
第1章 变化中的金融服务部门综述
金融系统以及竞争性金融服务机构
金融系统的目的与内涵
- 目的:鼓励个人和机构储蓄,并把这些储蓄提供给计划投资新项目、需要信贷的个人和机构,使得经济增长、就业增加以及生活水平提高。
- 内涵
- 包含金融机构体系、金融监管体系、信用体系和法律体系等多个层次
- 体系越来越显得多元化
银行面临的竞争性挑战
- 银行在提供储蓄和投资服务、支付和风险防范服务、流动性和贷款服务方面的市场份额随着其它金融机构的进入而急剧减少
- 由于金融市场效率的提高,最大的客户也能不通过银行而获得资金(例如通过公开市场借款),使得传统的银行不再是必需的。
- 不同观点
- 银行之所以还存在,是因为政府通常通过廉价的存款保险和低成本贷款来对该行业进行补贴。
- 银行市场份额的下降是由于过多的政府监管,限制了该行业的竞争能力。
- 银行并不是走向死亡,而是正在变化(提供新的服务并改变其形式),这反映了目前市场需求的变化。
银行的主要竞争者
- 储贷协会 Saving Associations
- 储贷协会致力于销售储蓄存款、提供住房抵押贷款以及其他面向个人和家庭的各种形式的贷款
- 信用合作社 Credit Unions
- 信用合作社是汇集成员储蓄并向同一组织的成员提供贷款的非营利性机构
- 边缘银行 Fringe Banks
- 边缘银行包括付薪日贷款者、抵押商店和现金支票工厂店,承担高风险,以高利率提供小额贷款给短期现金短缺的家庭和个人
- 货币市场基金 Money Market Funds
- 货币市场基金由个人或机构投资而集中短期流动性资金,并将这些资金投资于高质量的短期证券
- 共同基金(投资公司)Mutual Fund(Investment Companies)
- 共同基金向公众销售股份,这些股份的收益和回报来自专业管理的股票、债券和其他债券组成的资产池
- 对冲基金 Hedge Funds
- 对冲基金以资产池形式销售的股份,主要迎合不同资产(包括在商品、房地产及其他流动性差的更具风险性的非传统投资)的广泛的投资者,较少受约束
- 证券经纪商和交易商 Security Brokers and Dealers
- 他们代表客户和自己的投资账户买卖证券
- 投资银行 Investment Banks
- 投资银行为金融市场中筹资的公司和政府提供专业咨询,帮助客户在金融市场融资,并向寻求兼并和证券交易的企业提供专业咨询
- 财务公司 Finance Companies
- 财务公司向商业企业(例如汽车和设备交易商)和消费者(个人和家庭)提供贷款,这些资金从开放市场或其他金融机构借得
- 金融控股公司或集团 Financial Holding Companies
- 它是通常一个集团作为多元服务的提供者,包括信用卡公司、保险和财务公司以及证券经纪/交易公司,有些持有经营银行业务公司的股票,而有些不持有
- 人寿和财产/灾害保险公司 Life and Property-Casualty Insurance Companies
- 它们通过向公众销售各种保险产品,防范个人或财产损失的风险,并管理企业及个人退休基金的年金计划
- 融资租赁 Financial Leasing
- 指出租人根据承租人(用户)的请求,与第三方(供货商)订立供货合同,根据此合同,出租人出资向供货商购买承租人选定的设备。同时,出租人与承租人订立一项租赁合同,将设备出租给承租人,并向承租人收取一定的租金。
所有这些金融服务提供商提供的服务都趋于集中,并且提供对方提供的创新服务
法律文件如美国的《1999年金融服务现代化法案》(《格雷姆-里奇-比利雷法案》),已经允许上面提到的许多金融机构向公众提供一站式的金融服务。
如果允许银行同工业公司联营,可能会消除竞争,使银行面临新的威胁,并有可能削弱保障存款人和纳税人免于损失的安全网络,因此对这种联营进行了严格的限制
银行与银行体系
银行是什么
- 银行发挥的经济作用 The economic function it performs
- 它们在资金从借方向贷方转移中充当金融中介的角色,并提供对商品、服务进行支付的服务。
- They are involved in transferring funds from savers to borrowers and in paying for goods and services.
