Categories,Characteristics, and Compensation Structures of Altermative Investments
Categories and Characteristics
Definition of alternative investment
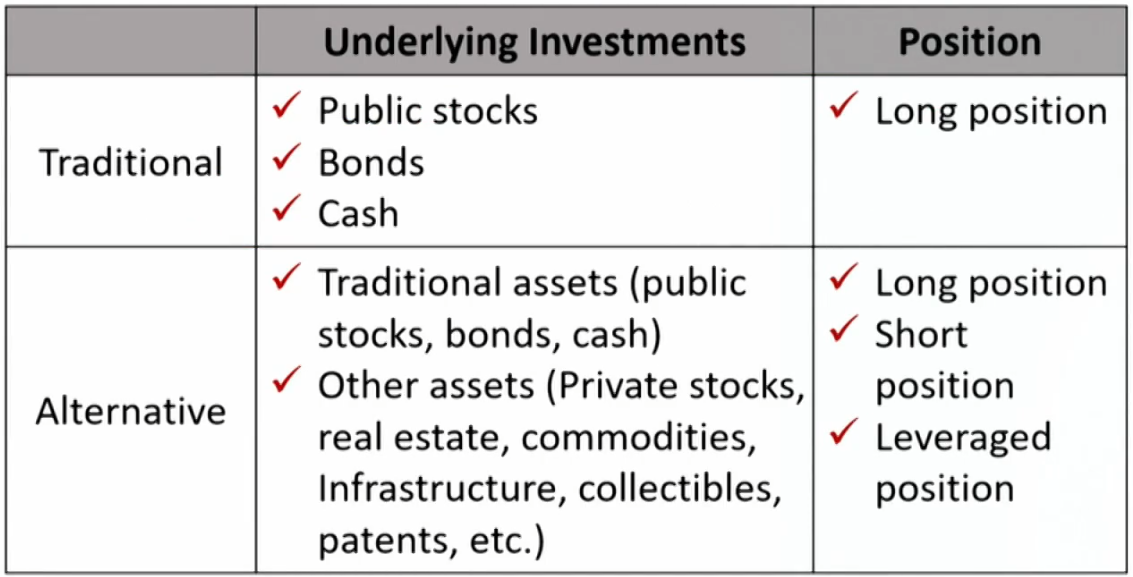
Characteristics of alternative
- Diversifying power: returns that are uncorrelated with or only slightly correlated with traditional investments.另类投资与其它投资关联度低,从而降低系统性风险
- Can be correlated in periods of financial crisis.
- Higher expected returns
- Illiquidity: the investment trades infrequently.交易少
- Inefficiency: market prices cannot reflect all availableinformation due to relatively low degree of competition.市场不有效
- Opportunities of arbitrage and superior risk-adjusted return
- Narrow specialization of the investment managers专业性高.
- Less regulation and less transparency than traditional investments透明度低
- Limited reliable historical risk and return data.数据少
- Unique legal and tax considerations.税少
- Higher fees, often including performance or incentive fees管理费高
- Concentrated portfolios.另类投资本身很集中
- Restrictions on redemptions (i.e., "lockups" and "gates"")难赎回
Market participants
- Endowments, pension funds, Sovereign wealth funds, and family offices.
Investment Method
Three methods for alternative investments
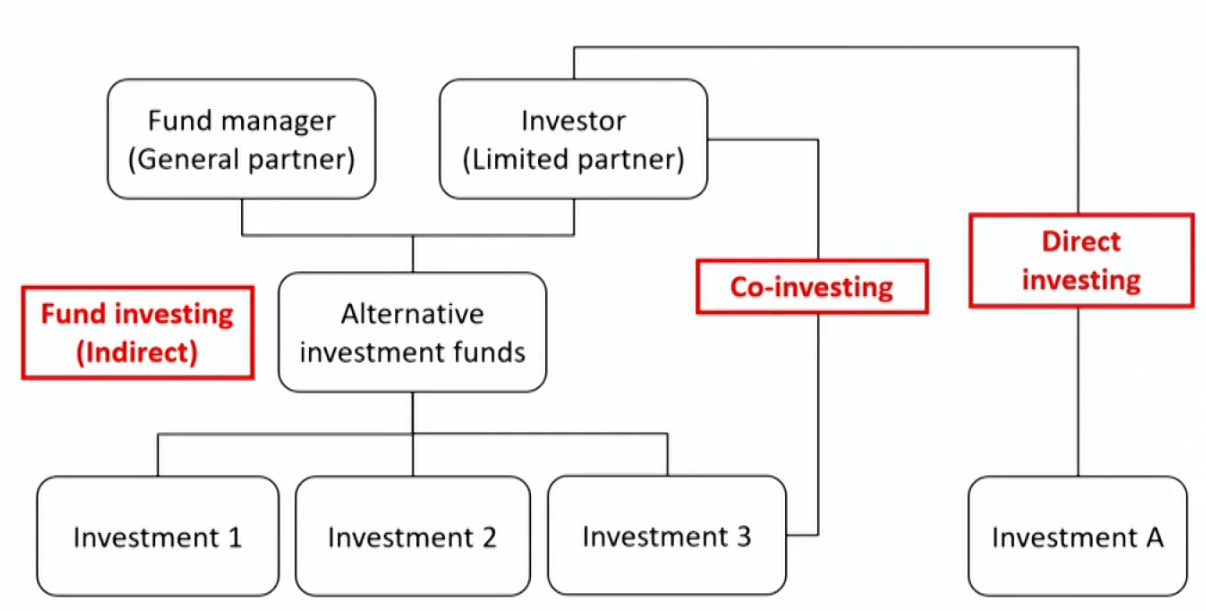
- Fund investing间接投资(GP, LP):Indirect method. Investor contributes capital to a fund,and the fund identifies, selects, and makes investments on the investor's behalf.
- Investment decisions are limited to either investing in the fund or not.
- Fund investors are typically unable to affect the fund's underlying investments.
- Investment decisions are limited to either investing in the fund or not.
- Co-investing两种都有:The investor invests in assets indirectly through the fund but also possesses rights (known as co-investment rights) to invest directly in the same assets.
