年内是否能公允变现
- Liabilities
- Obligations owed by an entity from previous transactions that are expected to result in an outflow of economic benefits in the future.
- Current and Non current liabilities (Long term liabilities)
- Equity
- Residual interest in assets that remains after subtracting a firm's liabilities.
Current Assets
- Current assets are held for the purpose of trading or expected to be sold, used up, or otherwise realized in cash within one year or one operating cycle of the business, whichever is greater.
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Account receivable
A contra account备抵账户 is allowance for bad debts坏账准备. - Inventory存货
Unsold units of product on hand. - Short-term marketable securities短期交易性金融资产
Non-Current Assets
- Non-current assetsare not expected to be sold or used up within one year or one operating cycle of the business,whichever is greater.
- Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E 固定资产如机器设备)
A contra account is accumulated depreciation累计折旧. - Intangible assets无形资产
Patents, trademarks, copyright and goodwill商誉,收购的溢价,不摊销.
A contra account is accumulated amortization累计摊销 - Long-term investment长期股权投资
- Deferred tax assets递延所得税资产
- Property, plant, and equipment (PP&E 固定资产如机器设备)
Components and Format-Liability, Owner's Equity & Analysis of Balance Sheet
Liability
- Liabilities are creditors' claims on the company's resource.
- Accounts payable
- Unearned revenue
Cash received in advance whereas the revenue will be recorded on future income statement. - Accrued expense应计费用
Cash paid later whereas the expense is recorded now. - Tax payable应交税费
Taxes accrued during the past year but not yet paid. - Long-term debt长期负债中超出一年要偿还的部分
- Current portion of long term debt当年要还的钱,属于流动性资产;剩余的属于非流动性负债
- Deferred tax liabilities递延所得税负债
Owners' Equity
- Owners'equity is the residual claim on a company's resources (E = A - L).
- Capital股本
- Additional paid-in-capital资本公积
Capital in excess of par.超过一元部分的溢价 - Treasury stock库存股
No voting right, no dividend
Stock repurchased回购 by the firm but not yet retired. - Retained earnings(Net income - Dividend)留存收益
- Accumulated other comprehensive income累计其它综合收益
- Minority interest少数股东权益
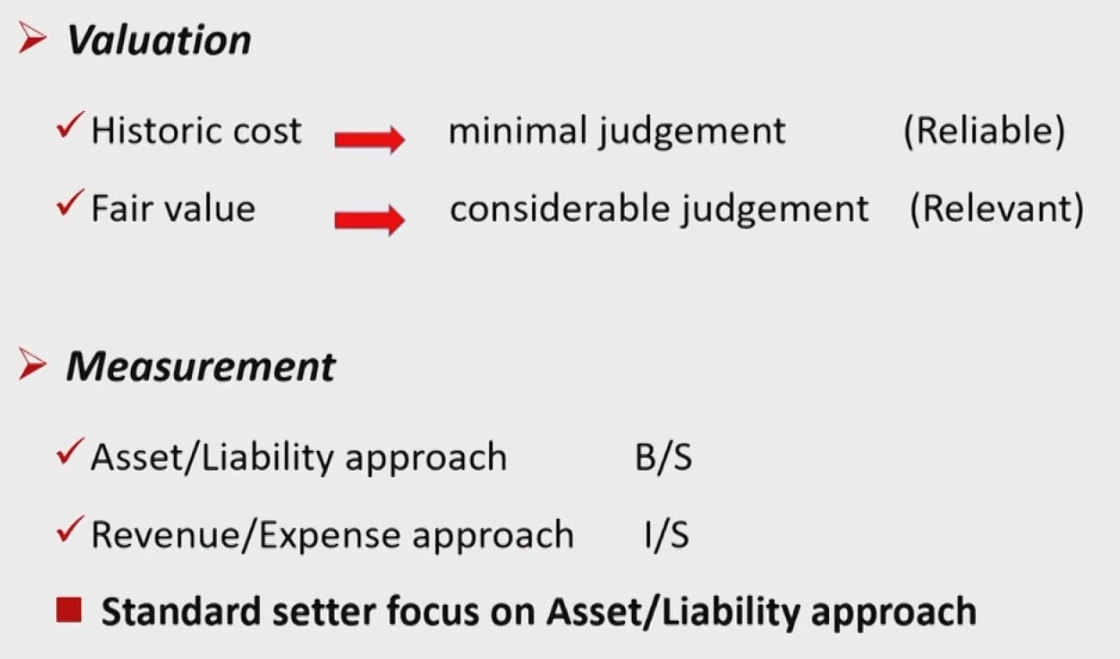
Measurement of Financial Elements计量属性
- Historical cost历史成本法
- The amount originally paid for the asset.
- Amortized cost摊余成本法
- Historical cost adjusted for amortization of discount/premium.
- Current cost重置成本法
- The amount the firm would have to pay today for the same asset.
- Realizable value可变现现值
- The discounted value of the asset's expected future cash flows.
- Fair value
- The amount at which two parties in an arm's-length transaction would exchange the asset. (Willingness,Knowledgeable, Unrelated)
Analysis of Balance Sheet
- A balance sheet can be used to assess a firm's liquidity,solvency, and ability to make distributions to shareholders.
- From the firm's perspective, liquidity is ability to meet its short-term financial commitments.
- Solvency is the ability to meet the company's long-term financial obligations.
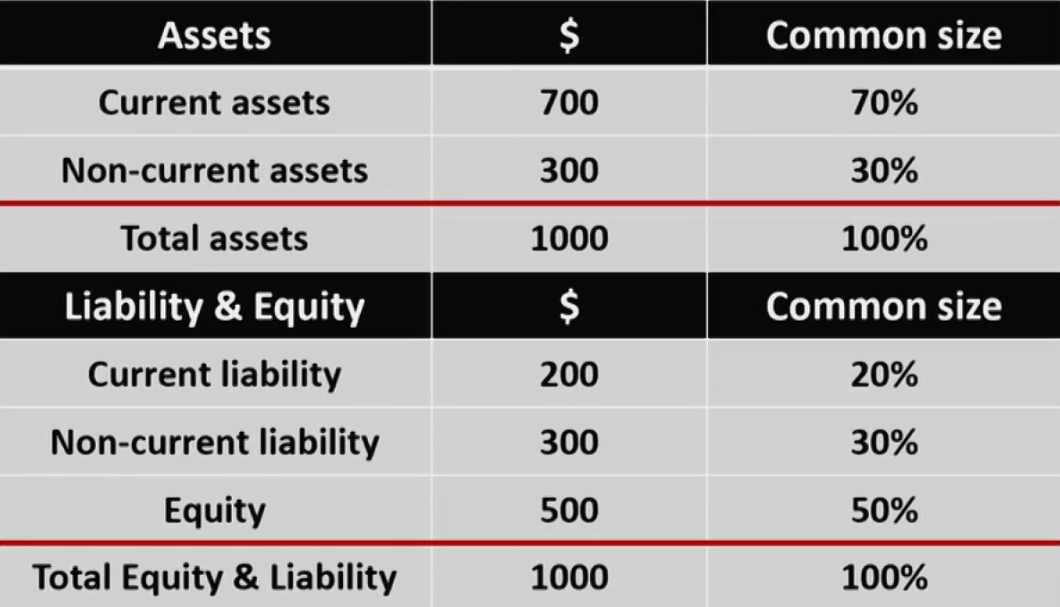
Common-size balance sheet
- Item in the balance sheet account / total assets
Classification of Financial Assets
Financial Assets
- Financial assets are a company's investments in stocks issued by another company or its investments in the notes, bonds, or other fixed-income instruments issued by another company (or issued by a governmental entity)
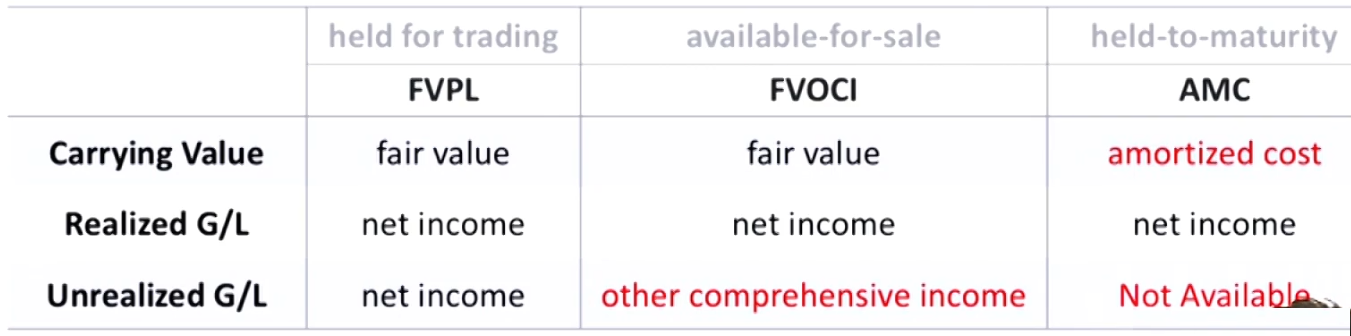
Financial Assets Classification
- Previous Standard
- Held for trading
- Available-for-sale
- Held-to-maturity
- Current Standard
- Financial assets are measured at amortized cost (AMC以摊余成本考虑的金融资产)
- Financial assets are measured at fair value through other comprehensive income (FVOCI以公允价值计量且其变动计入其他综合收益的金融资产)
- Financial assets are subsequently measured at fair value through profit and loss(FVPL以公允价值计量且其变动计入当期损益的金融资产)
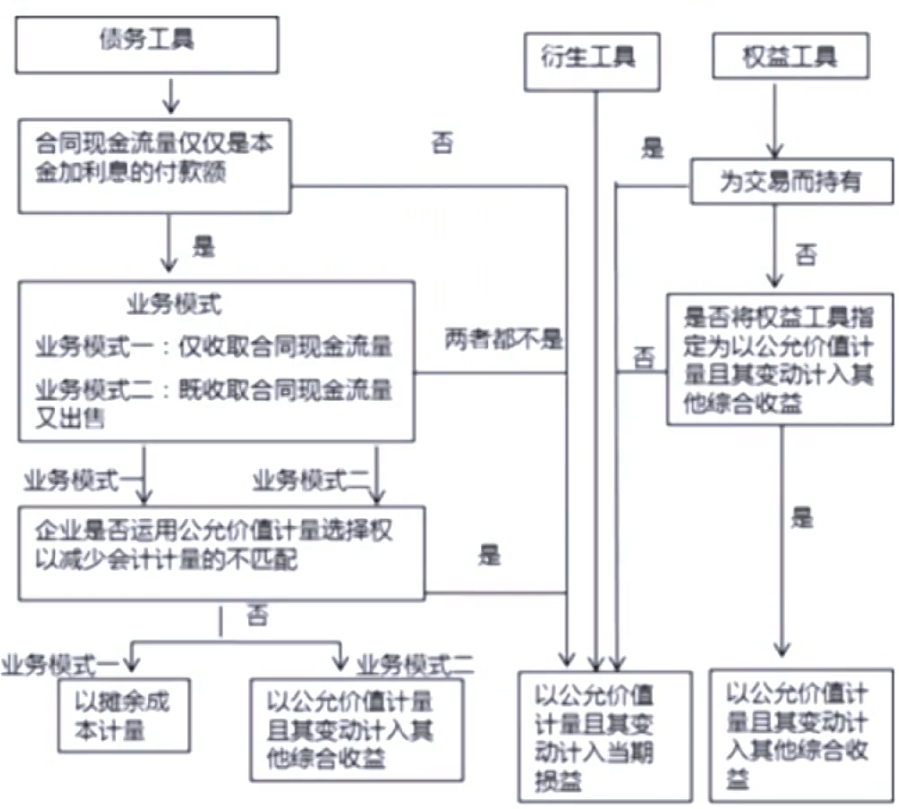
- Debt instruments are measured at AMC,FVOCl,or FVPL
- Equity instruments are measured at FVPL,or FVOCI
Measurement of Financial Assets
Measurement of Financial Assets
- All financial assets are measured at fair value when initially acquired(which will generally be equal to the cost basis on the date of acquisition)
- Subsequently, financial assets are measured at either fair value or amortized cost
General Principles of Measurements
会计处理
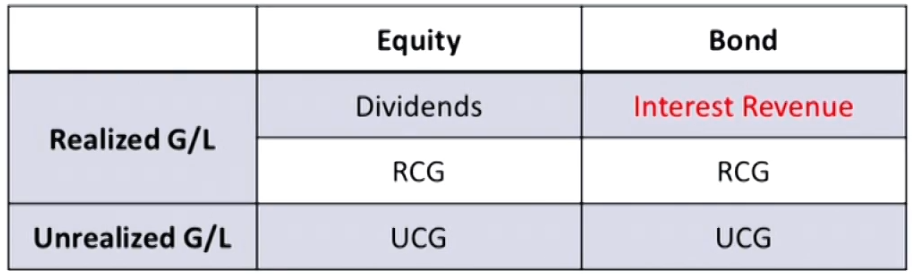
- Bond
- 计算出债券的现值,计入Cash和AMC
- 每期Coupon (C/F):面值 × 票息率,计入到Cash
- 每期Interset (I/S):AMC × 实际利率,计入到RE
- Coupon与Interset的差值计入到AMC,使得报表配平。此时的AMC等于债券现值
- 最后一年AMC与Cash抵消
- AOCI
- 出售时要出售的百分百部分结转到RE
Understanding the C/F
Cash Flow Classification
Components and Format
- Information about a company's cash receipts and cash payments during an accounting period.
- Information on the CFS come from two sources
- Income statement items
- Changes in current balance sheet accounts
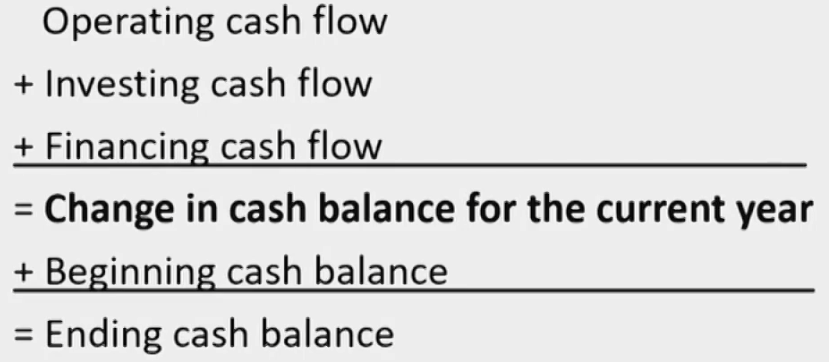
- Cash flow from operating activities (CFO经营性现金流)
- include the company's day-to-day activities that create revenues and other activities that affect a firm's net income.