- 银行向客户提供的服务 The services it offers its customers
- 历史上,银行因其提供广泛的金融服务被人们所认识,这些服务包括结算和借记账户、信用卡、储蓄计划以及向企业、个人消费者和政府提供贷款
- Historically, banks have been recognized for the great range of financial services they offer-from checking and debit accounts, credit cards, and saving plans to loans for businesses, customers and governments.
- 现在,银行的服务项目在快速地扩大,包括投资业务(证券承销)、保险、财务计划、公司兼并咨询、向企业和消费者提供风险管理服务以及其他很多金融创新的服务。它逐渐变成了一般金融服务的提供者。
- Today service menus expand to security underwriting, insurance protection, financial planning, advice for merging companies,the sale of risk-management services to biz and consumers, and numerous other innovative financial products. it becomes General Financial-Service Providers
- 银行存在的法律基础 The legal basis for its existence
- 供随时按要求(例如签发支票、刷卡或者以其他方式进行电子转账)提取存款
- any business offering deposits subject to withdrawal on demand (such as writing a check,swiping a plastic card through a card reader, or otherwise completing an electronic transfer of fund
- 提供商业性质贷款(例如向试图扩大商品存货或购买新设备的私人企业提供信贷)
- making loans of a commercial or business nature(such as granting credit to private businesses seeking to expand the inventory of goods on their shelves or purchase new equipment)
- 国会后来对银行的定义是:必须由联邦存款保险公司(FDIC)管理并参与存款保险的机构。
- Defined by federal government of the United States(1900s), any institution that could qualify for deposit insurance administered by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
- 在美国联邦法律下,银行不再由其提供的服务而定义,而是通过政府机构对其存款进行保险来定义
- Under U.S. federal law, banks are no longer defined by the services they provide, but rather by the insurance of their deposits by government agencies
银行体系
- 多种类型的银行
- 商业银行(Commercial Banks):向企业、个人和机构出售存款和发放贷款
- 金融中心银行(Money Center Banks):位于主要金融中心的大型商业银行
- 社区银行(Community Banks):规模较小、以本地为中心的商业银行和储蓄银行
- 储蓄银行(Savings Banks):吸引储蓄存款,向个人和家庭发放贷款
- 合作银行(Cooperative Banks):帮助农民、牧场主和消费者获得商品和服务
- 抵押银行(Mortgage Banks):为新房提供抵押贷款,但不接受存款
- 投资银行(Investment Banks):代表公司客户承销新证券的发行
- 商人银行(Merchant Banks):向企业提供债务和权益资本
- 产业银行(Industrial Banks):由其他公司拥有的提供信贷和接收存款的国家特许贷款公司
- 国际银行(International Banks):存在于不止一个国家的商业银行
- 批发银行(Wholesale Banks):为企业和政府服务的大型商业银行
- 零售银行(Retail Banks):主要服务于家庭和小企业的小型银行
- 专用银行(Limited-purpose Banks):提供有限的服务,如信用卡公司和次级贷款机构