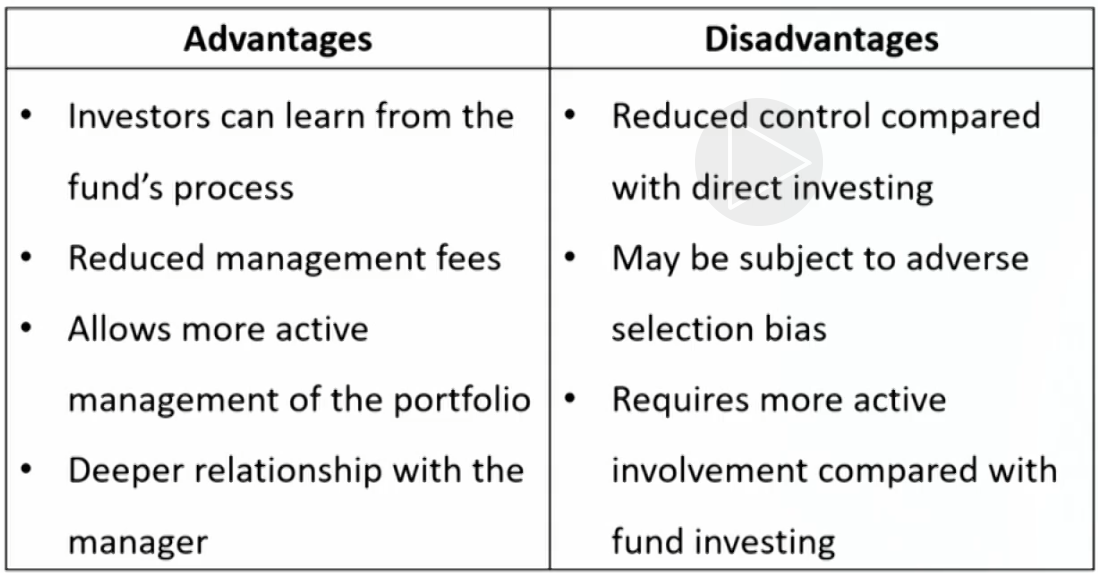
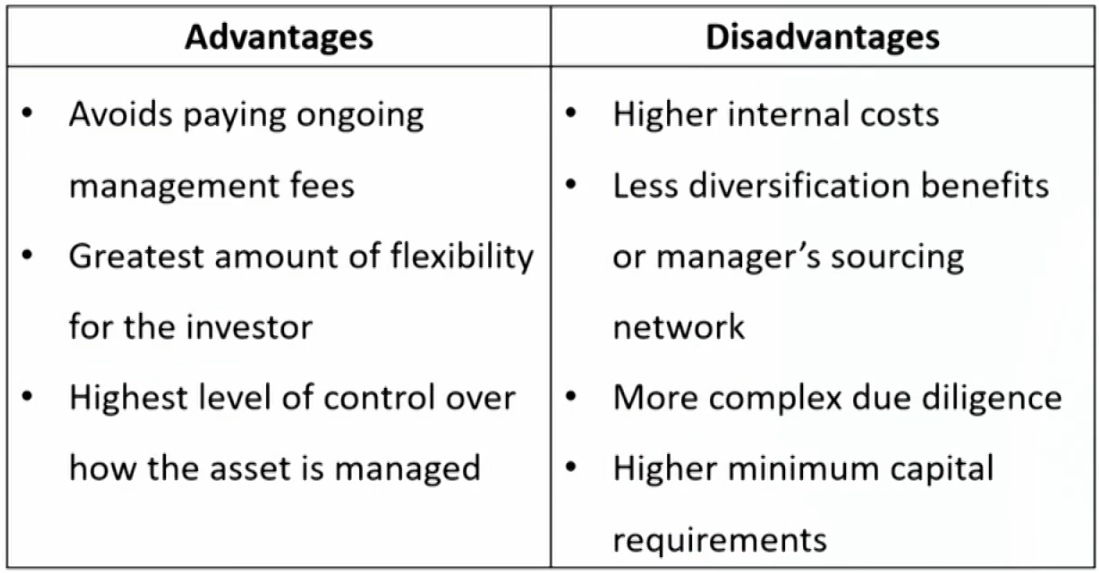
- Direct investing自己直接投:An investor makes a direct investment in an asse without the use of an intermediary.
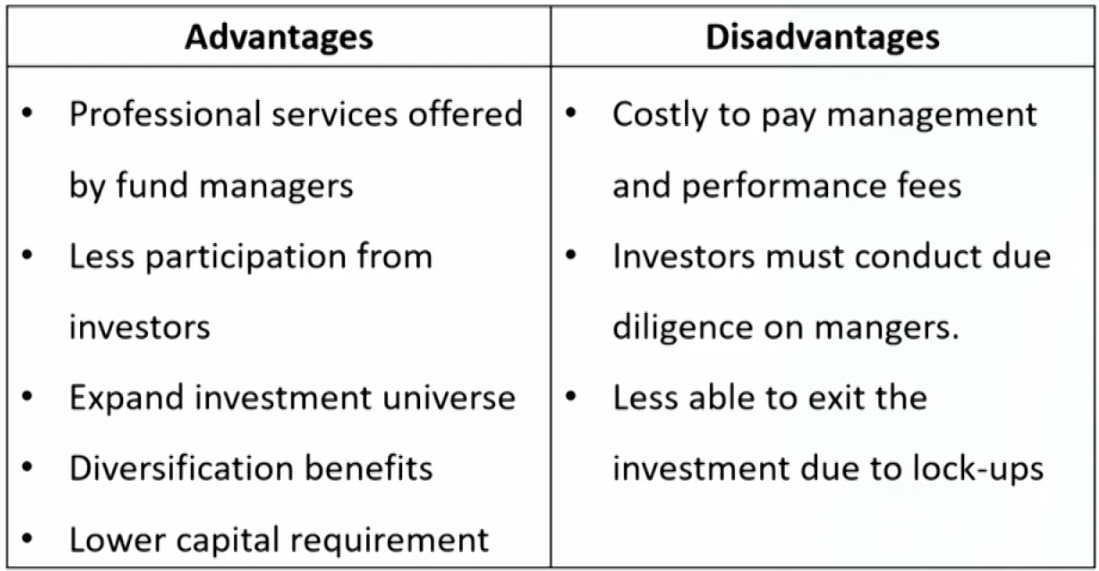
- Great flexibility and control when it comes to choosing their investments, selecting their preferred methods of financing, and planning their approach.
- Typically reserved for larger and more sophisticated专业 investors.
Due diligence of three methods
- Direct investing: the focus of the due diligence is the company itself, at a very detailed level.
- Fund investing: the investor is responsible for conducting due diligence on the fund manager.
- Co-investing: the investor will conduct direct due diligence on the portfolio company with the support of the manager.
Fund investing strucutre
- General partner(GP, manager): runs the fund and bears unlimited liability for anything that might go wrong.
- Limited partners (LP, investors): are outside investors who own a fractional interest in the partnership based on the amount of their initial investment.