- Cash flow from investing activities (CFI投资性现金流)
- Consists of activities of purchasing and selling long-term assets and other investments,exclude any securities considered cash equivalents and securities held for dealing or trading purposes.
- Cash flow from financing activities(CFF融资性现金流)
- Include financing activities of obtaining or repaying capital.
- non-cash transaction(不产生现金流但对资产有影响的活动,如同种类的两笔大小相同方向相反的现金流)不计入现金流量表,而是在现金流量表的supplementary information或footnotes里披露
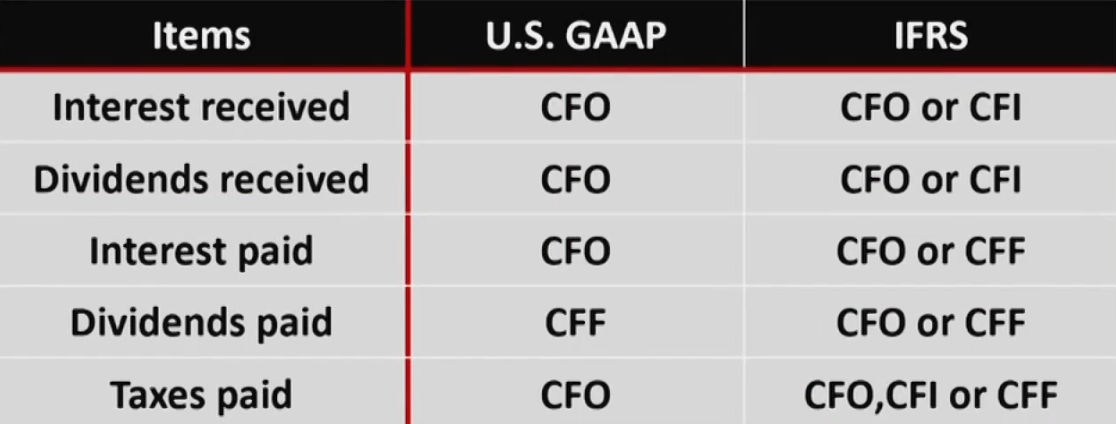
- 现金流对应的税在不同类别里分别记录
U.S. GAAP Cash Flow Classification
- CFO
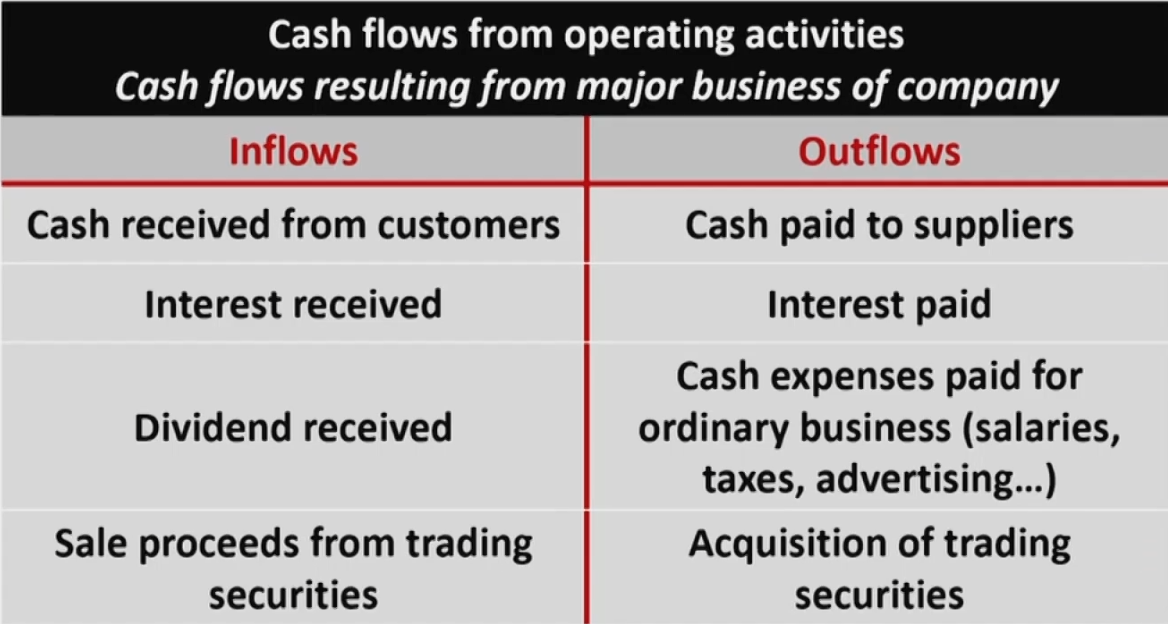
- CFI
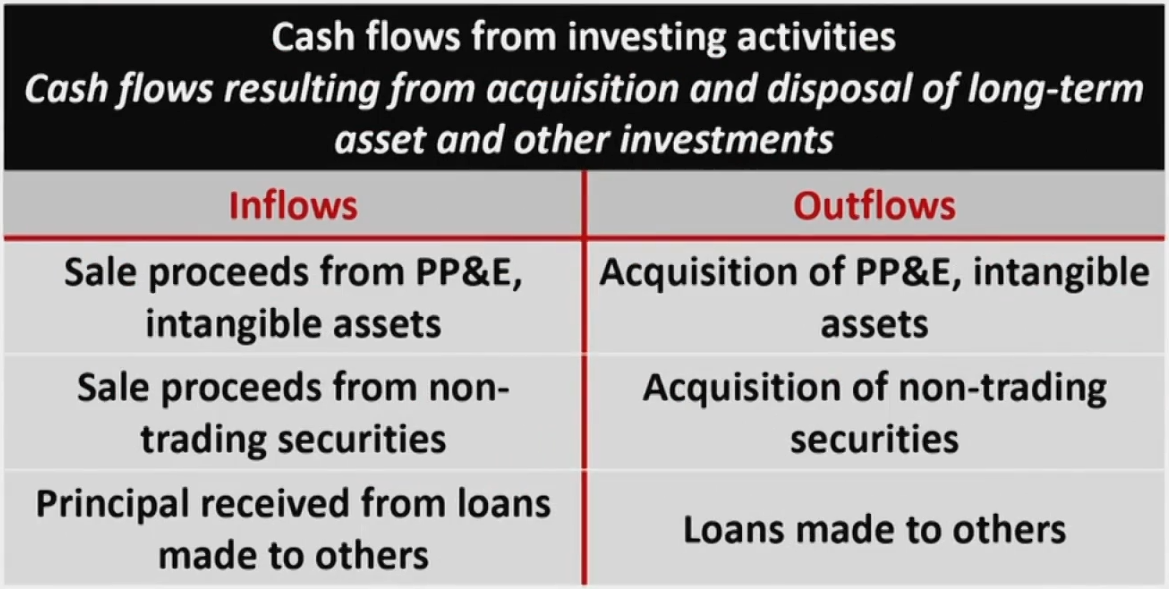
- CFF

U.S. GAAP vs. IFRS
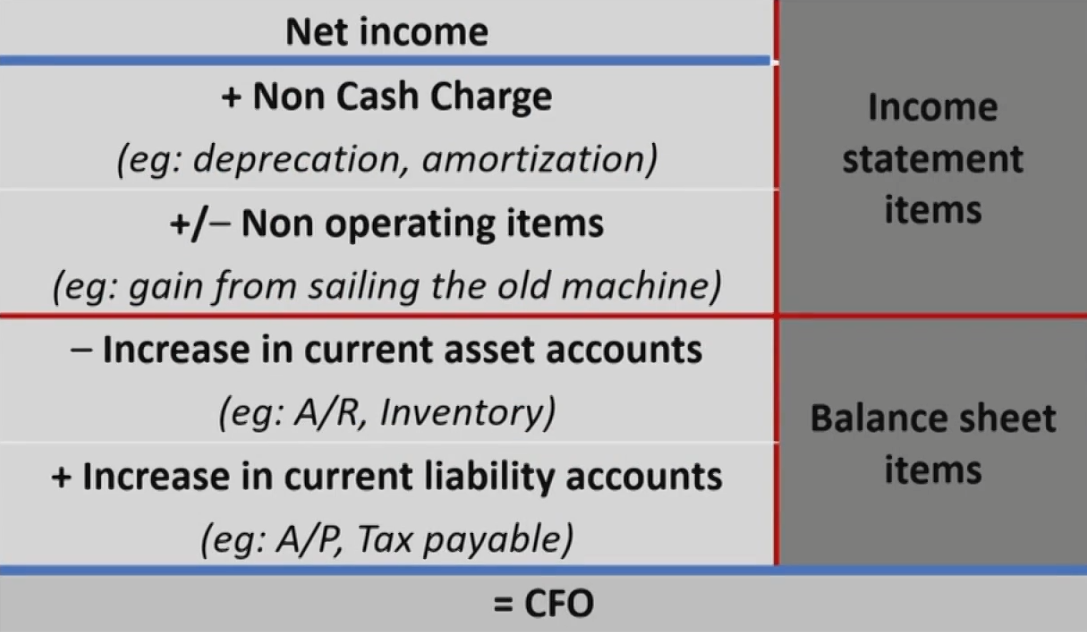
Calculation of CFO
Methods to Calculate Cash Flow
- CFO calculation
- Direct method直接法: begin at the top of the income statement and identify cash inflows and outflows.
Provides information on the specific sources of operating cash receipts and pay-ments - Indirect method间接法: begin at the bottom of the income statement with net income and make necessary adjustments.
Mirrors a forecasting approach and it is easier and less costly
- Direct method直接法: begin at the top of the income statement and identify cash inflows and outflows.
- Calculation of CFO-Direct Method直接计算

- Calculation of CFO-Indirect Method从NI调整
Calculation of CFI
Sources of CFI
- Long-lived assets
- Cash used in purchase PP&E and other intangible assets
- Cash received from sale of PP&E and other intangible assets
- Non-trading securities
- 注意利息是CFO还是CFI
CFI Calculation
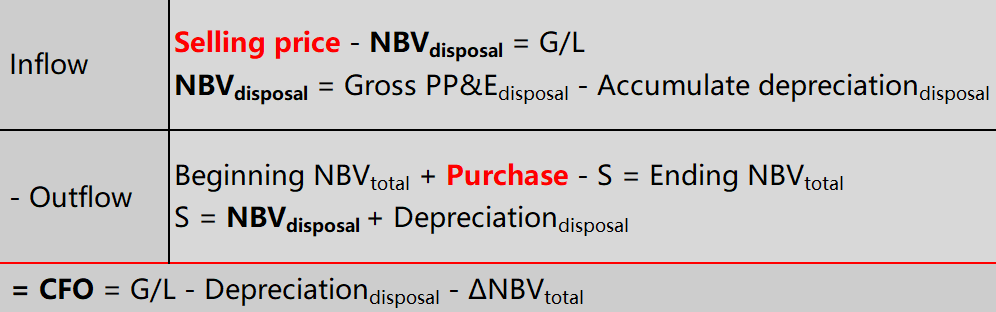
Calculation of CFF
- Step 1: Review long-term debt and stock
- Increases supply cash and decreases use cash.
- Step 2: Dividend paid
- ΔDividend payable应付股利变动 = Dividend declared期间宣告股利 - Dividend paid期间发放股利
Dividend一般都会发放,因此Dividend payable总为0 - ΔRetained earning留存收益变动 = Net Income净利润 - Dividend declared期间宣告股利
- ΔDividend payable应付股利变动 = Dividend declared期间宣告股利 - Dividend paid期间发放股利
Analysis of Cash Flow
Analysis of Cash Flow
- Analyst should evaluate the sources, uses and main drivers of each type of cash flow:
- Evaluate where the major sources and uses of cash flow are between operating, investing, and financing activities.
- Evaluate the primary determinants of CFO/CFI/CFF.
Examine the major sources and uses of cash
- Operating Cash Flow
- An indication of the company's earning quality.
- Investing Cash Flow
- Increasing capital expenditures, a use of cash, is usually an indication of growth.
- Financing Cash Flow
- The nature of company's capital sources.
- Cash requirement for debt repayments, share repurchase, or dividend payments.
Common Size Cash Flow Statement
- Show each item as a% of Revenue
\frac{\text { Cash flow statement account }}{\text { Revenue }} - Show each inflow as a % of total inflows; Show each outflow as a % of total outflows
\frac{\text { Cash inflow }}{\text { Total cash inflows }} \quad \frac{\text { Cash outflow }}{\text { Total cash outflows }}
Free Cash Flow
Free Cash Flow
- Free cash flows are the cash flows available for distribution after fulfilling all obligations (operating expenses and taxes) and without impacting on the future growth plans of the company (working capital and fixed capital增量)
- Free cash flow to firm (FCFF): Cash available to creditors and shareholders after all operating expenses and necessary investments have been made
- Free cash flow to equity(FCFE): Cash available to common stockholders after all borrowing costs (principal and interest) have been paid from FCFF.