- 银行家银行(Bankers' Banks):向银行提供服务,如支票结算和证券交易
- 少数银行(Minority Banks):主要关注属于少数群体的客户
- 国家银行(National Banks):在联邦宪章下,通过美国货币监理署(Comptroller of the Currency)行使职能
- 州立银行(State Banks):在各州银行委员会颁发的特许状下运作
- 投保银行(Insured Banks):维持由联邦存款保险计划(如FDIC)支持的存款
- 成员银行(Member Banks):隶属于联邦储备系统
- 联营银行(Affiliated Banks):全部或部分被控股公司控股
- 虚拟银行(Virtual Banks):只在互联网上提供服务
- 边缘银行(Fringe Banks):提供发薪日贷款、产权贷款、现金支票或经营典当行(pawn shops)和租赁自置(rent-to-own)公司
- 全能银行(Universal Banks):提供当今市场上几乎所有的金融服务
- 货币中心银行和社区银行
- 货币中心银行是巨大的行业领导者,服务延伸至各地区、国家和大洲,并面临着来自全球各大金融机构的激烈竞争
- 社区银行通常规模较小,并且服务限于当地社区、城镇和城市,向公众提供的服务项目虽然较少但却颇为人性化、菜单化
- 社区银行的数量在减少,但是它们仍然是所服务社区的强有力竞争者。
中国大陆银行体系
以资本所有权形式划分,包括以下三种银行
- 国有控股的商业银行
- 最大股东是国家或国有机构。主要有中国工商银行、中国银行、中国建设银行、中国农业银行和交通银行。
- 企业集团所有的银行
- 招商银行、光大银行、华夏银行、中信实业银行、平安银行都是由各企业集团筹资建立的。企业集团是银行的最大股东。
- 股份公司制银行
- 未公开上市的银行,例如江苏银行、上海银行、浙商银行股份有限公司、恒丰银行、渤海银行等
- 公开上市的银行,例如上海浦东发展银行、中国民生银行、招商银行、福建兴业银行、南京银行、北京银行、宁波银行、华夏银行等
- 民营银行,例如中国民生银行和浙江商业银行等
- 中国大陆股份公司制银行股权结构比较复杂,包括国家股,企业股,社会公众股,地方政府与企业持有大部分股份
中国大陆银行业的法律基础
- 按照中国第八届全国人民代表大会常务委员会第十三次会议于1995年5月10日通过的《中华人民共和国商业银行法》及2003年12月27日通过的修改之后的规定,中国大陆的商业银行是指依照本法和《中华人民共和国公司法》设立的吸收公众存款、发放贷款、办理结算等业务的企业法人。
- 从中国立法部门给出的权威定义可以看出,不同于美国在通过《金融服务现代化法案》后为管理和监管银行而改变之前的商业银行的定义,中国目前对商业银行的定义依然按照分业监管的思路对商业银行从业务角度出发制定了严格的定义。
银行与其主要竞争者向公众提供的服务
银行与其竞争者在经济中承担的职能
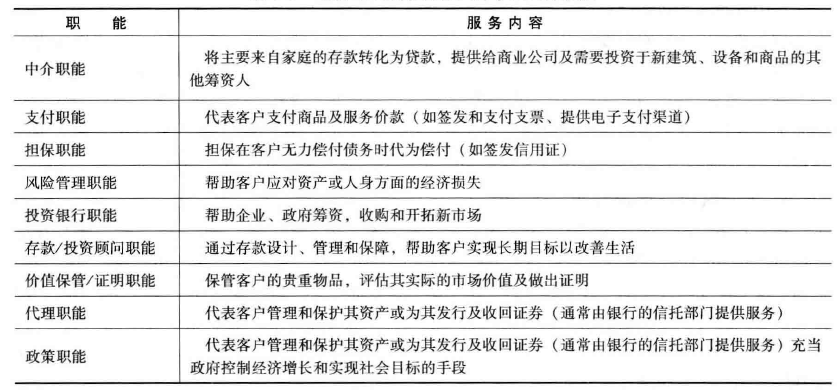
历史上银行一直提供的服务 Traditional Services Offered By Banks
- 货币兑换 Currency Exchange
- 将一种货币兑换成另一种货币,并收取手续费,
- 由于外汇交易具有风险并需要一定的专业知识,因此外汇交易主要由大银行经营。
- 商业票据贴现和向企业提供贷款 Discounting Commercial Notes and Making Business Loans
- 当地商人将自己的债权(应收账款)卖给银行,以迅速换取现金
- 储蓄存款服务 Savings Deposits
- 贵重物品的保管和价值证明 Safekeeping of Valuables
- 向政府提供信用支持 Government Activities with Credit
- 政府在发给银行执照时要求银行用部分存款资金购买政府债券。
- 支票账户(活期存款)的提供 Checking Accounts
- 提供信托服务 Fiduciary Services
- 这类服务的提供者通常作为遗嘱的受托人,管理已去世顾客的财产,保管贵重财物,用其财产向债权人进行支付,进行适当的投资,确保法定继承人得到遗产
过去一个世纪开拓的业务 More Recent Services Offered by Banks
- 发放消费者贷款 Granting Consumer Loans
- 金融咨询 Financial Advice
- 现金管理 Managing Cash
- 金融中介为企业代收和代付款项,在企业需要现金前,将其暂时的现金盈余投资于短期付息证券和贷款
- 设备租赁 Equipment Leasing
- 通过租赁协议,借款机构购买设备并将它租给企业
- 风险资本贷款 Venture Capital Loans
- 公司从投资者处筹集资金并支持新企业,当新企业出售或上市时获得利润
- 由于该项贷款有较大风险,一般由银行控股公司的风险资本子公司来操作
- 保险销售政策 Selling Insurance Policies
- 俗称买保险