- Play passive roles and are not involved with the management of the fund.
- There exists a principal/agent problem between GP and LPs.
Key partnership documents
- Limited partnership agreements (LPAs)合伙协议
- A legal document that outlines the rules of the partnership and establishes the framework that ultimately guides the fund's operations.
- May be dense with provisions and clauses.
- Side letters
- Exist ouside the LPA.
- E.g. , notice requirements in the event of litigation.
Compensation and Fees
Compensation structures
- Management fee
- Also known as base fee.
- Typically ranging from 1% to 2% of AUM(hedge fund)交的钱 or committed capital (PE fund)承诺交的钱.
- Performance fee
- calculated on profits net of management fees基础是管理费外 or on profits independent of management fees基础包括管理费
- Also known as incentive fee or carried interest.
- Typically 20% of excess returns
- Hurdle rate超过约定回报率才有激励费: a return level that LPs must receive before GP begin to receive incentive fees.
- Hard hurdle rate超过门槛的部分: the GP earns fees on annual returns in excess of the hurdle rate.
- Soft hurdle rate超过之前的部分: the fee is calculated on the entire annual gross return as long as the set hurdle is exceeded.
Usually has a catch-up provision.
- High water mark水位不断上升: reflects the highest value used to calculate an incentive fee.
- The incentive fees are only paid when assets under management are above the highest value (net of fees) previously recorded.
- Protects clients from paying twice for the same performance.
- Waterfall of PE: a provision that specifies how distributions from a fund will be split and how the payouts will be prioritized.如何给不同类别的合伙人分钱
- Deal-by-deal (or American) waterfalls: performance fees are collected on a per-deal basis每完成应该项目就分配一次. GPs get paid before LPs receive their initial investment on the entire fund.利好GP
- Whole-of-fund (or European) waterfalls: GP does not participate in any profits until the LPs receive their initial investment and the hurdle rate has been met.LP拿够后才到GP,利好LP
- Clawback provision of PE: right of LPs to reclaim overdistributed performance fee.利好LP
- Are usually activated when a GP exits successful deals early on but incurs losses on deals later in the fund's life.即使不再是GP合伙人,也要为任期内错误决策付出代价,归还酬金给LP
- Is only as good as the creditworthiness of the GP.
- Catch-up clause of PE: allows fund managers to earn incentive fee on all profits, given hurdle rate has been achieved.利好GP
- Profits are distributed only to the limited partners until the hurdle rate is reached.超过hard hurdle rate部分优先全给GP,直到与hard hurdle rate下的收益达到约定百分比,之后就按百分比分成
- Additional profits are split, with 100% going to the fund manager until the fund manager receives an incentive fee on all of the profits.

Custom fee arrangements
- “2 and 20” and “1 and 10” are common, but variations exist.
- Fees based on liquidity terms and asset size.
- Longer lockups are generally associated with lower fees.锁定期长的手续费低
- Discount fees for larger investors or for placement agents.
- Founders' shares entitle investors to a lower fee structure.越早投入手续费越低
- Either/or fees: managers agree either to charge a 1% management fee or to receive a 30% incentive fee above the hurdle, whichever is greater.管理费和激励费只受高的
Different Alternative Investments
Hedge funds对冲基金
Characteristics of hedge funds
- Private placement offering
- Limited number of investors and large initial investments.
- Lighter regulatory compliance burden
- Light investment restrictions
- Creatively selects investments in different geographic regions
- Leverage is often used
- Generally takes both long and short positions
- Generate high returns (absolute or risk adjusted basis)
- Management fees and incentive fees
- Lockup periods: Investors may be required to keep their money in the hedge fund for a certain period before they are allowed to redeem shares.
- Soft lockup: an expensive redemption fee is charged.
- Notice periods: investors may be required to give notice,typically 30-90 days, of their intent to redeem.赎回要提前通知
- The goal of hedge fund redemption restrictions is typically to increase hedge fund manager flexibility.
Categories of hedge funds
- Hedge funds are typically classified by strategy.
- Equity hedge strategies
- Event-driven strategies
- Relative value strategies
- Macro strategies
- Hedge fund categorization is important to allow investors to review aggregate performance data, select strategies, and select appropriate performance benchmarks.
Forms of hedge fund investments
- Individual hedge fund
- Extensive due diligence, high minimum invesmtnet.
- Funds of hedge funds母基金
- Diversification
- Able to negotiate better redemption terms
- Making hedge funds accessible to smaller investors
- Expertise in conducting due diligence on hedge funds尽职调查简单
- Drawbacks: more complex(higher) fees structures
Risk and return of hedge fund investments
- Self-reporting and survivorship bias
- Higher returns and lower volatility. → Higher Sharpe ratio.
- Asymmetric distribution of returns
- Higher downside deviation. → Lower Sortino ratio
- Drawdown: cumulative negative returns in a certain period.
- Risk diversification properties
- First came to prominence with the dot-com bubble.
- Expanded it further through direct allocations after 2008.
- Using market prices or quotes for valuation
- Common approach: the average quote, (bid + ask) / 2平均计价
- Conservative approach: bid prices for long position and ask prices for short position最差情况计价
- Valuation in highly illiquid or non-traded investments缺少流动性导致的偏差
- "Mark-to-model" basis模型不准确
- Returns maybe smoothed or overstated价格被平滑
- Volatility of returns understated低估波动性
Equity hedge strategies权益对冲策略
- Focus on public equity markets and take long and short positions in equity and equity derivative securities.
- Generally use a "bottom-up" security-specific approach.
- Main types:
- Market neutral对冲风险
- Fundamental L/S growth成长性基本面分析
- Fundamental value价值基本面分析
- Short biased做空有问题的公司
- Sector specific
- Market neutral
- Long positions in undervalued securities and short positions in overvalued securities.
- Maintains a net position that is neutral with respect to market risk and other risk factors (size, value, industry, etc).
Portfolio beta is close to zero. - Require the application of leverage.
- Are generally stable, low-return portfolios but are exposed to occasional spurts of volatility.
- Fundamental L/S growth
- Use fundamental analysis to identify companies expected to exhibit high growth and capital appreciation.
- Take long positions in these companies while short companies under downward pressure.
- Portfolios tend to end up long biased.
- Fundamental value
- Use fundamental analysis to identify companies deemed undervalued.
- Takes long positions in these companies and sometimes hedges the portfolio by shorting index ETFs or more growth- oriented companies deemed overvalued.
- Portfolios tend to end up long biased, value biased, and small-cap biased.
- Short biased
- Focus on shorting overvalued equity securities (against limited or no long-side exposures).