FCF Formulas

Financial Analysis Techniques
Ratio Analysis-Activity Ratios
Categories of Common Ratios
- Activity ratio
- Efficiency in using assets to generate revenue.经营效率
- Liquidity ratio
- Ability to meet short-term obligations.短期债务偿还能力
- Solvency ratio
- Ability to meet long-term obligations.长期债务偿还能力
- Profitability ratio
- Ability to generate profit.盈利能力
Activity Ratios经营比率
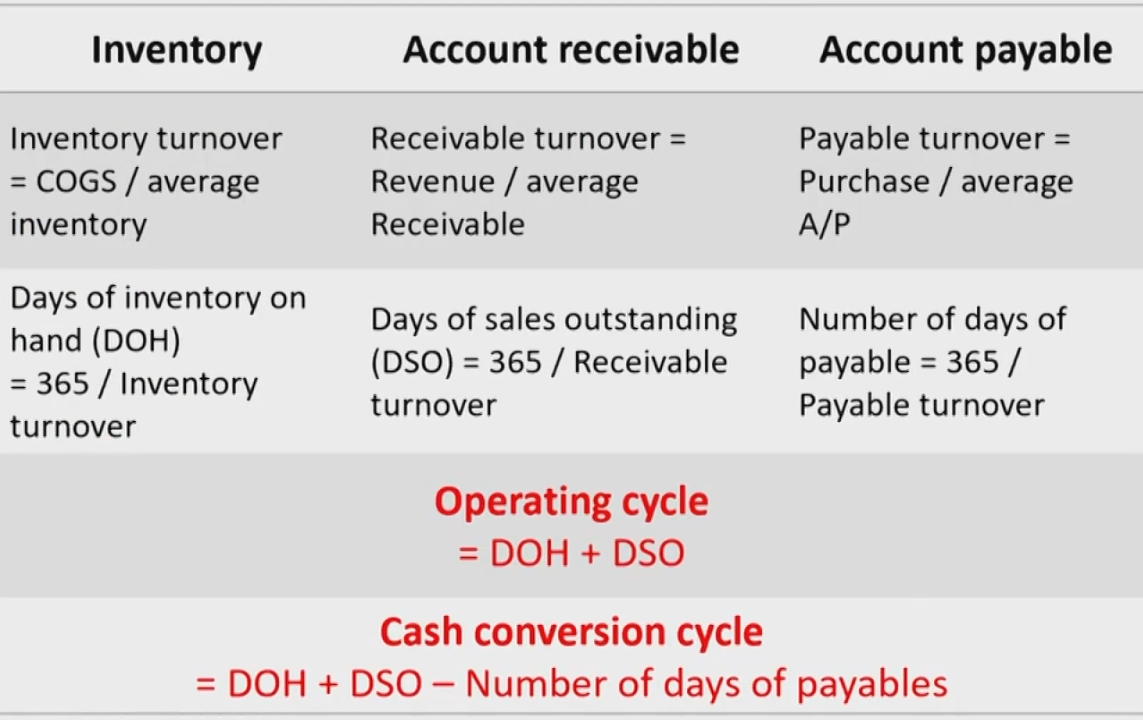
- Inventory turnover存货周转率 = COGS销货成本 / Average inventory
- Average inventory: 平均的gross inventory
- COGS: 减记后的COGS
- Days of inventory on hand(DOH) = 365/Inventory turnover
- Receivable turnover应收账款周转率 = Revenue(最好是赊销的收入) / Average Receivable
- Days of sales outstanding(DSO) = 365 / Receivable turnover
- Payable turnover应付账款周转率 = Purchase(最好是赊购的支出) / average Accounts payable
- Number of days of payable = 365 / Payable turnover
- Total asset turnover总资产周转率 = Revenue / Average total assets
- Fixed asset turnover固定资产周转率 = Revenue / Average net fixed assets
- Working capital turnover营运资本周转率 = Revenue / Average WC
- Working capital = Current assets - Current liabilities
- 平均值可以取期初期末的平均值
Operating Cycle & Cash Conversion Cycle
Ratio Analysis - LiquidityRatios & Solvency Ratios
Liquidity Ratios短期的偿还能力
- A firm's ability to meet short-term obligations
- Current Ratio = Current assets/ Current liabilities
- Quick Ratio =(Cash + short-term marketable security + Receivable)/ Current liabilities
- Cash Ratio =(Cash + short-term marketable security)/ Current liabilities
- Defensive interval =(Cash + short-term marketable security + Receivable)/ Daily cash expenditures
Solvency Ratios长期的偿还能力
- Debt-to-equity债务股本比 = Total Debt / Total shareholder's Equity
- Total debt is the sum of interest-bearing short-term & long-term debt
- Debt-to-capital资本负债率 = Total Debt /(Total Debt +Total shareholder's Equity)
- Debt-to-long capital长期资本负债率 = Long-term Debt /(Long-term Debt +Total shareholder's Equity)
- Debt-to-assets = Total Debt / Total Assets
- Debt-to-EBITDA=Total Debt / EBITDA
- Financial leverage = Average total assets / Average total Equity
Coverage Ratios利息的偿还能力
- Interest coverage = EBIT/ Interest
- Fixed charge coverage =(EBIT+ lease payments)/(Interest + lease payments)
Ratio Analysis -Profitability Ratios & Dupont Analysis
Profitability Ratios: Profit / IS Items
- Gross profit margin毛利率 = Gross profit / Net revenue
- Operating profit margin经营利润率 = EBIT / Net revenue
- Pretax margin税前利润率 = EBT/Net revenue
- Net profit margin销售净利率 = Net income / Net revenue
Profitability Ratios: Profit / BS Items
- Return on asset (ROA) = Nl / Average total assets(Definition)
- ROA =[NI + Int(1-t)]/ Average total assets(For analysis)
- Operating ROA = EBIT/ Average total assets
- Return on equity(ROE) = NI / Average total equity
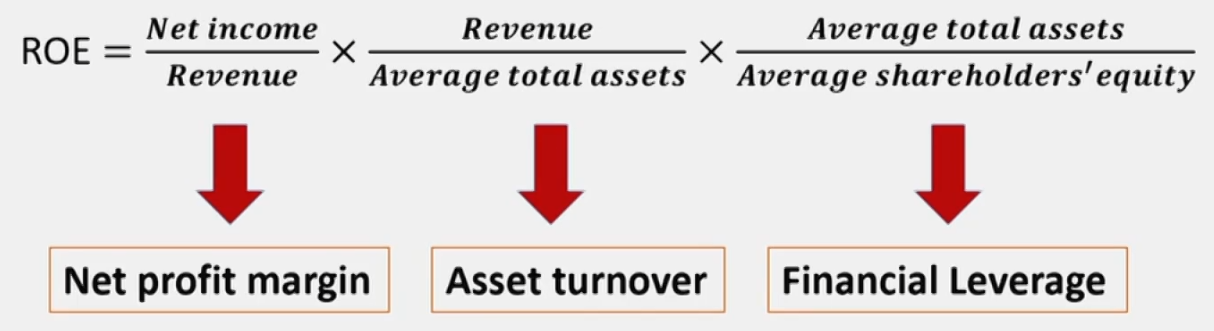
Dupont System of Analysis
- Two-part approach
- ROE = ROA x Financial Leverage Ratio
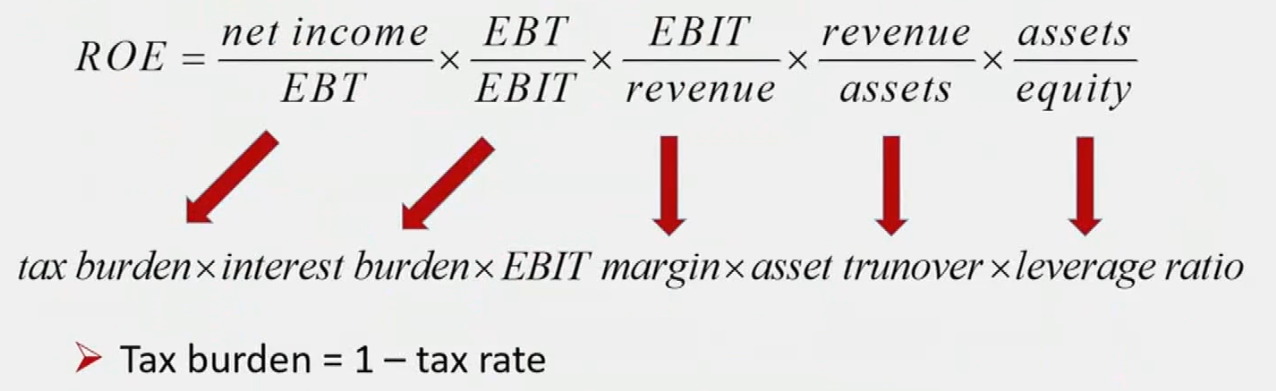
- THREE-part approach
- FIVE-part approach
Equity, Credit Analysis & Segment Analysis
Equity Analysis
- Dividend payout ratio股利支付率 = dividends / net income
- Retention rate利润留存率 = 1- dividend payout ratio
- Sustainable Growth Rate可持续增长率 = ROE x Retention Ration = ROE x(1- Dividend payout ratio)
Credit Analysis
- Credit risk
- The risk of loss caused by a counterparty's or debtor's failure to make a promised payments.
- Credit analysis
- Z-score
Z = 1.2A + 1.4B + 3.3C + 0.6D + 1.0E
A = WC / TA
B = RE / TA
C = EBIT / TA
D = MV of Equity / BV of Debt
E = Revenue / TA
lf Z < 1.81 Bankruptcy
- Z-score
Segment分部 Reporting
- A company must disclose separate information about any operating segment which the segment constitutes 10% or more of the company's revenue, asset or profit.
- For each reportable segment, the following information should be disclosed:
- Segment revenue;
- Capital expenditure during the current year;
- Depreciation and amortization expense;
- Interest revenue and interest expense;
- Income tax expense or income.
Segment Ratios
- Segment Margin = Segment Profit / Segment Revenue
- Segment Turnover = Segment Revenue / Segment Assets
- Segment ROA = Segment Profit / Segment Assets
- Segment Debt Ratio = Segment Liabilities / Segment Assets
Inventories存货
Inventory Recognition
Inventory Recognition
- Following costs are included in inventory cost
- Purchase cost购买成本:including import关税 and tax-related duties,transport运输费 and related insurance, handling fee, less trade discounts折扣 and rebates返点
- Conversion costs转换成本:including direct labor直接劳动力,包括一线员工、车间管理的工资, fixed固定成本 and variable overhead costs可变成本
- 资本化,Cash减少,Inventory增加,计入现金流量表的COGS
- Following costs are expensed in the period incurred
- Abnormal waste of materials非正常损耗, labor, or overhead.
- Storage costs(unless required as part of production产成品的储存成本).
- Administrative overhead and selling costs.行政管理人员工资
- 费用化,Cash减少,RE减少,计入利润表的Expense
- 达到出售状态之前的必要支出
Cost of Good Sold
- When the inventory is sold, inventory goes to income statement as COGS.
- Beginning inventory + Purchases - COGS = Ending inventory
Valuation Methods
Inventory Valuation Methods
- Under IFRS, the permissible methods are:
- Specific identification个别计价法
- First-in,first-out.(FIFO)先进先出法,资产负债表准确
- Weighted average cost月末一次加权平均,入库时盘点
计算期初时存货的加权平均值,作为所有存货的价格
Preferred by IFRS
- Under GAAP, the permissible methods are:
- Specific identification
- First-in,first-out.(FIFO)
- Last-in,first-out.(LIFO)后进先出法,现金流量表准确
- Weighted average cost
Analysis of Inventory Valuation Method
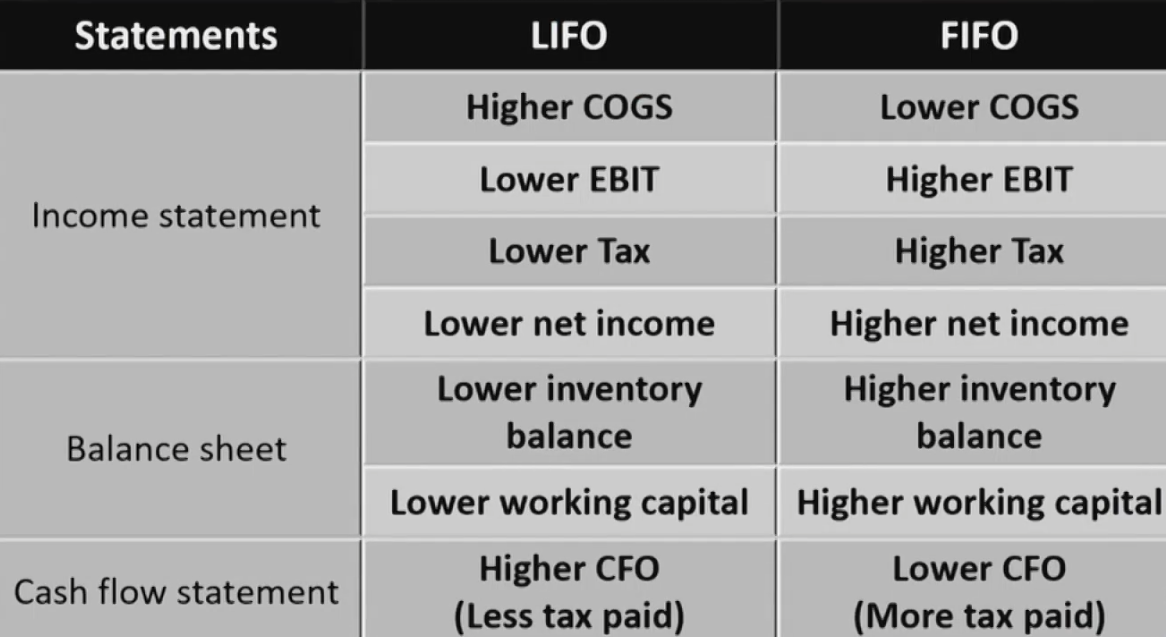
- LIFO provides the most useful estimate of COGS on the I/S.最新数据体现在利润表
- FIFO provides the most useful estimate of Inventory value on the B/S.最新数据体现在资产负债表
- Inperiods of rising prices

Periodic & Perpetual Assumption存货的盘点制度
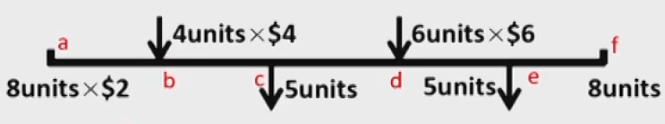
Periodic & Perpetual Assumption
- Periodic inventory system实地盘存制
- COGS and inventory ending value are determined at the end of an accounting period.计算最终剩余的存货,根据BASE法则计算COGS,只能最后知道
- Need a "purchase" Account用于计算Purchase
- Perpetual inventory system永续盘存制
- COGS and inventory ending value are updated continuously.每卖出一次存货,就更新一次COGS,实时知道
- "Purchase" Account is not needed.
Inventory Valuation Methods

Summary of periodic & perpetual inventory system

- Same result for FIFO & Specific identification method.
- FIFO Periodic与FIFO Perpetual结果相同,因为成本相同,Specific同理
- May be different result for LIFO & AVCO.
- LIFO Periodic 可能出现寅吃卯粮,此时与LIFO Perpetual结果不同,Weighted average同理
Impairment of Inventory under IFRS & GAAP存货减记
Inventory Impairmentin IFRS
- Inventory should be measured at the lower of the cost账面净值 or Net realizable value可变现净值NRV
- NRV = Selling price预期产成品售价 - Selling cost必要支出(广告费、进一步加工费等)
- If cost > NRV
- Inventory is written down减记 to NRV on B/S.
- A loss is recognized in I/S.
- Can be written up but limited to the amount of the original write-down and a gain is recognized in I/S.转回不能超过最初值
Inventory Impairment in GAAP
- Inventory is the lower of the cost or market市场价值,重置成本.