- 销售和管理退休基金 Selling Retirement Plans
- 银行、信托部门、共同基金和保险公司积极管理企业提供给雇员的退休基金
证券经纪和证券承销服务 Security Brokerage and Security Underwriting
- 近年来,银行服务所要实现的最重要目标之一就是交易证券、执行证券交易客户的买入卖出指令(证券经纪业务)及推销新证券为公司及其他机构筹集资金(证券承销业务)
- 1933年美国通过《格拉斯-斯蒂格尔法》,银行不能从事上述大部分的证券经纪业务和证券承销业务
- 1999 年秋《金融服务现代化法案》通过,银行被允许可以和证券公司合并。
- 共同基金、年金以及其他的投资产品 Offering Mutual Funds and Annuities
- 其预期收益率虽比传统银行存款现期回报率高,但风险也大,因为银行存款受到存款保险的保护
- 年金包括长期储蓄基金,从规定的未来时期开始(如退休后)每年向年金持有者支付一定数量的现金
- 共同基金是专业化管理的投资基金,它所投资的股票、债券及其他证券要符合基金的公开目标(如收益最大化或长期资本升值)。
- 商业银行业务 Offering Merchant Banking Services
- 向大型公司提供商业银行服务。如括暂时购买公司股票以帮助成立新公司或帮助现有公司扩展业务
- 上述服务的银行成为公司暂时的持股人,承担所购股票价值减少所带来的巨大风险。
- 风险管理和套期保值业务 Offering Risk Management and Hedging Services
- 向其客户提供金融工具防范风险敞口损失而收取费用
- 风险套期保值工具如互换、期权和期货合约的大量出现
- 最近的信贷危机表明这一业务不断造成了不稳定的市场条件。
影响所有金融机构的主要趋势 Trends Affecting Banks and Other Financial Service Firms Today
- 服务增殖 Service Proliferation
- 业务多元化的趋势明显加快,对银行业产生了积极的作用,开辟了新的主要收入来源-非利息服务手续费(银行称之为手续费收入)
- 相对于贷款利息等传统的收入来源来说,该项收入可能会继续增长。
- 竞争日趋激烈 Rising Competition
- 监管放松Government Deregulation
- 资金组合对利率日益敏感 Increased Interest Rate Sensitivity
- 金融机构不得不提供更高的收益率,
- 技术进步与自动化 Technological Change and Automation
- 合并及地理扩张 Consolidation and Geographic Expansion
- 电子化 E-Banking and E-Commerce
- 集中化 Convergence
- 集中化就是企业跨产品线的活动,以便使原来仅提供一种产品的企业进入其他产品线并扩大销售基础
- 在大的银行、保险公司和证券经纪/交易商中尤为明显,它们急切地进入彼此的业务领域,提供同样或类似的服务
- 全球化 Globalization
习题
什么是银行?银行和其它金融机构有什么不同
- What is a bank?
- A bank should be defined by what it does; in this case, banks are generally those financial institutions offering the widest range of financial services.
- How does a bank differ from most other financial-service providers?
- Other financial service providers offer some of the financial services offered by a bank,but not all of them within one institution.
根据根据现行美国联邦法律,一家企业如何才能成为合格的商业银行?
- Under U.S. law what must a corporation do to qualify and be regulated as a commercial bank?
- Under U.S. law, commercial banks must offer two essential services to qualify as banks for purposes of regulation and taxation, demand (checkable) deposits and commercial loans. More recently, Congress defined a bank as any institution that could qualify for deposit insurance administered by the FDIC.