- Can be useful in terms of weathering periods of market stress.
- Have a difficult time overall posting meaningful long-term returns.
- Sector specific
- Exploit manager expertise in a particular sector and use quantitative (technical) and fundamental analysis to identify opportunities.
- The more complex a sector or the more opaqueness in accounting practices, the more value sector-specific managers bring.
Event-driven strategies事件驱动策略
- Event-driven strategies seek to profit from defined catalyst events, such as an acquisition or restructuring.
- Is based on bottom-up security-specific analysis.
- Tend to be long biased.
- Main types:
- Merger arbitrage购买要合并的公司
- Distressed/restructuring认为有利好事件
- Special situations有标志性事件
- Activist成为股东控制公司
- Merger arbitrage
- Long the stock of the company being acquired and short the stock of the acquiring company when the merger or acquisition is announced
- The primary risk in merger arbitrage is that the announced combination fails to occur and the deal spread re-widens to pre-merger levels.
- Moderate expected return → application of leverage.
- Distressed/restructuring
- Focus on securities of companies either in or perceived to be near bankruptcy.
- Purchase fixed-income securities trading at a significant discount to par.
- Or purchase the so-called fulcrum debt instrument expected to convert into new equity upon restructuring.
- Special situations
- Focus on opportunities to buy equity of companies engaged in restructuring activities other than mergers, acquisitions,or bankruptcy.
- Activist
- Secure sufficient equity holdings to allow them to influence corporate policies or direction.
- Try to create business catalysts, moving the investment towards a desired outcome
Relative value strategies相对价值策略
- Seek to profit from a pricing discrepancy between related securities based on an unusual short-term relationship,expecting the discrepancy will be resolved over time.
- Main types
- Convertible bond arbitrage
- Fixed income
- Volatility
- Multi-strategy
- Convertible bond arbitrage
- A market-neutral investment strategy seeks to exploit a perceived mispricing between a convertible bond and its component parts.
- The classic convertible bond arbitrage trade is to purchase a convertible bond that is believed to be undervalued and to hedge its risk using a short position in the underlying equity.
- Fixed income(general)
- Focus on the relative value within the fixed-income markets,with an emphasis on sovereign debt and sometimes the relative pricing of investment-grade corporate debt.
- Strategies may incorporate long-short trades between two different issuers, between corporate and government issuers, between different parts of the same issuer's capital structure, or between different parts of an issuer's yield curve.
- Fixed income (high yield)
- Focus on the relative value of various higher-yielding securities, including ABS, MBS, and high-yield loans and bonds
- Opaque mark-to-market pricing and illiquidity issues are significant considerations.
- Volatility
- Typically use options to go long or short market volatility.
- A short-volatility strategy involves selling options to earn the premiums and benefit from calm markets.
It can experience significant losses during unexpected periods of market stress. - A long-volatility strategy tends to suffer the cost of small premiums in anticipation of larger market moves.
- Multi-strategy
- Trade relative value within and across asset classes or instruments.
Looks for any available investment opportunities. - The goal is to initially deploy (and later redeploy) capital efficiently and quickly across various strategy areas as conditions change.
- Trade relative value within and across asset classes or instruments.
Macro and CTA strategies宏观策略
- Macro strategies
- Emphasize a top-down approach to identify economic trends.
- Use long and short positions to profit from a view on overall market direction because it is influenced by major economic trends and events.
- Generally benefit most from periods of higher volatility.
- Managed futures funds (Commodity trading advisers, CTA)
- Making diversified directional investments primarily in the futures markets on the basis of technical and fundamental strategies.
- May include investments in a variety of futures, including commodities, equities, fixed income, and foreign exchange.
Diversification benefits has diminished. - Mean-reverting markets is unfavorable.
Private capital私募
Overview of private capital
- Private capital is the broad term for funding provided to companies that is sourced neither from the public markets,nor from traditional institutional providers.
- Comprising private equity私募股权投资 and private debt私募债权投资.
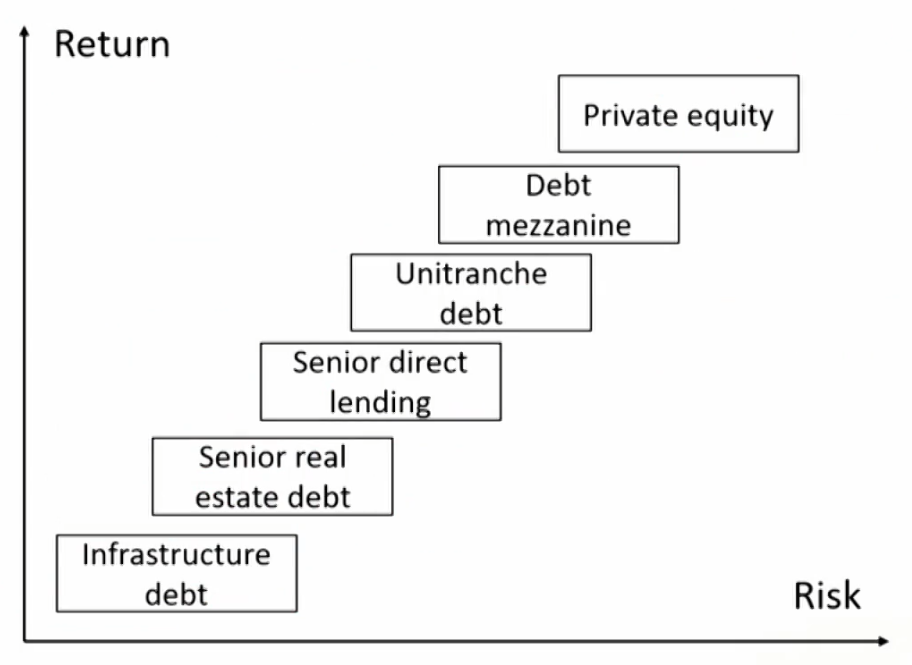
- Comprising private equity私募股权投资 and private debt私募债权投资.
Diversification benefits of private capital
- Investments in private capital funds can add a moderate diversification benefit to a portfolio of publicly traded stocks and bonds.
- Correlations with public market indexes vary from 0.47 to 0.75.
- Private equity investments may offer vintage diversification.
- Private debt investments, which offer more options than bonds can also serve diversification goals.
Categories of Private Equity Invests私募股权投资
- Private equity (PE): investment in privately owned companies or in public companies with the intent to take them private.投资私有公司或者最终使其私有化
- Portfolio companies: the companies owned by private equity funds.