- If replacement cost > NRV
market = NRV - If replacement cost < NRV - normal profit margin
market = NRV - normal profit margin - If NRV - normal profit margin < replacement cost < NRV
market = replacement cost
- If replacement cost > NRV
- If cost > market
- Inventory is written down to market on B/S.
- A loss is recognized in I/S.
- No subsequent written up is allowed.不允许转回
Impact of Inventory Impairment
- Inventory write-down reduces both profit and the carrying value of inventory.
- 减记导致存货账面价值以及留存收益减少
- Write-down brings higher COGS, Reversal of the write-down brings lower COGS. 减记导致COGS增加,转回导致COGS减少
- Inventory write-down has negative effect on profitability,liquidity(current ration), and solvency ratios.
- Inventory write-down has positive effect on activity ratios(inventory turnover, total asset turnover).
Inventory turnover ratio & days of inventory on hand
- Ratios should be compared with industry benchmark and across several years.
- High inventory turnover and low DOH indicate high inventory management efficiency. But, it may indicate the company doesn't keep adequate inventory along with a low sale growth rate.生产跟不上使得存货周转率上升
- Inventory written down also results in high inventory turnover and low DOH which indicate poor inventory management.存货减记使得存货周转率上升
Inventory Adjustments
- If there is an active market exists, for the agricultural and forest products, minerals and mineral products, it may be measured at net realizable value(fair value - costs to sale and complete).有活跃市场的林农矿一手交易者的存货可以用NRV记账
- Any gain or losses resulting from changing in value should be recognized in I/S both under IFRS and US GAAP.
Inventory Report and Disclosure(U.S.GAAP & IFRS)
- Cost flow method used(LIFO, FIFO, etc.)
- Total carrying amount of inventories
- Disclose the carrying value of inventory which is valued at net realizable value (Fair value - selling costs)是否使用可变现净值法
- COGS for the period
- The amount of inventory write downs减记的净额
- The amount of reversal of inventory write downs and the events or circumstances of reversal (IFRS only)转回的原因
LIFO Reserve & LIFO Liguidation后进先出储备和后进先出清算
LIFO Reserve
- LIFO reserve is the difference between the reported LIFO inventory carrying amount and the inventory amount that would have been reported if the FIFO method had been used.
- LIFO Reserve = FIFO Inventory - LIFO Inventory
- LIFO COGS - ΔLIFO Reserve = FIFO COGS
Changes in Inventory Valuation
- Changes in accounting policy
- From other methods to LIFO → Prospective application
- Other changes → Retrospective application
- Disclosure in footnotes
- Useful in facilitating comparisons with other firms or industry average
LIFO & FIFO Conversion
- Income statement changes
- \mathrm{COGS}_{\mathrm{FIFO}}=\mathrm{COGS}_{\mathrm{LIFO}}-\Delta \text{LIFO Reserve}
- \mathrm{NI}_{\mathrm{FIFO}}=\mathrm{NI}_{\mathrm{LIFO}}+\Delta \mathrm{LIFO Reserve}\times(1-\text{Tax Rate} )
- Balance sheet changes
- \mathrm{Inventory_{FIFO}}= \mathrm{Inventory_{LIFO}}+ \text{LIFO Reserve}
- \mathrm{RE}_{\mathrm{FIFO}}=\mathrm{RE}_{\mathrm{LIFO}}+\text { LIFO Reserve }_{\text {Ending }} \times(1-\text { Tax Rate })
要求所得税税率不变 - \mathrm{Cash}_{\mathrm{FIFO}}=\mathrm{Cash}_{\mathrm{LIFO}}-\text { LIFO Reserve }_{\text {Ending }} \times\text { Tax Rate }
要求所得税税率不变
LIFO Liquidation
- In normal situation (prices are rising and inventory quantities are stable or increasing), the LIFO reserve will increase.
- 物价上涨 + 存货不减:LIFO Reserve>0, ΔLIFO Reserve>0
- 物价下降 + 存货不减:LIFO Reserve<0, ΔLIFO Reserve不确定
- 物价上涨 + 存货有减:LIFO Reserve>0并最终为0, ΔLIFO Reserve<0
- 物价下降 + 存货有减:LIFO Reserve<0, ΔLIFO Reserve<0
- A LIFO liquidation occurs when purchased volume is less than sales volume.库存减少使得LIFO reserve下降
- Even if the price is rising, LIFO reserve may decline.
- COGS no longer reflects recent prices, and an analyst should adjust COGS for decrease in LIFO reserve.导致现金流量表的指标的反应能力下降
- LIFO liquidation results in higher profit margin and higher income tax, and higher profits can not be sustainable.卖出压箱底的存货
Long-Lived Assets
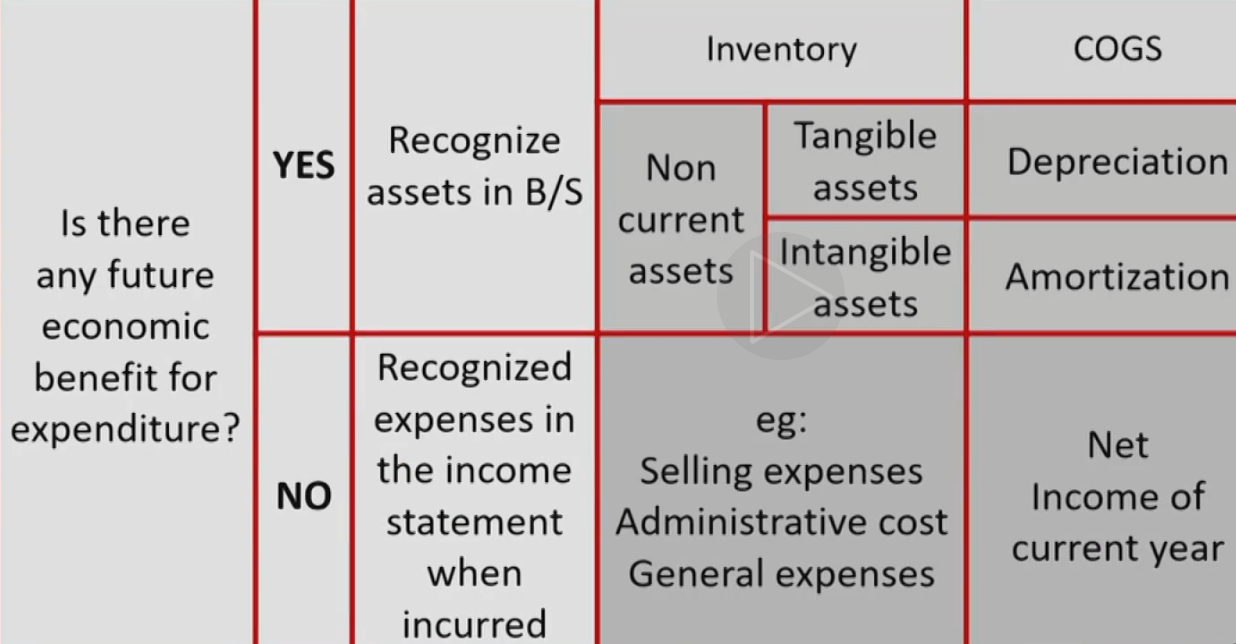
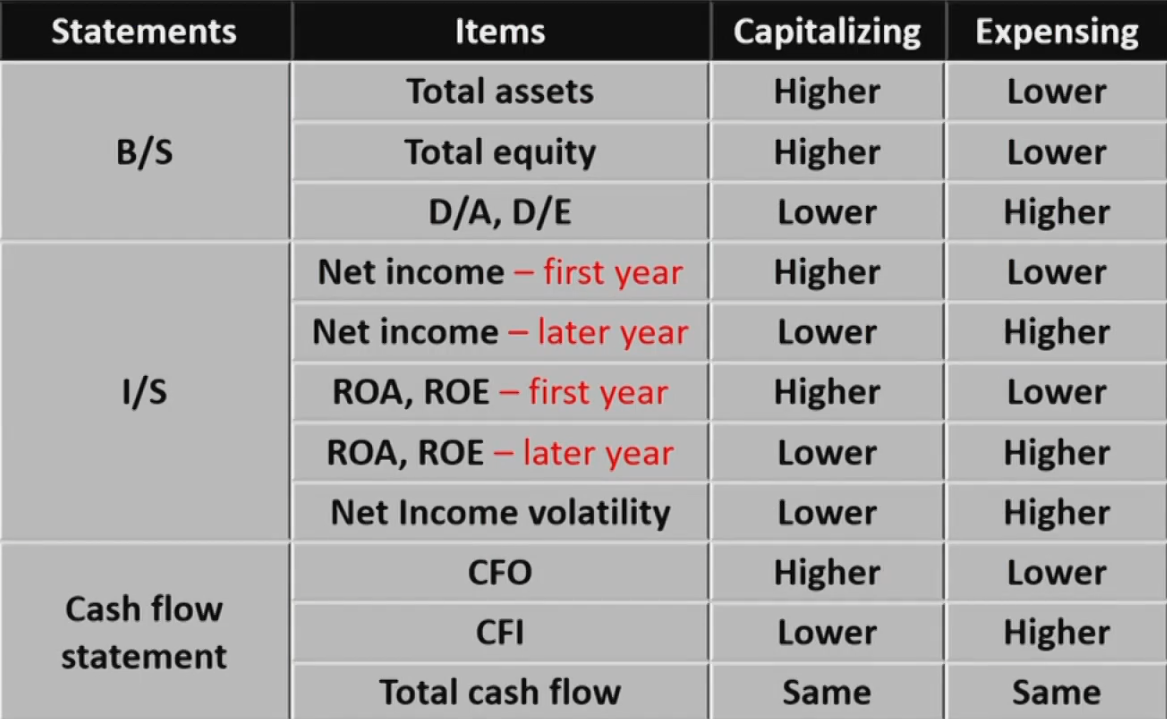
Capitalizing资本化 vs. Expensing费用化
Capitalizing vs.Expensing
- How to treat an expenditure depending on the nature of the expenditure
- Capitalize as an asset on the B/S
- 能带来未来的收益。Cash减少,PP&E增加。逐步反映到现金流量表
- The asset capitalized today will be expensed in the future 通过折旧摊销逐步反映到利润表
- Capitalized expenditures are classified as CFI 作为CFI流出
- Recognize as an expenses in the I/S
- 不能带来未来的收益。Cash减少,RE减少。直接反映到现金流量表
- Expensed expenditures are classified as CFO 作为每日经营的CFO流出
Costs of Tangible Assets
- Only costs necessary for the machine to be ready for use can be capitalized.必要支出才能资本化
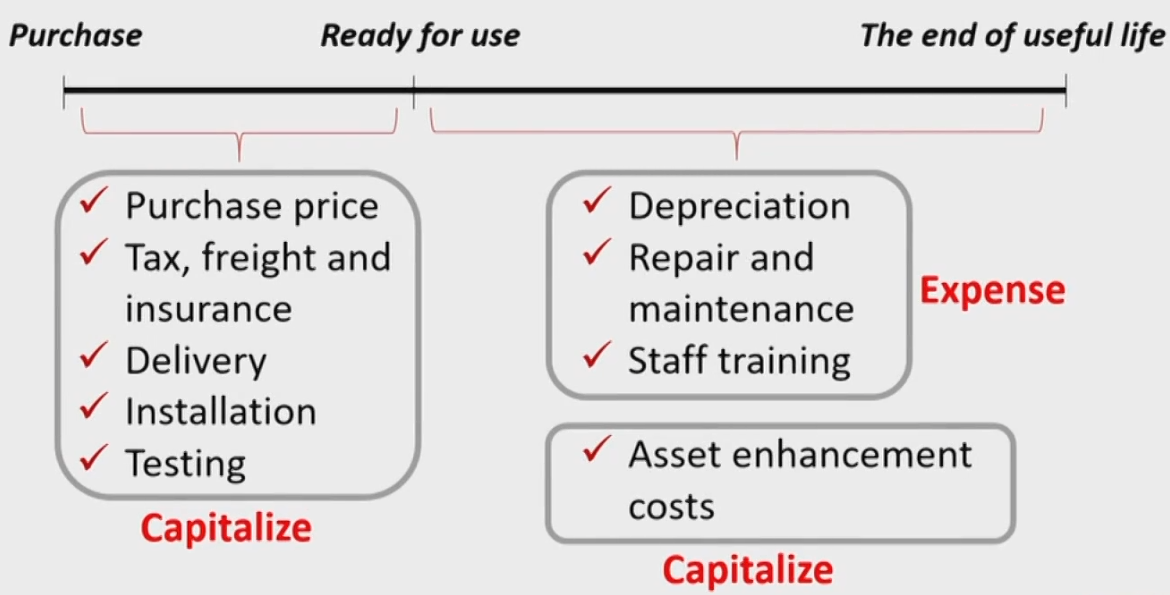
Capitalizing Interest Costs
- During the asset construction period, incurred interest must be capitalized as that asset's cost资产构建期间借贷的利息不计入Interest expense
- If the asset is constructed for sale, the borrowing costs are classified as inventory
- If the asset is for producing, the borrowing costs are classified as PP&E
- Under IFRS, interest income earned from temporary investment of borrowed fund can be deducted from capitalized interest借贷的闲置资金用于投资,产生的收益会抵消费用化利息
- Capitalized interest expenditures are classified as CFI under both IFRS and US GAAP.
- Expensed interest may be classified as CFO or CFF under IFRS, but classified as CFO under US GAAP.
- Implication for analysis: treat as normal interest
- For interest coverage ratio, analyst should include both the capitalized interest and the expensed interest
- If a company is depreciating interest that it capitalized in a previous period, income should be adjusted to eliminate the effect of that depreciation.费用化利息折旧导致EBIT增加
Intangible Assets无形资产
Intangible Assets
- Internally generated
- Generally cannot be capitalized on balance sheet(except for R&D costs研发)
- Purchased Separately
- Patents, Copyrights, Trademarks, Franchises, Licenses.
- Unidentifiable intangible asset
- Goodwill
Research & Development
- Research研究阶段
- IFRS & GAAP: should be expensed as incurred必须费用化
- Development开发阶段
- IFRS: Expensed as incurred except for certain criteria are met - technical feasibility of completing the intangible assets.技术可行后可以选择资本化
- GAAP: Expensed as incurred except for cost of software development.只有软件开发才有机会资本化
- Software development cost under US GAAP
- For sales: Once technological feasibility is established, subsequent production costs can be capitalized.如果是用来卖的,技术可行后可以选择资本化
- For own use: Can be capitalized if the project will be completed and the software will be used as intended. 如果是自用的,能够按期完工后可以选择资本化
Goodwill
- Goodwill = total cost to purchase the target company - Fair value of acquiree's net identifiable assets
- Net identifiable assets = fair value of identifiable assets - fair value of the liabilities and contingent liabilities
- 商誉 = 收购价 - (对方营运资本的公允价值 - 对方商誉 + 对方或有负债)
- If the purchase price less than the fair value of acquiree's net identifiable assets, it's called "bargain purchase". Any gain from bargain purchase is recognized in I/S.