为什么银行要拓展经营范围以成为提供一站式金融服务的联合体?你认为这种做法可取吗?
- Why are some banks reaching out to become one-stop financial-service conglomerates?Is this a good idea?
- There are two reasons that banks are increasingly becoming one-stop financial service conglomerates. The first reason is the increased competition from other types of financial institutions and the erosion of banks' traditional service areas.The second reason is the Financial Services Modernization Act which has allowed banks to expand their role to be full service providers.
哪些公司是与银行最相近、最强有力的竞争者?它们提供哪些服务与银行进行直接竞争?
- Which businesses are banking's closest and toughest competitors?
- Among a bank's closest competitors are savings associations,credit unions, money market funds, mutual funds, hedge funds, security brokers and dealers, investment banks, finance companies, financial holding companies, and life and property-casualty insurance companies.
- What services do they offer that compete directly with banks'services?
- All of these financial service providers are converging and embracing each other'’s innovations. The Financial Services Modernization Act has allowed many of these financial service providers to offer the public one-stop shopping for financial services.
银行的金融市场份额正发生哪些变化?为什么?如果目前的趋势持续,你预见将会出现怎样的银行和金融系统?
- What is happening to banking's share of the financial marketplace and why?
- The Financial Services Modernization Act of 1999 allowed many of the banks closest competitors to offer a wide array of financial services thereby taking away market share from “traditional" banks.
- What kind of banking and financial system do you foresee for the future if present trends continue?
- Banks and their closest competitors are converging into one-stop shopping for financial services and this trend should continue in the future
银行向公众提供哪些不同的服务?与它们相近的竞争者提供哪些服务?
- What different kinds of services do banks offer the public today?
- Banks offer the widest range of services of any financial institution. They offer thrift deposits to encourage saving and checkable (demand) deposits to provide a means of payment for purchases of goods and services. They also provide credit through direct loans, by discounting the notes that business customers hold, and by issuing credit guarantees. Additionally, they make loans to consumers for purchases of durable goods, such as automobiles, and for home improvements, etc.
- Banks also manage the property of customers under trust agreements and manage the cash positions of their business customers. They purchase and lease equipment to customers as an alternative to direct loans.
- Many banks also assist their customers with buying and selling securities through discount brokerage subsidiaries, the acquisition and sale of foreign currencies, the supplying of venture capital to start new businesses, and the purchase of annuities to supply future funding at retirement or for other long-term projects such as supporting a college education.
- What services do their closest competitors offer?
- All of these services are also offered by their closest competitors.Banks and their closest competitors are converging and becoming the financial department stores of the modern era.
什么是金融百货公司?什么是全能银行?为什么这些机构在现代金融系统中变得如此重要?
- What is a financial department store? A universal bank?
- Financial department store and universal bank refer to the same concept. A financial department store is an institution where banking, fiduciary, insurance, and security brokerage services are unified under one roof. A bank that offers all these services is normally referred to as a universal bank.
- Why do you think these institutions have become so important in the modern financial system?
- These have become important because of convergence and changes in regulations that have allowed financial service providers to offer all services under one roof
依据金融理论,为什么银行及其他金融中介会存在于现代社会?
- Why do banks and other financial intermediaries exist in modern society,according to the theory of finance?
- There are multiple approaches to answering this question.
- The traditional view of banks as financial intermediaries sees them as simultaneously fulfilling the financial-service needs of savers (surplus-spending units) and borrowers (deficit-spending units), providing both a supply of credit and a supply of liquid assets.
- A newer view sees banks as delegated monitors who assess and evaluate borrowers on behalf of their depositors and earn fees for supplying monitoring services.
- Banks also have been viewed in recent theory as suppliers of liquidity and transactions services that reduce costs for their customers and, through diversification, reduce risk.
- Banks are also critical in the payment system for goods and services and have played an increasingly important role as a guarantor and a risk management role for customers.
近几年银行和金融服务市场是如何变化的?现在是什么强大的力量正在重塑金融市场和机构?你认为哪些力量在将来仍会持续存在?
- How have banking and the financial-services market changed in recent years?
- Financial serve markets are converging in terms of the services they offer, making it difficult to distinguish between one another.