- Primary private equity strategies
- Certainty around valuation increases as the portfolio company matures and moves into later-stage financing.对于不同时期的公司采用不同手段
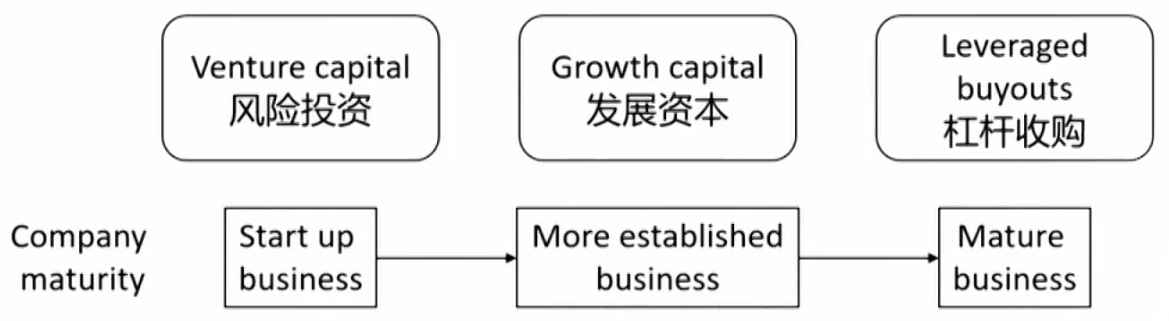
- Certainty around valuation increases as the portfolio company matures and moves into later-stage financing.对于不同时期的公司采用不同手段
Venture capital
- Venture capital(VC) entails investing in or providing financing to private companies with high growth potential.对成长公司提供风险投资
- Typically start-ups or young companies.
- Higher expected returns with higher risks
- Venture capitalists are active investors directly involved with their portfolio companies.
- May also provide financing in the form of debt (commonly,convertible debt).
- Formative stage
- Pre-seed capital, or angel investing, is capital provided at the idea stage对idea投资. The amount of financing at this stage is typically small and sourced from friends and family.
- Seed stage generally supports product development and marketing efforts. The first stage at which VC funds invest.验证可行性
- Early stage, or start-up stage financing goes to companies moving toward operation but before commercial production and sales.开始少量生产
- Later stage financing(expansion VC) is provided after commercial production and sales have begun but before an IPO takes place.开始量产,准备上市
Support initial growth, a major expansion, product improvements, or a major marketing campaign.
Management selling control of the company to VC. - Mezzanine stage financing is provided to prepare to go public.上市准备时期
It represents the bridge financing.
Growth capital
- Growth capital: the firm takes a less-than-controlling interest in more mature companies looking for capital to expand or restructure operations, enter new markets, or finance major acquisitions.
- A.k.a. growth equity or minority equity investing.
Leveraged Buyouts
- Leveraged Buyouts arise when private equity firms establish buyout funds to acquire public companies or established private companies, with a significant percentage of the purchase price financed through debt.
- The target company's assets typically serve as collateral for the debt, and the target company's cash flows are expected to be sufficient to service the debt.
- A highly leveraged transaction.
- Tpyes of LBO
- Management buyouts(管理层收购): the current management team is involved in the acquisition.
- Management buy-ins(管理层换购): an external management team acquires a company and replaces the existing management team.
- The returns of LBO depend greatly on the use of leverage
- LBO investments enjoy more certainty than VC investments.
Exit Strategies
- Trade sale: the sale of a company to a strategic buyer, such as a competitor.股票卖给战略投资者或竞争者
- Pros: immediate cash, higher price (synergies), fast and simple, lower costs and transparency than IPO.
- Cons: possible management opposition, limited potential buyers, lower attractiveness to employees.
- Initial public offering (IPO): the portfolio company sells its shares to public investors.通过上市盈利
- Pros: highest price, management approval, publicity, futur upside potential.潜在收益最大
- Cons: higher cost, long lead times, market risk, disclosure requirements, a potential lockup period, IPOthreshold.
- Special purpose acquisition company(SPAC): a shell company via an IPO through which sponsors raise a blind pool of cash aimed for merger or acquisition with private firms.
- Pros: extended time for disclosure, lower volatility of share pricing, flexibiltiy, high-profile and seasoned sponsors.
- Cons: capital risk due to potential redemptions, stockholder overhang after merger, spread between the announced and true equity value because of the dilution.
- Recapitalization: a company issues debt to fund a dividend distribution to equity holders.发行债券以特别红利的形式发给自己
- Not a true exit strategy.
- Secondary sales: sale to another PE or other investors.股票卖给下一家PE或投资者
- Write-off/Liquidation: liquidates the portfolio company before moving on to other projects.破产清算
Risk and return of private equity
- Investors require a higher return for accepting the higher risk,including illiquidity and leverage risks.
- Private equity return indexes rely on self-reporting and are subject to survivorship bias, backfill bias数据是他们说的,不一定准
- This typically leads to an overstatement of returns.投资数据不客观
- Failure to mark to market will understate measures of volatility and correlations with other investments.低估波动性和相关系数
Categories of private debt私募债权投资
- Direct lending放贷给对方
- Providing capital directly to borrowers.
- Smaller number of investors than traditioanl debt.
- Usually higher interest rates to mid-market companies.
- Venture debt放贷给初创企业
- Provided to start-up or early-stage companies that may be generating little or negative cash flow.
- Lack of substantial assets for pledging as debt collateral.
- Mezzanine debt风险最高的债权投资,仅次于股权投资
- Private debt that is subordinated to senior secured debt but is senior to equity in the borrower's capital structure.
- Investors commonly demand higher interest rates and may require options for equity participation.
- Distressed debt放贷给困境中的企业
- Buying the debt of mature companies with financial difficulty expecting companies may restructure and revive.
- Collateralized loan obligations (CLO)
- It pools several loans and then divides that pool into various tranches.
- Unitranche debt单一层级债
- consists of a hybrid or blended loan structure combining different tranches of secured and unsecured debt into a single loan with a single, blended interest rate.
- Real estate debt or infrastructure debt放贷给公司做基础设施建设
- Specialty loans
Risk and return of private debt
- Investors in private debt could realize higher returns from the illiquidity premium.
- Overall, investing in private debt is riskier than investing in traditional bonds.
Commodities大宗商品
Characteristics of commodities
- Investment returns are based on changes in price rather than income stream such as interest, dividends or rent.收益主要来源于价差,不是票息类
- Holding physical commodities incurs transportation and storage costs.
- Trading in physical commodities is primarily limited to a smaller group of entities in the physical supply chain.
- Most commodity investors do not trade actual physical commodities but, rather, trade commodity derivatives.主要使用衍生工具
- The relative importance, amount, and price of individual commodities evolve with society's preferences and needs.