Depreciation Methods
Depreciation Methods
- Straight-line depreciation
\text {Depreciation expense} =\frac{\text { cost }- \text { residual value }}{\text { useful life }}- residual value: 最终残值,也叫salvage value,可以更新
- cost: 如果有减值,折旧费根据更新后的cost计算
- Accelerated depreciation(double-declining balance,DDM)
\text { Depreciation expense } =\frac{2}{\text { useful life }} \times(\text { original cost }- \text { accumulative depreciation })- 时刻判断余额是否达到residual value,最后一年折现到residual value
- 不受残值的有限
- Units of production
\text {Depreciation expense} = \frac{(\text { original cost }- \text { residual value })}{\text { Total capacity during the useful life}} \times \begin{gathered} \text { Actual output } \\ \text { in current period } \end{gathered}- 不受使用寿命的影响
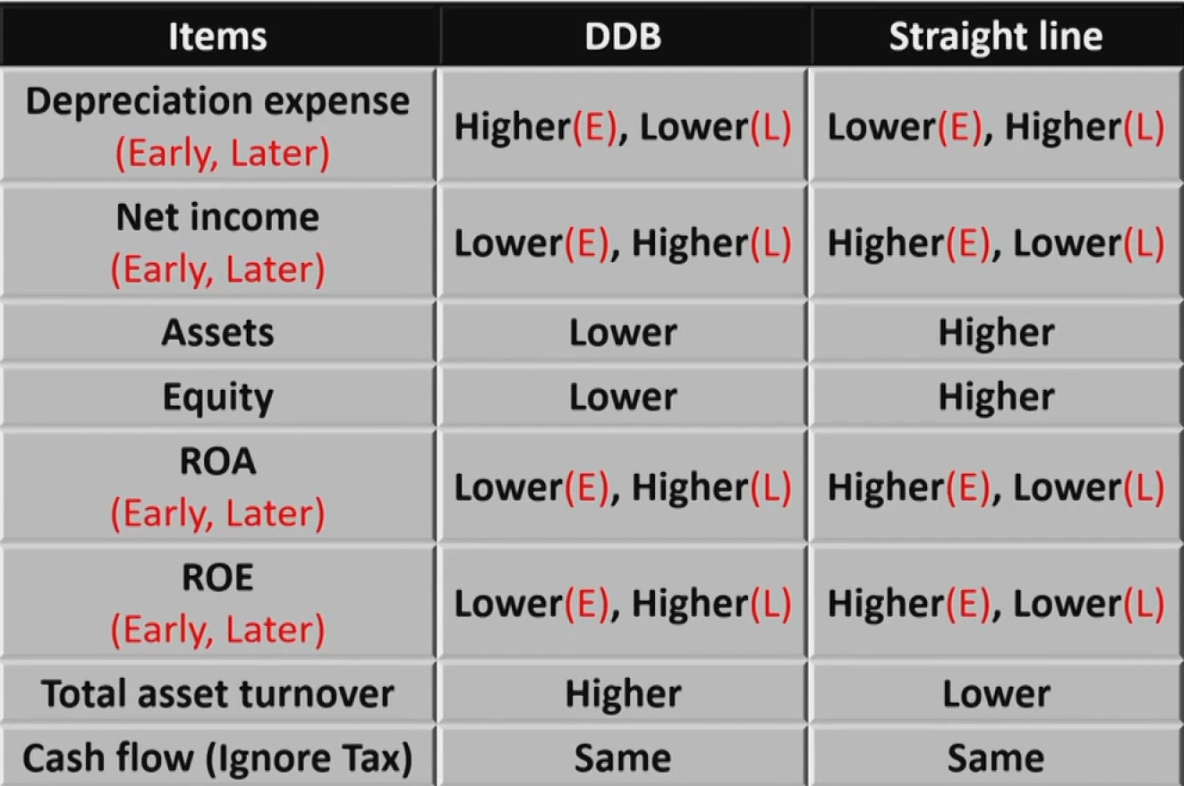
- 不受使用寿命的影响
- Declining balance depreciation
\begin{align} &\text {Depreciation expense}=\text {current book value} \times \text{ depreciation rate} \\ &\text {depreciation rate}=1-\sqrt[n]{\frac{\text {residual value}}{\text {cost}}} \end{align}
Accounting Treatments of Depreciation
- Allocation of depreciation expense
- COGS → Affect gross profit margin
- SG&A → Affect operating expense
- longer useful life & higher residual value
- Lower depreciation expense and higher net income.
- Estimation of residual value:
IFRS: allowed either upward or downward
GAAP: downward only
Amortization of Intangible Asset
- Intangible asset with a finite useful life要摊销和折旧
- Amortization over useful life
- Similar amortization methods as depreciation methods for tangible assets
- Intangible asset with an infinite useful life不摊销可能折旧
- Do not amortization
- Impairment tested at least annually每年减值测试。其它的资产出现减值迹象才测试
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
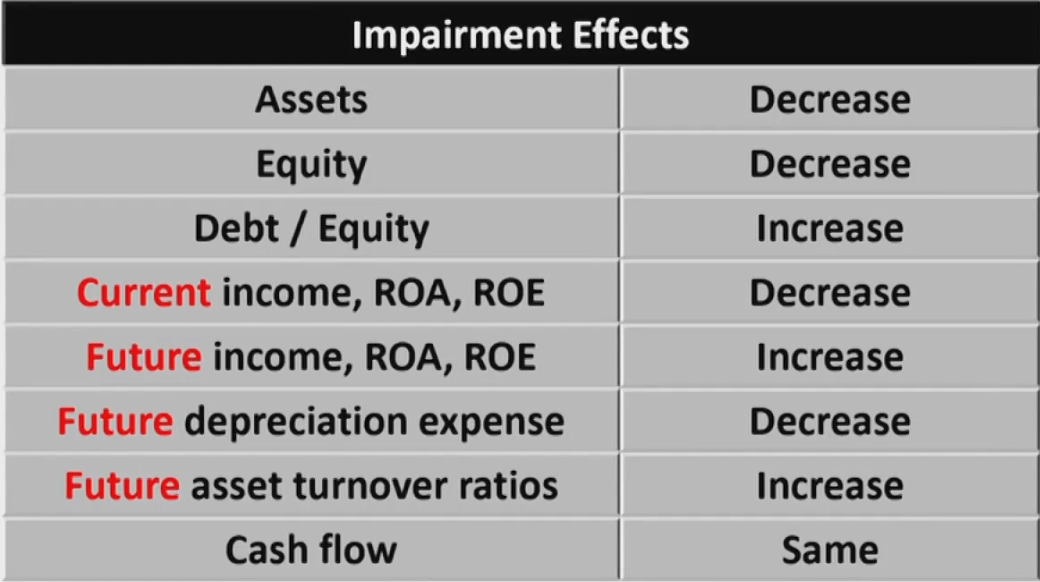
Principle of Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
- Held for use → Different impairment test treatment for GAAP and IFRS
- Held for sale
- A long-lived asset reclassified as held for sale from held for use should do the impairment test when reclassified.use转化为sale时要测试
- No depreciation from reclassification on.转为sale后不再需要折旧
- Test to see if Carrying value(NBV) > fair value - cost to sell.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets Held-for-Use: IFRS
- Impairment happened if carrying value of assets > recoverable amount
- Recoverable amount is the higher of NRV(fair value - selling cost出售的收益)and value in use( PV of future cash flows未来收益的现值)
- Impairment loss = carrying value - recoverable amount
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets Held-for-Use: GAAP
- Step one: DO the impairment test
- Carrying value of assets > Undiscounted future cash flows generated by assets未来收益的简单求和
- Step two: IF pass the test,THEN measure the loss
- Impairment loss = carrying value - fair market value(如果有公允价值) or PV of future CF未来收益的现值
Recoveries of Impairment减值恢复
- Under U.S.GAAP
- Held for use: Recoveries are not allowed
- Held for sale: Recoveries are allowed, but is limited to the previous impairment loss.
- Under IFRS
- The impairment loss can be reversed (except for goodwill),but is limited to the previous impairment loss.
Reporting Models of Long-Lived Assets & Disposal of Long-Lived Assets
Reporting Models of Long-Lived Assets
- U.S.GAAP: Historical Cost 全都用历史成本计量
- IFRS:
- Investment property投资性房地产: Historical Cost or Fair Value
- Other long-lived assets其它长期资产: Historical Cost or Revaluation Model重评估
Historical Cost Model [both IFRS and GAAP]
- Long-lived assets on the balance sheet are reported at amortized cost.
- carry value = original cost - accumulated depreciation - impairment charges
Fair Value Model [IFRS only]
- IFRS allows to value investment properties using either cost model or fair value model,
- Investment property held for the purpose of earning rental投资性房地产 income or capital appreciation or both.
- Using the fair value model:
- Investment property is carried at fair value.
- Any gain or loss arising from a change in the fair value of the investment property is recognized in profit and loss.确认为G/L,不计入AOCI
- Don't depreciate the assets不需要折旧摊销
Revaluation Model [IFRS only]
- Carrying amounts of Long-lived assets are the fair values at the date of revaluation, and should consider accumulated depreciation and amortization.定期更新成公允价值,之后折旧摊销
- If the fair value initially increase after purchase, the difference between the fair value and purchase cost should be reported in revaluation surplus as O.C.I in equity
- 公允价值增加先抵消之前RE的减值,再增加AOCI
- Subsequent decrease in fair value should write-off the revaluation surplus recorded previously first until zero and then go to income statement.
- 公允价值减少抵消之前AOCI的增加,再减少RE
- When an asset is retired or disposed of, any related amount of revaluation surplus included in equity is transferred directly to retained earnings.
- 处置资产后,直接结算AOCI到RE
- G/L is sales minus carrying amount
Disposal of Long-Lived Assets
- If a long-lived asset is sold
- A G/L of disposal, the difference between cash proceeds and book value of the assets sold at the time of sale, should be reported in income statement.
- If a long-lived asset is abandoned
- A loss, the book value of disposed long-lived assets at the time of abandoned, should be reported in income statement.
- If a long-lived asset is exchanged
- A G/L reported at fair value of the asset given up (or fair value of asset newly acquired 公允价值的收益和账面价值的收益二选一) in income statement.
Income Taxes
Tax Reporting税务报表 & Financial Reporting
Differences between Two Systems税会差异

- 当期应纳所得税结合递延所得税负债和递延所得税资产得到所得税费用
Deferred Tax Items
- Sources of Differences
- Temporary / Timing differences暂时性差异,以后会被翻转弥补,如折旧。导致递延所得税项目Deferred Tax Items
-
- Permanent differences永久性差异,如国债的免税,存在永久性差异时,应纳所得税不等于EBT×t
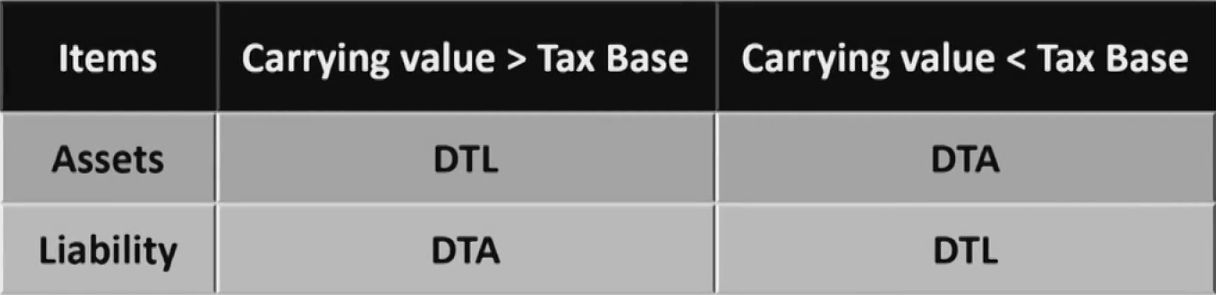
- Deferred tax liabilitiy(DTL)导致将来多交税,如股票的浮盈: A liability caused by temporary differences应纳税暂时性差异.
- Deferred tax asset(DTA)导致将来少交税,如股票的浮亏: An asset caused by temporary differences可抵扣暂时性差异.
- Both DTLs and DTAs are presented on the balance sheet, not Netted不允许相互抵消
- 同一笔业务只会产生一个,如初期产生应纳税暂时性差异,之后转回应纳税暂时性差异
Tax reporting & Financial Reporting
- Tax reporting
- Taxable income = Taxable revenue - Tax deductible expense
- Taxes payable = Taxable income × Tax rate
- Income tax paid = Actual cash outflow for income tax. (Actual cash outflow for tax in CFS)
- Financial reporting
- Pretax income (Accounting profit) = Earning before tax
- Income tax expense = current taxes payable + △DTL - △DTA
Effective Tax Rate实际税率 & Statutory Tax Rate法定税率
Permanent Differences
- Permanent differences: differences in tax and financial reporting that will not reverse in the future.
- Permanent differences will not cause deferred tax items 不产生DTA或DTL
- Reasons for permanent differences:
- Income or expense items not allowed by tax legislation如国债免税导致的
- Tax credits for some expenditures 税收优惠
- It will results statutory rate ≠ effective tax rate 存在永久性差异时,实际税率不等于法定税率
- Tax disclose 必须披露为什么实际税率不等于法定税率
Tax Base计税基础 & Carrying Value账面价值
Tax Base
- Tax base税务机关眼中资产的价格
- Tax base of asset: amount deductible for tax purposes in future periods as economic benefits are realized将来在纳税申报表可抵扣费用
- Tax base of liability: the carrying value of the liability minus any amounts that will be deductible on the tax return in the future.将来在纳税申报表不可抵扣费用
- Permanent differences
- tax base and carrying value will be the same
- Timing differences
- tax base and carrying value will be different
Tax Base and Accounting Base of Assets
- Depreciable assets
- Accounting base = Original cost - accumulated accounting depreciation - impairment
- Tax base = Original cost - accumulated tax depreciation
- Research in R&D
- Accounting base(Expensed as incurred) = 0(费用化了,没有形成资产)
- Tax base(Capitalized强制资本化) = Original cost - accumulated amortization
- Account receivable
- Accounting base = Invoiced amount - allowance for bad debt
- Tax base = Invoiced amount(do not recognize allowance不考虑坏账准备)
Tax Base and Accounting Base of Liabilities
- Customer advance预收账款
- Accounting base(accrual accounting) → Unearned revenue treat as a liability
- Tax base(cash accounting) → Revenue is recognized no liability arise → 0
- Warranty liability保修费用
- Accounting base(accrual accounting) → A liability is recognized for future obligation
- Tax base(cash accounting) → Recognize a expense when a cash outflow incurred → 0
Determine DTA/DTL
- Tax loss carrying forward亏损弥补 also results in a DTA.