- Banking is becoming a more volatile industry due, in part, to deregulation which has opened up individual banks to the full force of the financial marketplace. At the same time the number and variety of banking services has increased greatly due to the pressure of intensifying competition from nonbank financial-service providers and changing public demand for more conveniently and reliably provided services. Adding to the intensity of competition, foreign banks have enjoyed success in their efforts to enter countries overseas and attract away profitable domestic business and household accounts.
- What powerful forces are shaping financial markets and institutions today?
- Service Proliferation
- Rising Competition
- Government Deregulation and then Reregulation
- Crisis, Reform, and Change in Banking and Financial Services- An Increasingly Interest-Sensitive Mix of Funds
- Technological Change and Automation
- Consolidation and Geographic Expansion
- Convergence
- Globalization
在上述的许多力量中,你能解释为什么这些力量对银行和其他金融机构的管理及其股东造成了许多问题?
- Can you explain why many of the forces you named in the answer to the previous question have led to significant problems for the management of banks and other financial firms and their stockholders?
- The net result of recent changes in banking and the financial services market has been to put greater pressure upon their earnings, resulting in more volatile returns to stockholders and an increased bank failure rates.
- Some experts see banks' role and market share shrinking due to restrictive government regulations and intensifying competition.
- Institutions have also become more innovative in their service offerings and in finding new sources of funding, such as off-balance-sheet transactions.
- The increased risk faced by institutions today, therefore, has forced managers to more aggressively utilize a wide array of tools and techniques to improve and stabilize their earnings streams and manage the various risks they face.
20年后,你认为金融服务业将会怎样?这对于现在的金融服务业管理规划有什么意义?
- What do you think the financial services industry will look like 20 years from now?
- There appears to be a trend toward continuing consolidation and convergence.There are likely to be fewer financial service providers in the future and many of these will be very large and provide a broad range of financial services under one roof. In addition, global expansion will continue and will be critical to the survival of many financial service providers.
- What are the implications of your projections for its management today?
- Management of financial service provider will have to be more technologically astute and be able to make a more diverse set of decisions including decisions about mergers, acquisitions and global expansion well as new services to add to the firm.
第2章 政府政策及监管对银行业和金融服务业的影响
引言
监管的目的
- 确保公众储蓄的安全 Safeguard the public’s savings
- 维持金融系统稳定 Bring stability to the financial system
- 维护客户的权益 Prevent abuse of financial-service customers
金融机构必须遵守和其他产业相比更繁重和更复杂的一些规章制度
Financial institutions must contend with some of the heaviest and most comprehensive rules applied to any industry.
监管的争议
对于经理和股东而言,他们通常觉得这些政府强加于他们的规章繁杂累赘(Burdensome)且成本高昂(Costly),并且给创新和效率造成了不必要的损害(Damaging to innovation and efficiency)
银行监管与监管机构
为什么银行受到严格监管 Why are banks closely regulated
- 银行是公众储蓄存款的主要存储地 Banks are among the leading holders of the public's savings
- 银行可以通过可支配存款进行放贷和投资来创造货币 Their power to create money in the form of readily spendable deposits by making loans and investments (Leverage)
- 银行向个人和企业提供消费和投资贷款 They provide individuals and business with loans that support consumption and investment spending.(Y=C+I+G+X-M)
- 银行与联邦、州和地方政府的关系由来已久 Banks have a long history of involvement with federal, state, and local governments.
- 在银行业发展早期,当政府不愿直接向居民征税时就依赖低成本的银行信贷和银行税收来供应军需和筹资
- Traditionally: cheap bank credit, taxation of banks to finance armies, supply funds unwilling to raise through direct tax...
- 近年来,政府在经济政策的制定实施、征税和政府支出配置上还有赖于银行的协助
- Currently: assist in conducting economic policy, collecting taxes, and in dispensing government payments...
银行监管机构
- 美国银行监管机构
- 在美国,政府通过二元制银行体系对银行进行监管,即联邦和州相关机构都有强大的对银行监管的权力
- In the United States, banks are regulated through a dual banking system. Both federal and state authorities have significant regulatory powers.