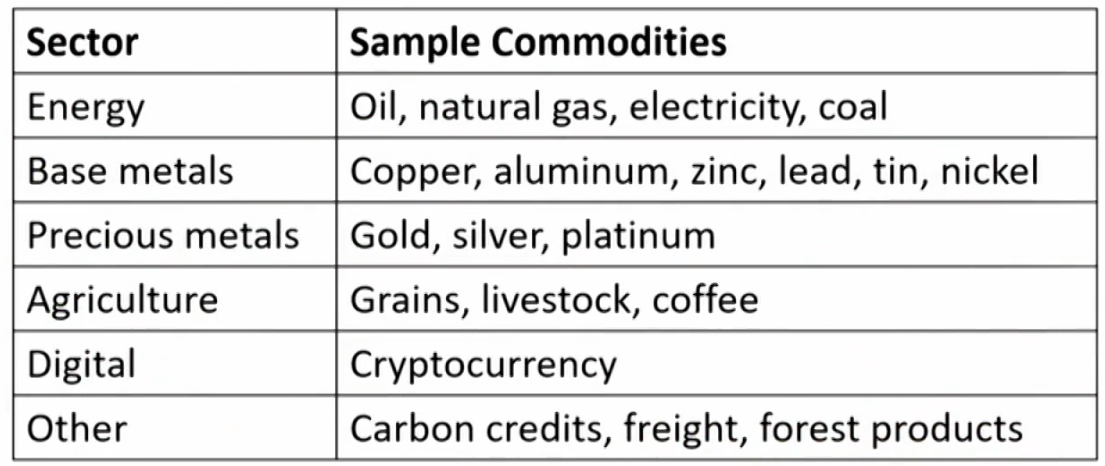
Forms of Commodity Investments
- Direct investment
- Derivatives
- Exchange-traded products(ETPs, either funds or notes)
- Commodity Trading Advisors (CTAs)
- Funds specializing in specific commodity sectors
Characteristics of commodities investment
- Benefit of commodity investment
- Real hedge against inflation risk应对通货膨胀
- Effective for portfolio diversification because of low correlation with other investment returns与其它投资关联度低,适合加入组合分散化风险
- Risk of commodity investment
- Commodity spot prices are a function of supply and demand供给导致价格波动大
- Demand levels are influenced by global manufacturing dynamics and economic growth.需求变动大
- Producers cannot alter commodity supply quickly because extended lead times are needed to affect production levels.供给调整满,跟不上需求
Commodity index
- To be transparent, investable, and replicable, commodity indexes typically set their prices based on futures contracts rather than underlying commodities.
- Different commodity indexes are composed of different commodities and index weights.
- Overall, low correlation with other asset classes.
- Effective for portfolio diversification
Commodity futures pricing
- Futures price ≈ FV of Spot price + FV of Storage costs - FV of Convenience yield
- Commodity futures price often do not adhere to a strict cost-of-carry relationship.
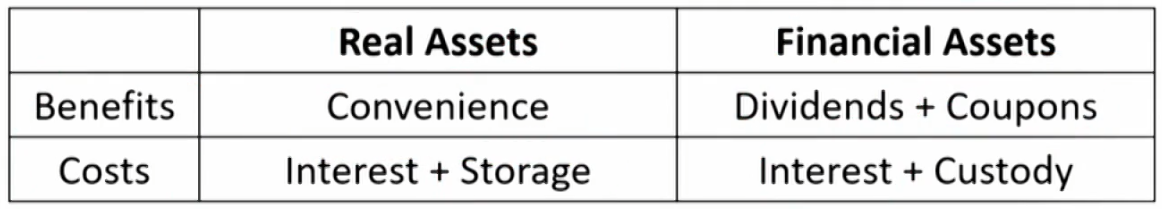
- Commodity futures price often do not adhere to a strict cost-of-carry relationship.
- Futures prices may be different from spot prices
- Contango: futures prices are higher than the spot price, the commodity forward curve is upward sloping.期货价格大于现货价格
Occurs when there is little or no convenience yield. - Backwardation: futures prices are lower than the spot price,the commodity forward curve is downward sloping现货价格大于期货价格
Occurs when the convenience yield is high.
- Contango: futures prices are higher than the spot price, the commodity forward curve is upward sloping.期货价格大于现货价格
Timberland and farmland林地农地
Characteristics of timberland and farmland
- Timberland
- Typically trading in larger units of land.体量大
- Flexibility: harvesting more trees when timber prices are up and delaying harvests when prices are down.灵活度更大,想砍就砍
- Return driver: biological growth; changes in spot prices and futures prices of cut wood; changes in the price of the underlying land.
- Farmland
- Typically trading in much smaller sizes体量小
- Provide a hedge against inflation.对抗通胀
- Little flexibility: farm products must be harvested when ripe.灵活度低,受农时影响
- Return driver: harvest quantities; commodity prices (e.g.,the price of corn); and land price changes.
Risk of farmland investment
- Value comes not just from the harvest but also from the offset to human activity比如失火.
2. Low liquidity买卖流动性差 - High risk of negative cash flow because fixed costs are relatively high(the land must be cared for and crops need fertilizer, seed, and so on)初期投资大,现金回笼慢
- Revenue is highly variable based on the weather.价格受天气影响大
- World trade and growing foreign agricultural competition result in declines of crop prices受国际贸易影响
Real Estate房地产
Categories
- Owner-occupied market
- Residential: single-family homes and multi-family units.
- Commercial: office buildings, retail shopping centers, and warehouses.
- Rental properties
- Lease contract: landlord/lessor and tenant/lessee
- Title/deed represents real estate property ownership covering building and land-use rights.