- difference × tax rate
- Tax loss carrying forward will result in a DTA 提前交税导致DTA
Calculation of Deferred Tax Items & Calculation of Income Tax Expense
Calculation of Deferred Tax Items
- Determine deferred tax amount - I/S approach
- Identify the difference between Taxable Income and Accounting Profit for the year
- If the difference is timing difference, changes of DTA or DTL is generated
- 税率变动时需要追溯向前调整
- Determine deferred tax amount - B/S approach
- Identify the difference between Accounting Base and Tax Base for every asset and liability item on balance sheet
- Calculate DTA or DTL ending balance based on the difference.
- 税率变动时不需要调整
Calculation of Income Tax Expense
- Income tax expense = current tax payable + △DTL - △DTA
Changes in Statutory Income Tax Rate
Calculation of Income Tax Expense
- Income tax expense = current tax payable + △DTL - △DTA
- current tax payable = taxable income x current tax rate
- Current tax payable, the ending balance of DTL or DTA are both calculated at the end of each fiscal year
- Current tax payable should use the current tax rate.
Current tax payable = taxable income x current tax rate - Calculate DTL and DTA should use future tax rate that expected to apply when the asset is realized or the liability settled.
DTA or DTL ending= temporary difference ending x new tax rate
- Current tax payable should use the current tax rate.
When the Tax Rate Changes
- DTA or DTL ending = Temporary difference ending x New tax rate
- When the tax rate changes, temporary difference ending does not change, but the DTA ending or DTL ending will change with the tax rate.
- △DTA and △DTL is generated
Income Tax Analysis
Recognition of DTA
- DTA should be assessed减值测试 at every balance sheet date to see whether the deferral will be recovered entirely.
- The carrying value of DTA should be reduced减值 to the expected recoverable amount可回收额 by increasing the amount of a contra account valuation allowance under US GAAP
- 在GAAP下,通过备抵账户减值
- 预计盈利能力不足时选择减值
- If any subsequent recovery of the deferral is expected to realize (future earning power is expected to increase),reduction of valuation allowance is allowed under GAAP
- 在GAAP下可以转回
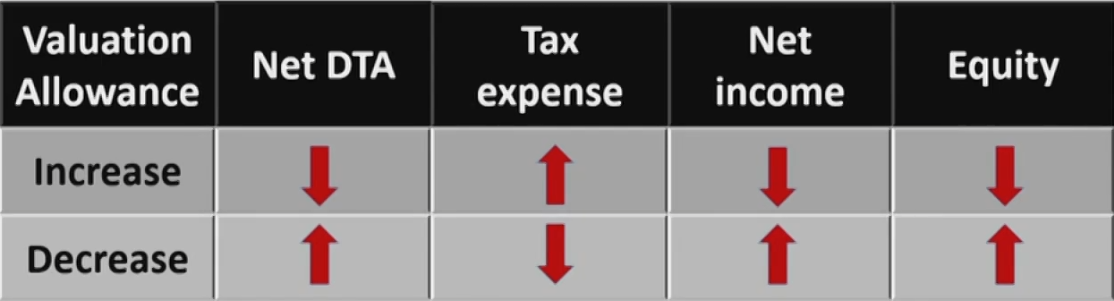
Net DTA
- A valuation allowance reduces a deferred tax asset
- Net DTA = DTA - Valuation allowance
- Allowance Is based on likelihood that the asset will not be realized (e.g. no taxable income expected)
- Valuation allowance can be used to manipulate income:
Recognition of DTL
- If DTL is to be reversed:
- Treated as true liability
- If DTL is unlikely to be reversed: 如债务被不停地被续上
- Treated as equity
Classification
- GAAP: Either current or non current on B/S, base on the classification of the related non-tax assets or liabilities.
- IFRS: Non current on B/S.
Long-Term Liabilities and Leases租赁
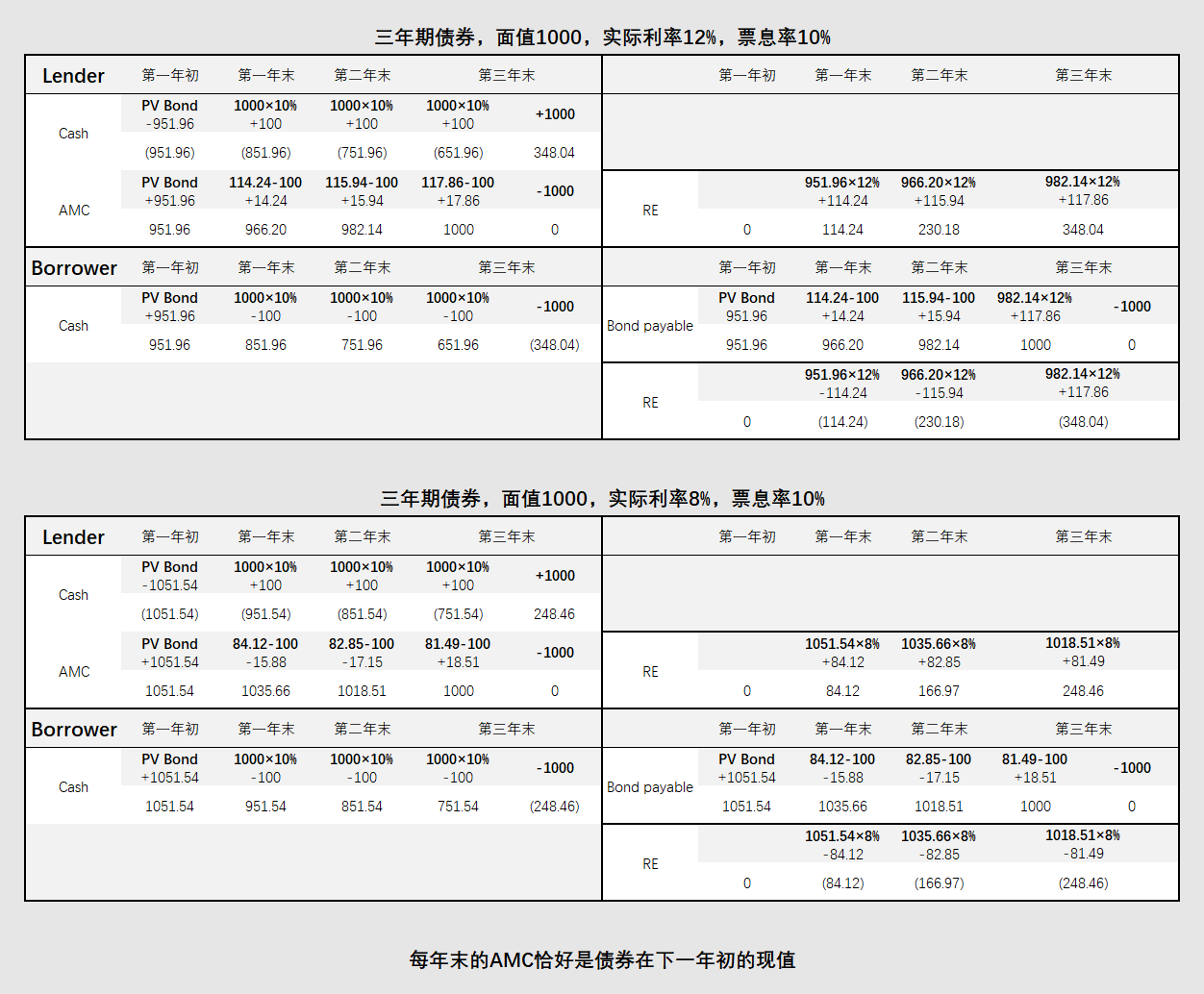
Accounting for Bond Amortization
- ΔBV = Amortization = Interest expense - Coupon payments
- Coupon paymants = Coupon rate x Par value
- Straight-line Method
- Amortization = (Par - PV) / n
- Effective interest rate method
- Interest expense = BV × Effective market rate
- Using financial calculator: FV = Par Value, PMT= Coupon Payment, I/Y = Effective market rate, N = T-t → BV = (-)PV
Analysis for Accounting Treatments
Cash Flow of Bond: CPA's View
- Periodic payment of Coupon:
- CFO outflow(GAAP)*
- CFO outflow or CFF outflow(IFRS)
- Principal: CFF
- Amount received at issuance: CFF inflow
- Principal repayment at maturity: CFF outflow
-
- Assume U.S. GAAP applies unless otherwise noted.
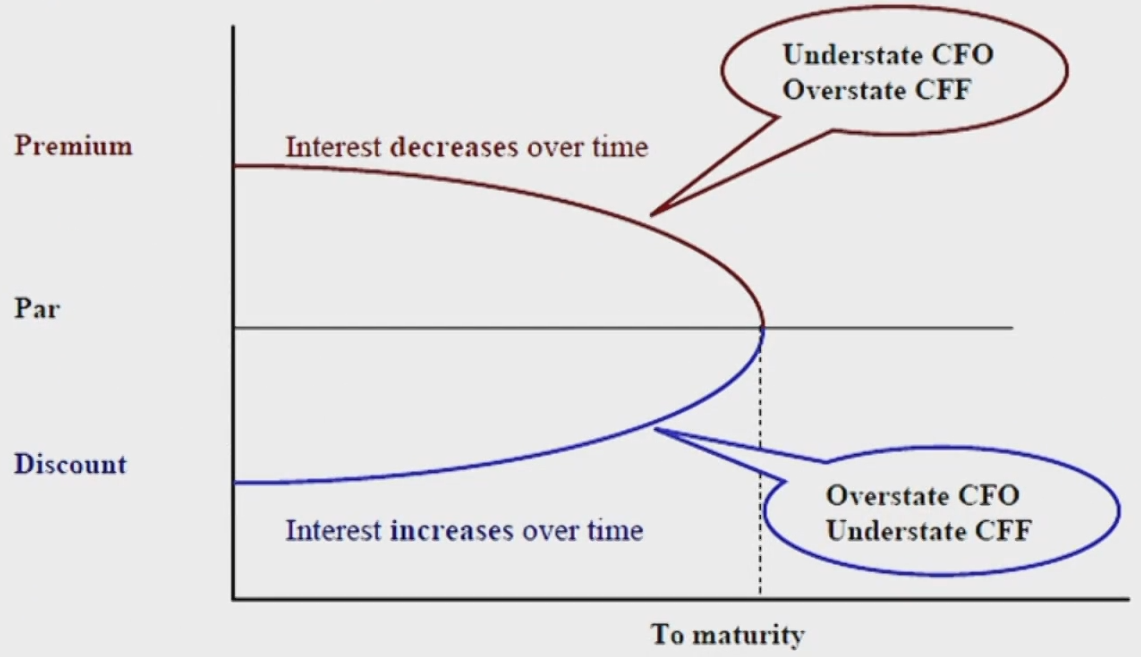
Cash Flow of Bond: CFA's View for Bonds Issued at Discount
- For analysis purpose, the interest expense and the amortization of the premium/discount should be separated.
- 将Cash CFO拆成RE CFO和AMC CFF
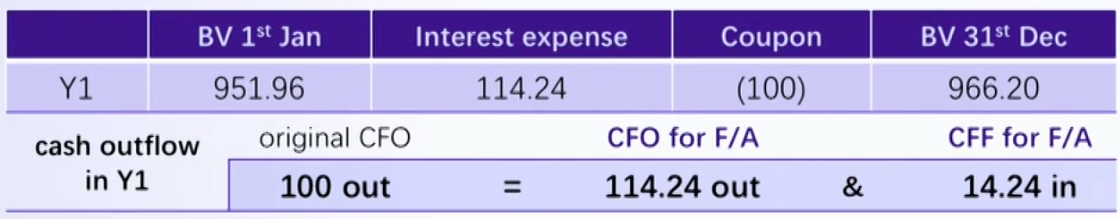
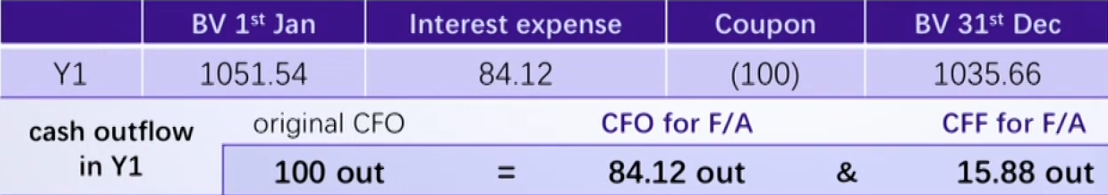
- 将Cash CFO拆成RE CFO和AMC CFF
- For borrower if without analyst's adjustment
Issuance Costs债券发行成本
Issuance Costs
- Issuance costs refer to printing costs, Legal and accounting fees, sales commissions, and other fees incurred during bond issuance
- Under U.S.GAAP
- Issuance costs are capitalized as asset(deferred charge) and allocated to I/S as an expense over the bond term.
- 债券发行成本导致Cash减少和“发行成本”增加,不反映在RE
- Bond payable不变,因此不改变实际利率
- “发行成本”逐年摊销到0,RE减少。如果提前结束债务关系,就提前确认为RE的损失
- Under IFRS
- Initial bond liability on B/S is reduced by amount of the issuance costs, increasing effective interest rate.
- 债券发行成本导致Cash和Bond payable减少,不反映在RE
- Bond payable减少,相当于债券融资被抵消一部分,实际利率被抬高
Derecognition of Debt
- A firm may choose to redeem bonds before maturity提前结束债务
- Interest rates reduction
- Firm has generated surplus cash through operation
- Funds from the issuance on the equity market is available
- Under U.S. GAAP, any unamortized issuance costs must be written off and included in the gain or loss calculation
- G/L on derecognition提前结束的现金流 = B/S carrying value - cash paid - unamortized issuance costs直接结清剩余的“发行成本”
Definition and Classification of Leases
Definition of Lease
- A lease is a contractual arrangement where by the lessor出租人, the owner of the asset, allows the lessee承租人 to use the asset for a specified period of time (lease term) in return for periodic lease payment租金.