- 这种体系的目的在于使州政府能更加严密地控制其境内的银行业运营,而且,联邦政府通过监管,确保银行在进行跨州业务扩展时,免于受到州及地区的不公平对待
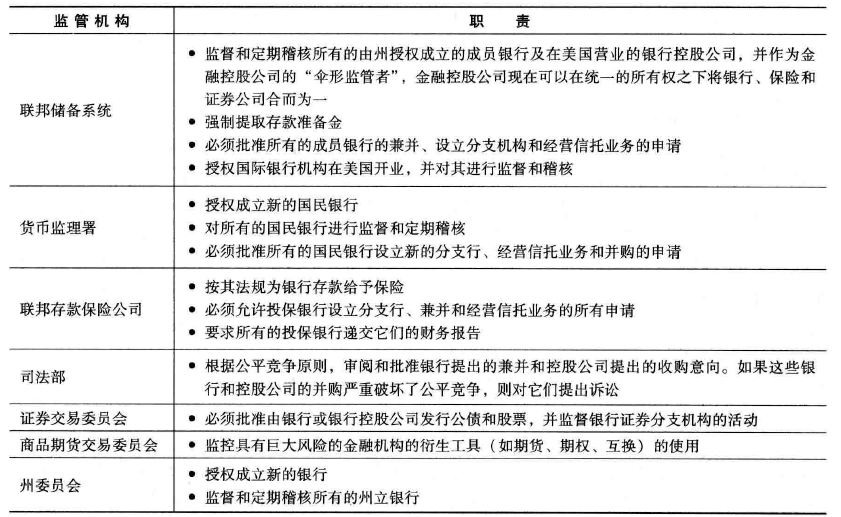
- 中国银行业的监管机构
- 1992年以前,中国人民银行作为全国唯一的监管机构,在国务院领导下承担对全国所有银行和非银行金融机构的监管职能
- 1992年10月,国务院证券委员会(证券委)和中国证监会同时成立,证券委由国务院14个部委的负责组成,是中国证券业监管的最高领导机构,而证监会则是证券委的监督管理执行机构,从而拉开了中国金融业分业监管的序幕。
- 1995年,《中国人民银行法》《商业银行法》先后颁布,确定了中国金融业分业经营的法律框架
- 1998年确定中国人民银行负责监管商业银行、信托投资公司、信用社和财务公司
- 2003年3月,中国银行业监督管理委员会成立,不仅依法统一监督和管理银行市场,实际上还承担了我国除证券业、保险业以外所有其他金融机构的监督和管理。至此,中国金融业多重机构分业监管的体制基本确立。
- 在中国大陆,中国人民银行与银行业监督管理委员会(简称银监会)对银行进行监管。
- 其他国家的监管机构
- 英国:证券投资委员会(SIB)监管证券业和投资业;英格兰银行监管银行业、金边债券和资金市场;英国贸工部下属的保险局监管保险业。
- 德国:德国联邦金融监管局,对银行金融机构进行监管,集银行监管、保险监管和证券监管职能于一身。
- 日本:对银行的监管由大藏省的银行局和日本银行共同负责,大藏省下属其他各局负责对其他金融机构的监管
监管对银行业的影响
- 取消监管则可能给一些银行带来经济损失
- 经济学家乔治。斯蒂格勒认为,属于监管性产业范畴内的企业实际上是在寻求管,这是因为监管通过垄断租的方式给它们带来好处,这种垄断租是由于监管当局阻止其他企涉入监管性行业所带来的
- One of the earliest theories (George Stigler)about regulation contends that firms in regulated industries actually seek out regulation,it brings benefits in the form of monopolistic rents because regulations often block entry into the regulated industry.
- 监管能提高客户对银行及其他金融机构的信任
- 最近,爱德华。凯恩提出,监管能提高客户对银行及其他金融机构的信任,这种信任反过来又会培养客户对银行的忠诚度
- A more recent theory (Edward Kane) argues that regulations can increase customer confidence, which may create greater customer loyalty toward regulated firms.
- 监管与银行间产生持续对抗
- 银行必定会通过金融创新想方设法规避这些新法规,从而达到银行价值的最大化
- Financial-service managers will search to find ways around new rules in order to reduce costs and allow innovation to occur.