Forms of real estate investment
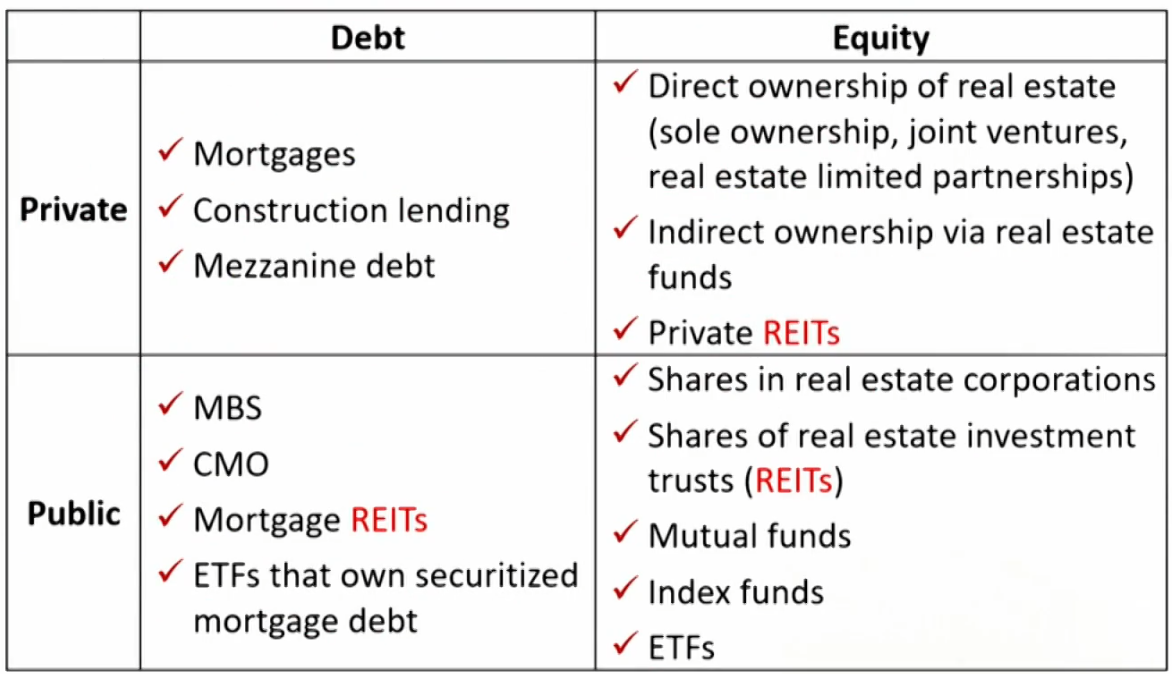
Characteristics of Real Estate
- Benifit
- Income generation and capital appreciation可以卖也可以收租
- Fixed rents may lessen cash flow impact放贷现金流稳定
- Diversification benefits和其他投资相关性低
- Inflation hedge if rents can be adjusted quickly for inflation.应对通货膨胀
- Risks
- Property value risk价格受经济影响
- Managment risk
- Construction delays and cost overruns建造花费时间,超预算
- Leverage risk高杠杆
Especially with higher loan-to-value ratio
Real estate index
- Appraisal index评估指数,砖家各抒己见
- Subjective, understate volatility主观,低估波动性
- Repeat sales (transaction-based) index基于交易数据
- Sample selection bias和样本选择有关
- REIT index信托基金指数
- Use the prices of publicly traded shares of REITs to construct the indices
- More frequently traded, more reliable is the index有活跃交易
Differences with other asset classes
- Large required capital investment → difficult too diversified
- Transaction costs are high → Illiquidity
- Diversity, as no two properties are identical
- Necessarily fixed location
- Price discovery in the private market is opaque
- Transaction activity may be limited in certain markets
- No investable index
- Typically requires professional operational management
Direct real estate investing
- Direct private investing involves purchasing a property and originating debt for one's own account.
- Advantages: control, taxes.
- Disadvantage: extensive time required to manage, need for local market expertise, large capital requirements,concentrated position.
- Many investors prefer to hire advisers or managers to manage the their direct real estate investment in a separate account.
Indirect realestate investing
- Indirect investing provides access to the underlying real estate assets through a variety of pooled investment vehicles.
- Intermediaries facilitate the raising and pooling of capital and the creation of investable structures.
- Types of indirect real estate investing
- Mortgages: whole loans or MBS.
- Private fund investing
- REITs
Private fund investing
- Most private real estate funds are structured as infinite-life open-end funds.
- Core real estate strategies: characterized by well-leased,high-quality institutional real estate in the best markets.
- Core-plus strategies will also accept slightly higher risks derived from non-core markets.
- Finite-life closed-end funds are more commonly used to seek higher returns.
- Value-add investments may require modest redevelopment or upgrades, the leasing of vacant space, or repositioning the underlying properties to earn a higher return.
- Opportunistic investing accepts the much higher risks of development, major redevelopment, repurposing of assets,taking on large vacancies, and speculating on significant improvement in market conditions.
Real estate investment trusts (REITs)
- REITs are tax-advantaged entities that own, operate, and develop income-producing real estate property.
- Are not taxed at the corporate level.
Above 90% of taxable net rental income are distributed. - Most REITs are listed on stock exchanges.
Greater liquidity, lower trading costs, and better transparency.
- Are not taxed at the corporate level.
- Mortgage RElTs v.s.Equity RElTs
Infrastructure基础设施
Overview
- The assets are capital intensive大资本 and long lived收寿命长 for public use.
- Increasing use of public-private partnerships(PPPs)民间出大头: long- term contractual relationship between the public sector and the private sector.
- Investors may lease the assets back to the government, sell newly constructed assets to the government, or hold and operate the assets
Characteristics
- Strategically important战略性
- Monopolistic and regulated垄断性
- Stable long-term cash flows现金流稳定
- Significant capital investment初期投入大
- Long operational lives使用寿命长
- Defined risks风险各异
- Highly leveraged financial structure高杠杆
Categories by underlying assets
- Economic infrastructure assets support economic activity.
- Transportation assets高速、飞机场等
- Information and communication technology(ICT) assets基站等
- Utility and energy assets能源
- Social infrastructure assets are directed toward human activities.
- Educational, health care, social housing, and correctional facilities.
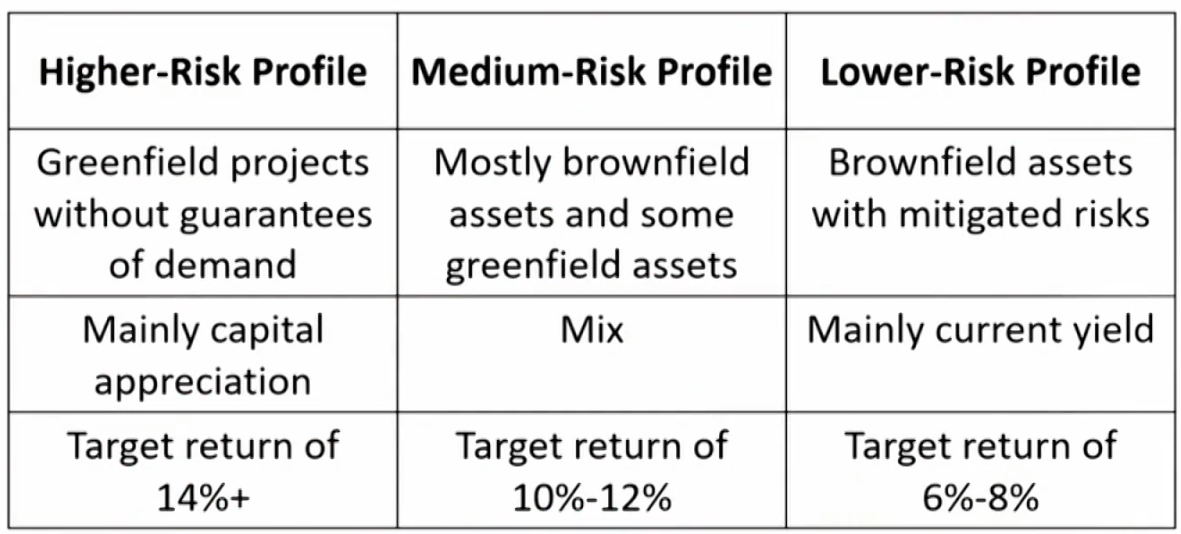
Categories by Stage of development
- Brownfield investment: investing in existing infrastructure assets.已经建了一部分
- Privatize or lease out government assets, sell and lease back.