- Two parties involved in leases
- Lessee: use the asset
- Lessor: owner of the asset
- Two types of lease
- Operating lease
- Finance lease
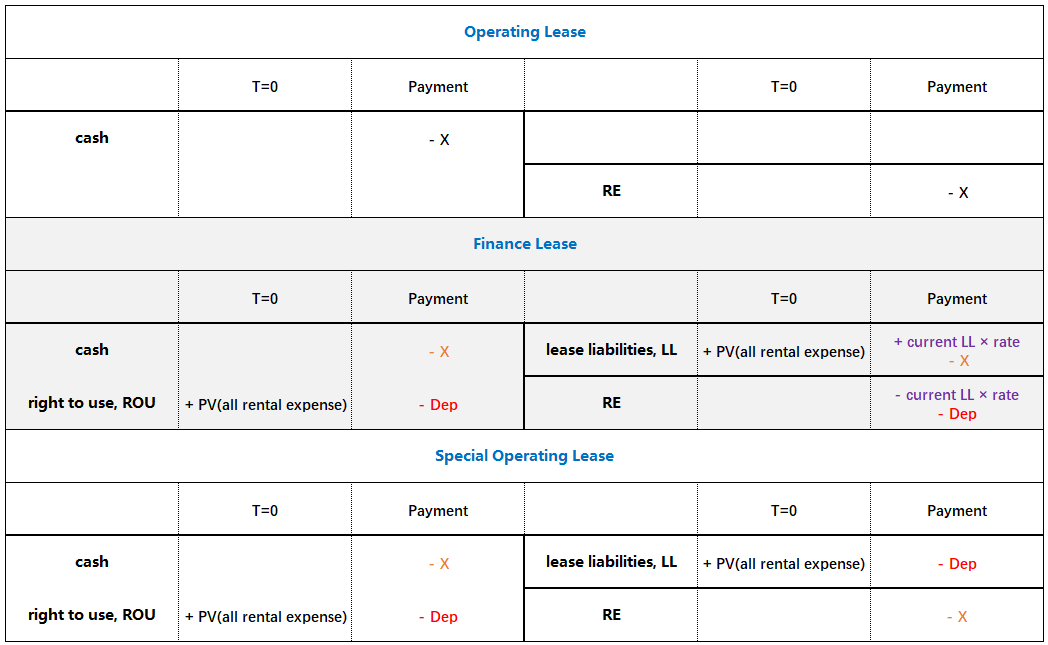
Classification of Leases
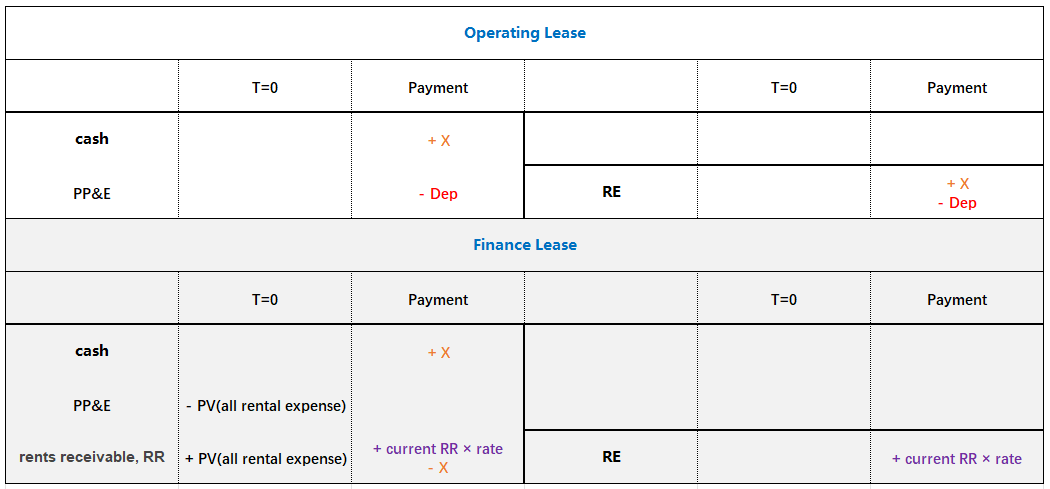
- Operating lease经营租赁
- Operating lease is basically a rental.
- 出租人对资产折旧,收到出租人的rental revenue(CFO in)
- 承租人向出租人支付rental expense(CFO out)
- Periodic lease payments are reported in I/S.双方现金流都计入I/S
- Finance lease / Capital lease融资租赁
- A finance lease is, in substance, a purchase of an asset with debt.借钱买资产
- 承租人对资产折旧,向出租人支付interest expense(CFO out)和capital payment(CFF out)
- 出租人收到承租人的interest expense(CFO in)和capital payment(CFF in)
- Lessee will report equal value of asset and liability on B/S.
- The lessee should record depreciation expense and interest expense in I/S.
Reasons to Lease
- For lessee:
- Lower fixed interest rate成本低
- Less or no down payments低首付
- Less covenants restrictions限制小
- For lessor:
- Less risk of obsolescence资产用不着了
- Tax benefits of ownership税务优势
Lease in IFRS and GAAP
- Lessee
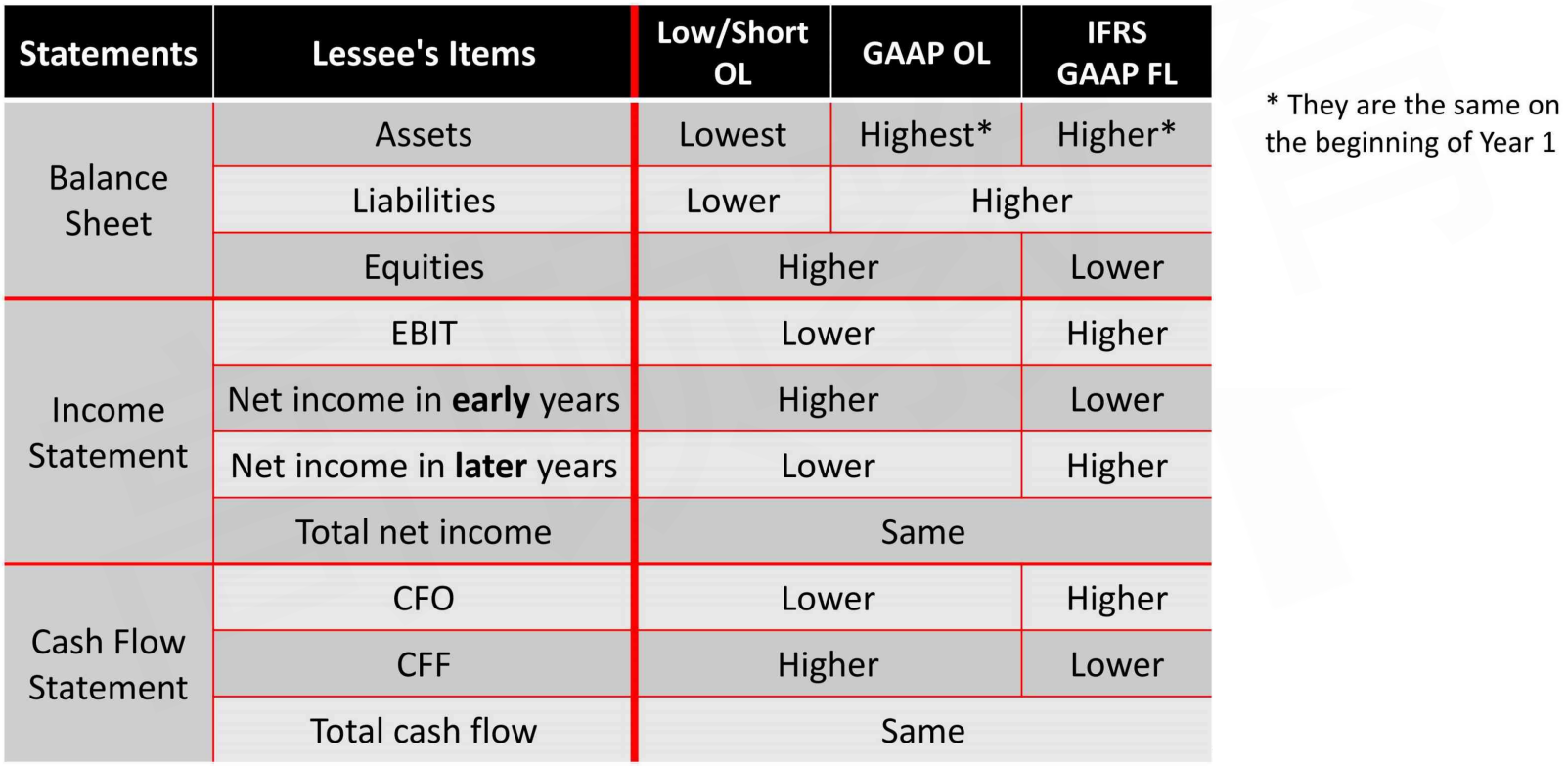
- IFRS: same method with finance lease按融资租赁处理,除了短期租赁和低价值租赁按经营租赁处理
- GAAP: difference between finance lease and special operating lease按融资租赁或美国特色经营租赁处理,除了短期租赁按经营租赁处理
- Exceptions for short-term lease短期租赁(GAAP, IFRS) and leases where leased asset is low value低价值租赁(IFRS): same method with operating lease
- Lessor
- A lease will be classified as a finance lease if any of the following criteria are met:
Transfers ownership of the asset to the lessee after the lease ends
Includes a bargain purchase option结束后可以低于市场价购买
Covers a period of time that is a major part of the asset's useful life
PV of lease payments that equal or exceed the major part of asset's fair value
Involves an asset that is so specialized被改造了 that it will have no alternative use to the lessor after the lease ends - Otherwise, it will be classified as an operating lease
- A lease will be classified as a finance lease if any of the following criteria are met:
Disclosure of Lease Arrangement
- Lessees and lessors are required to disclose:
- General description of leasing arrangements
- Nature, timing, and payments to be paid or received
In each of the next 5 years
Aggregated payments beyond 5 years - Lease revenue and expense for each period presented in the income statement
- Amounts receivable and unearned revenues from leases
- Restrictions imposed by lease arrangements
Accounting and Analysis For Lessee
Accounting
Analysis
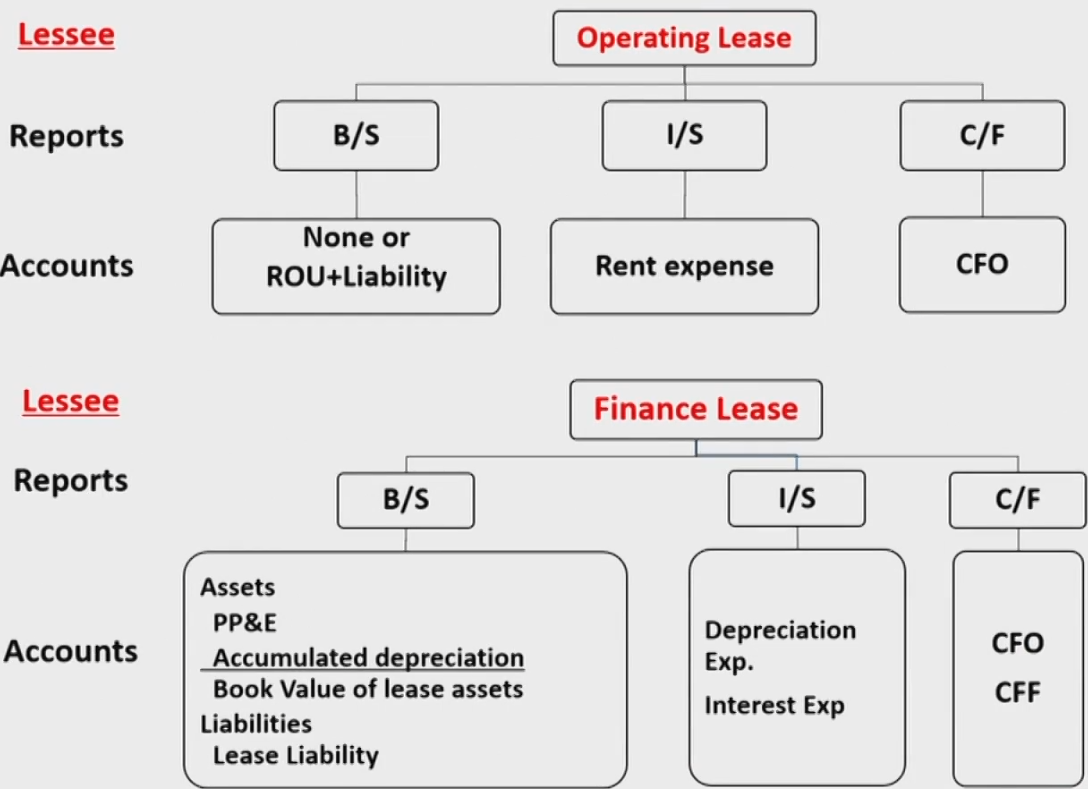
Accounting and Analysis for Lessor
Accounting
Analysis

Classification of Lessor
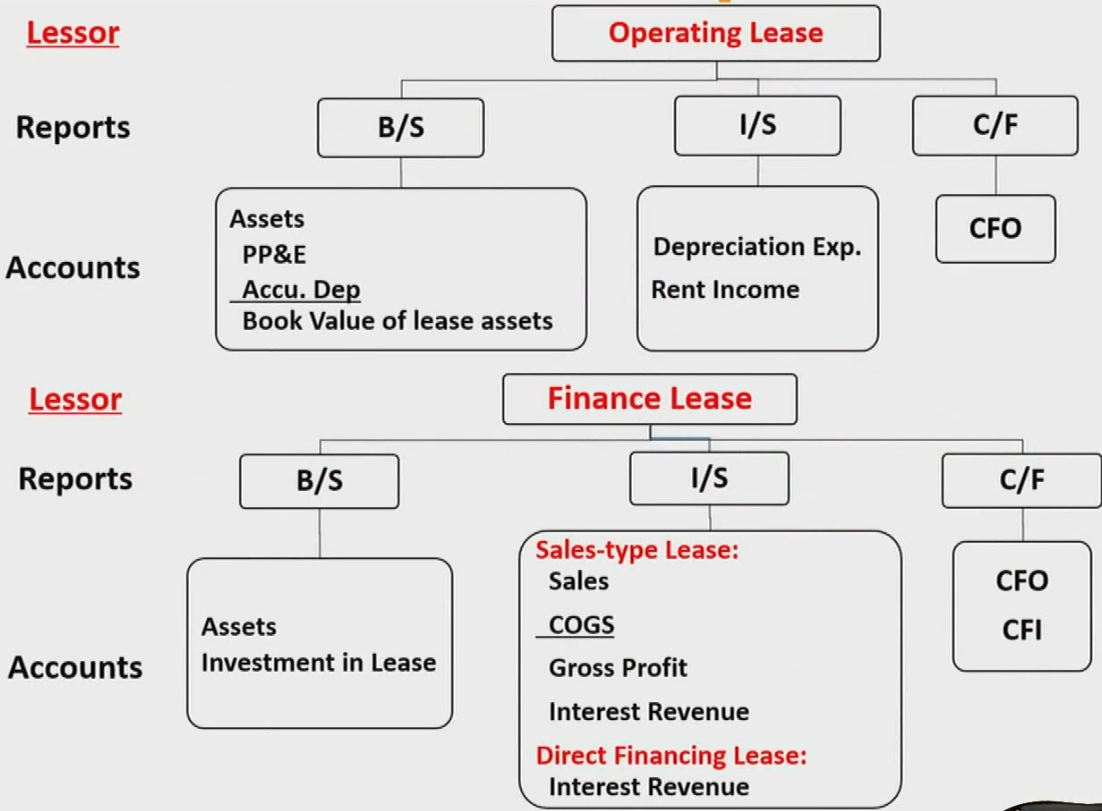
- Under U.S. GAAP, finance lease will be treated as either sales-type lease or direct financing lease.