- Less risky with lower expected return.
- predictable cash flows
- Greenfield investment: investing in infrastructure assets that are to be constructed.从零开始,要先除草
- Lease or sell to the government or to hold and operate.
- More risky with higher expected return.

Forms of Infrastructure Investments
- Direct investment
- Provides control and the opportunity to capture full value.
- Large investment, concentration and liquidity risks.
- Indirect investment
- Funds, ETFs, company shares
- Master Limited Partnerships (MLPs) trade on exchanges and are similar to REITs.
Generally distribute most free cash flow to their investors
Risk of infrastructure
- Demand risk → take-or-pay arrangements
- Operational risk → reputable and experienced operators
- Construction risk → fixed-price date-certain contracts
- Financial risk → derivatives
- Regulatory risk → clear PPP agreement or due diligence
- Political risk → political risk insurance
- Currency risk → adjustment mechanisms
- Tax/profit repatriation risks → adjustment mechanisms
Return of infrastructure
1.Returns depend on investment type.
Performance Calculation and Appraisal of Alternative Investments
Issues in Performance Appraisal
Challenges of performance appraisal
- Limited transparency
- Low portfolio liquidity
- High leverage and use of derivatives
- High product complexity
- Mark-to-market issues, especially for specialized products
- Limited redemption availability
- Difficulty in manager selection and diversification
- High fees, which can have a non-trivial impact on performance
Common approaches to performance appraisal
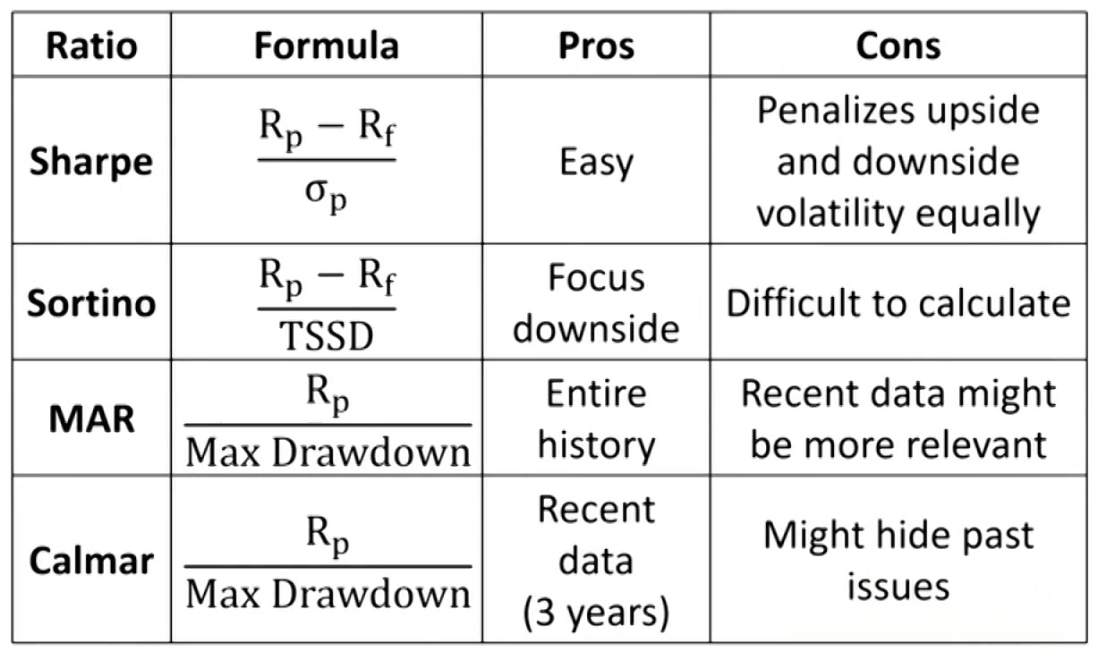
PE and real estate performance evaluation
- Private equity and real estate involve large initial capital outlays with capital inflows occurring much later in the investment cycle.
- Net cash position shows J-curve effect.
- Shorter-term risk metrics are highly inappropriate.
- As a general rule, the best way to evaluate such investments is the IRR of the respective cash flows.
- Multiple of invested capital (MOIC)/money multiple
- MOIC =(Realized value of investment + Unrealized value of investment)/(Total amount of invested capital)。
- Quartile ranking depicts manager's performance against a cohort of peer investment vehicles constructed with similar investment attributes and vintage year.
- Cap rate: the net operating income divided by the market valuel of the property.
Hedge fund performance evaluation
- Leverage has the effect of magnifying gains and losses.
- Hedge funds leverage their portfolios by using derivatives or borrowing capital from prime brokers.
- The hedge fund deposits cash or other collateral into a margin account with the prime broker.
- An inability to meet margin calls can force the hedge fund to liquidate the losing position, leadign to further losses.
- Illiquidity (Mark to market problem)
- Little chance of liquidating all the shares at quoted price.
- Funds may differ in which price or quote they use.
A more conservative and accurate approach is to use bid prices for long positions and ask prices for short positions. - Highly illiquid or even non-traded investments may have no reliable market values, it becomes necessary to estimate values. (Mark to model valuation)
- Investor redemptions may require the hedge fund manager to liquidate some positions at disadvantageous prices, while also incurring transaction costs.
- Ability to demand a long lockup depends on reputation.
- Ideally, redemption terms should be designed to match the expected liquidity of the assets being invested in.
- Funds of hedge funds may offer more redemption flexibility.