- The lessor's classification uses the same criteria that a lessee uses in determining whether the benefits and risks of owning the leased asset have been transferred to the lessee
If any of these criteria are met, the lessor will categorize the lease as a sales-type lease, assuming that collection of the future lease payments is probable - A direct financing lease applies when a lease doesn't meet the criteria to be considered a sale-type lease but yet results in the lessor relying on future lease receipts to recover the asset's cost
A lease is considered a direct financing lease under US GAAP if the lease contract provides for a third- party guaranteed residual value, which combined with the future lease payments by the lessee will equal or exceed the fair value of the leased asset - A financing lease is a type of lease transaction that converts the lessor's risk arising from ownership of the underlying asset (that is, asset risk) into credit risk
- The lessor's classification uses the same criteria that a lessee uses in determining whether the benefits and risks of owning the leased asset have been transferred to the lessee
- Under U.S. GAAP, if none of the criteria above is met, the lessor will classify a lease as an operating lease
- Under IFRS, no distinction between sales-type lease and direct financing lease. However, finance leases made by manufacturers or dealers are treated similarly as sales type lease in US GAAP
Brief Introduction of Pension Plans
Defined Contribution Plans存钱相同
- Employer
- Keeps all contributions current.
- Only financial liability is making contributions to employee's account.
- The plan must offer sufficient investment vehicles.
- Employee
- Own the plan and can transport account to other employment situations.
- Bear all risk/return consequences of investment.
- Must make all investment decisions given available investment vehicles.
- 不涉及负债
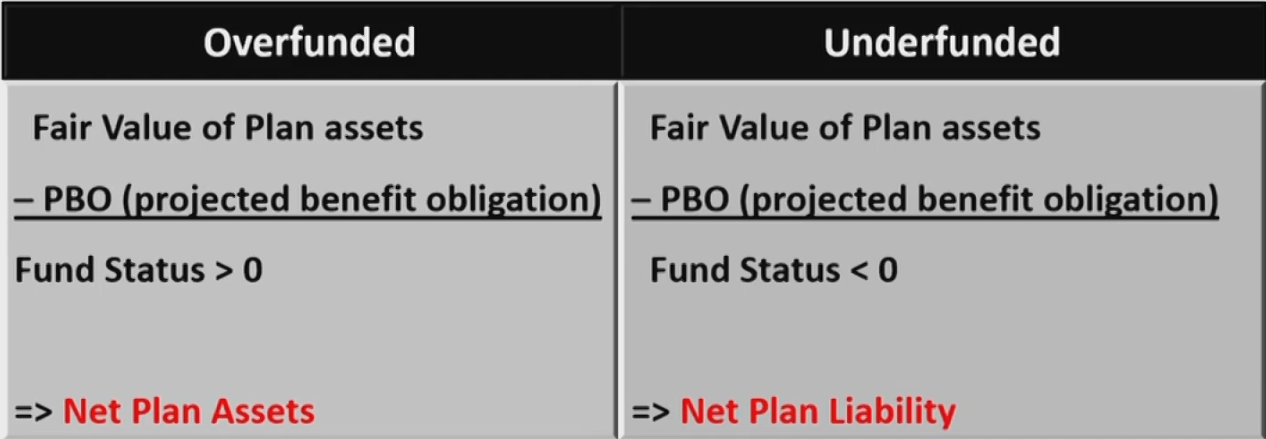
Defined Benefit Plans取钱相同
- Employer
- Liability of employer
- Determined by stated criteria usually related to years of service and salary.
- Sponsor (employer) is responsible for managing the plan asset.
- Employee
- Receive periodic payments starting at retirement.
- Not bear risk/return consequences of investment.
- 产生负债PBO
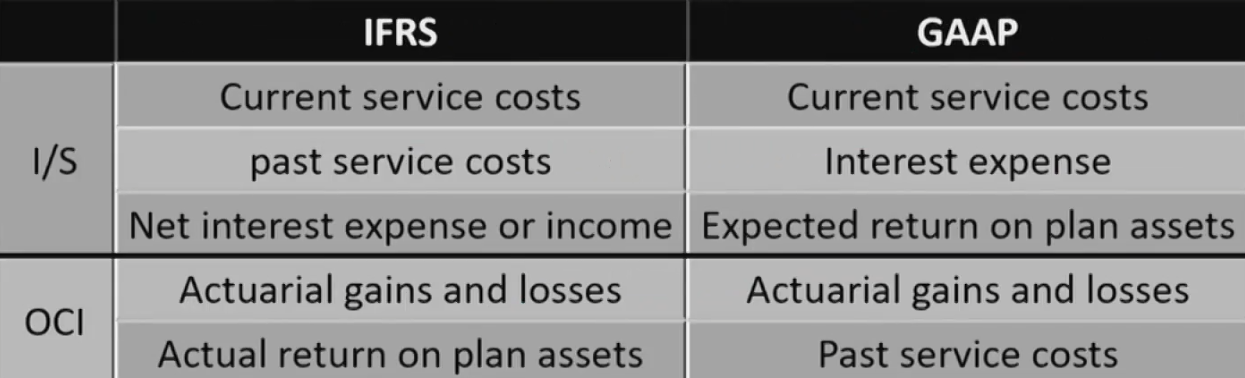
- Actuarial gains or losses will be recognized in OCI清算假设变动可能导致G/L,计入OCI
- 如平均寿命增加导致损失
Brief Introduction of the DB Accounting
Financial Reporting Quality
Financial Reporting Quality and Earnings Quality
- Financial reporting quality
- Provides decision-useful information: relevance and faithful representation
- Earnings Quality
- Provides sustainable and adequate return
- Relation
- Financial reporting quality and earnings quality are separated but interrelated with each other.
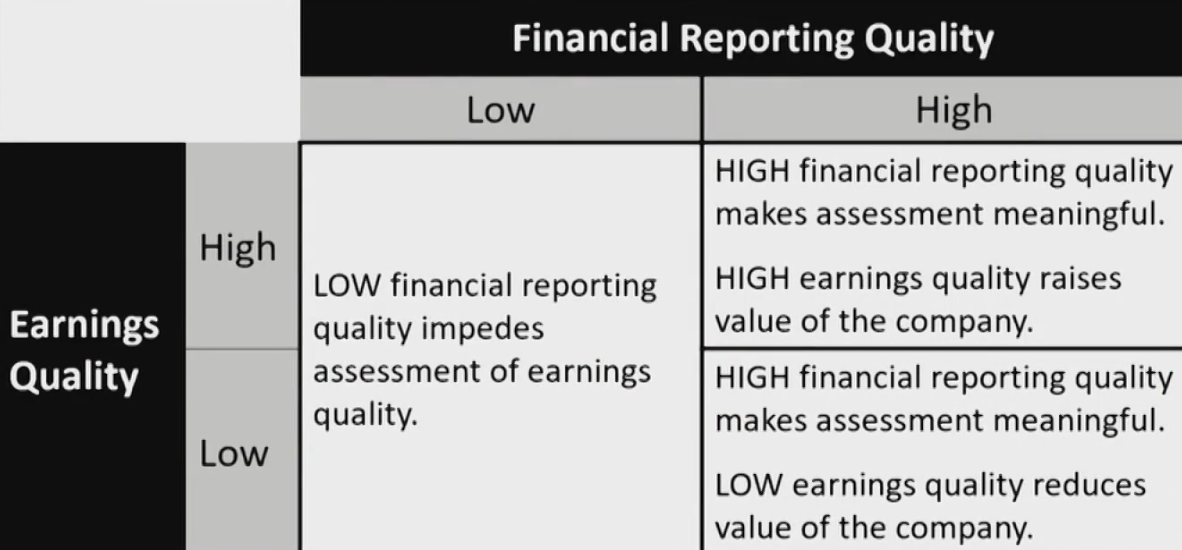
- Financial reporting quality and earnings quality are separated but interrelated with each other.
Quality Spectrum
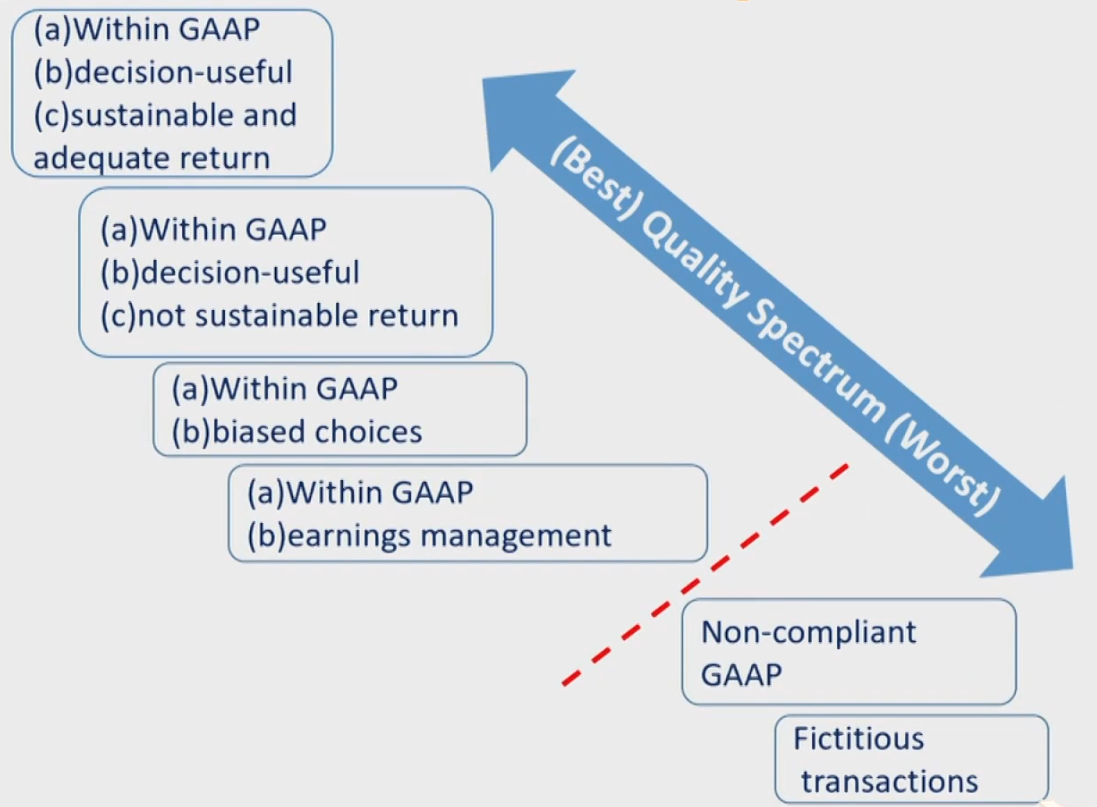
Conservative vs. Aggressive
- Aggressive Accounting
- 提前确认收入/延后确认费用
- 增加当期利润,但当期的高利润不具有持续性
- Conservative Accounting
- 延后确认收入/提前确认费用
- 减少当期利润,使得未来利润有所增长
- 依旧是有偏的
Fraud Triangle舞弊三角形

Discipline Mechanisms如何约束
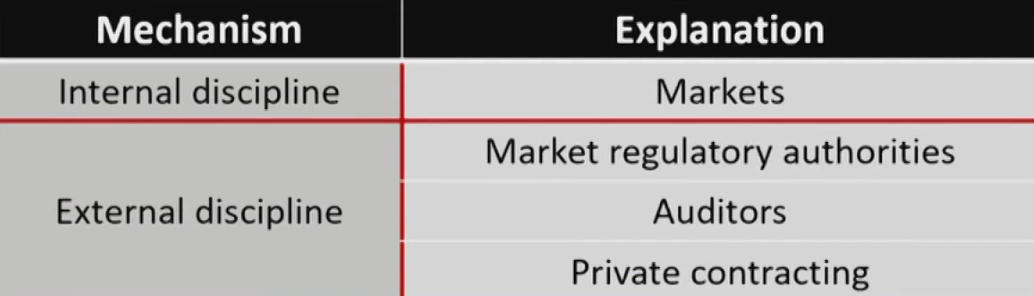
Accounting Manipulation Warning SignS
Financial Statements Analysis: Applications
Evaluating Past Financial Performance
- How have key ratios changed and why?
- How do key ratios and trends compare with competitors / industry?
- What aspects of performance are critical for a competitive advantage?
- How did the company perform in these areas?
- What is the company's business model and strategy - are they reflected in key measures?
Assessing Credit Risk-4C's
- Capacity
- Collateral
- Covenants
- Character
Assessing Credit Risk - Credit Scoring
- Credit rating agencies employ formulas that are weighted averages of several specific accounting ratios and business characteristics
- Scale and diversification: Size, product diversification,geographical diversification
- Operational efficiency: Such items as operating ROA, operating margins, and EBITDA margins fall into this category, along with degree of vertical integration
- Margin stability: Stability of profitability margins indicates a higher probability of repayment
- Leverage: Coverage ratios of operating earnings,EBITDA, or some measure of free cash flow to interest expense or total d
Equity Investments Analysis
Analyst Adjustment