主要的银行法规
促成今日银行监管机构的立法
- 《国民货币及银行法案》 National Currency and Bank Acts (1863-64)
- 美国银行史上第一批联邦法案就是在美国内战时期通过的《国民货币及银行法案》
- The first major federal government laws in U.S. banking sector were the National Currency and Bank Acts, passed during the Civil War.
- 通过新创建的美国财政部下属部门,即货币监理署或国民银行管理局(O0C),这些法案设立了一套授权银行设立的体系。
- These laws set up a system for chartering new national banks through a newly created bureau inside the U.S. Treasury Department, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC)
- 货币监理署不仅评估成立国民银行的必要性,批准成立国民银行,而且还定期稽核所有的国民银行
- Both charter new national banks and regularly examine those institutions.
- 《联邦储备法案》 The Federal Reserve Act (1913)
- 一系列严重的经济萧条和金融恐慌导致了第二个银行监管机构的诞生,即联邦储备系统(FederalReserve System)
- A series of financial panics in the late 19th and early 20th centuries led to the creation of the Federal Reserve System.(the Fed)
- 它的主要作用是银行的最后贷款人一一旦银行面临金融危机,它便会提供临时性贷款给银行,由此稳定金融市场,维持公众的信心。
- The Fed's principal roles are to serve as a lender of last resort and to help stabilize the financial markets and the economy
- 联邦储备系统在今天最重要的职能是控制货币和信贷状况以促进经济的平稳运行
- Their most important job today is to control money and credit conditions to promote economic stability.
- 《格拉斯-斯蒂格尔法案》 The Banking Act of 1933 (Glass-Steagall Act)
- 《格拉斯-斯蒂格尔法案》对于商业银行的有限限制长达60年之久
- It defined the boundaries of commercial banking by providing constraints that were effective for more than 60 years.
- 该法将商业银行、投资银行和保险公司的业务分离
- This legislation separated commercial banking from investment banking and insurance
- 联邦存款保险公司 Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation(FDIC)
- 保证公众存款达到最高赔偿额度(开始是2500美元,现在上升到250000美元)
- guarantee the public’s deposits up to a stipulated maximum amount in order to enhance public confidence in the banking system
- 《联邦存款保险公司修正法案》 The FDIC Improvement Act (1991)
- FDIC 逐渐遭到一些严厉的指责。
- The FDIC was the object of criticism during the1980s and 1990s
- 此法允许 FDIC 为保持偿付能力可以从国库借款
- This legislation permitted the FDIC to borrow from the Treasury to remain solvent (bankruptcy in 1980s)
- 1993年,联邦保险公司对银行基于不同的风险执行不同的保费
- Risk-based premium: Prior to 1993, the FDIC imposed fixed insurance premiums on all deposits eligible for insurance coverage
- 提高对联邦存款保险公司保险的限额 The Federal Deposit Insurance Reform Act(2005)
- 存款保险限额目前提高至25万美元
- It extends deposit insurance coverage on qualified retirement accounts from $100,000 to $250,000
社会责任法案 Social Responsibility Laws
- 《消费者信贷保护法案》 Consumer Credit Protection Act (known as Truth in Lending 1968)
- 要求银行清楚地告知客户贷款协议中客户的权责。
- Required that lenders spell out the customer's rights and responsibilities under a loan agreement.
- 《信贷机会均等法案》Equal Credit Opportunity Act (1974)
- 银行不能因为年龄、性别、出生地、宗教信仰或者因为贷款对象为公众福利领取者而拒绝提供贷款。1977 年
- Individuals and families could not be denied a loan merely because of their age, sex, race, national origin, or religious affiliation, or because they were recipients of public welfare.
- 《社区再投资法案》 Community Reinvestment Act (1977)
- 禁止银行歧视那些在其经营范围内,但却是其业务区周边的一些客户
- Prohibits U.S. banks from discriminating against customers residing within their trade territories merely on the basis of the neighborhood in which they lived.
- 《银行业平等竞争法案》Competitive Equality in Banking Act (1987)and 《储蓄真相法案》 the Truth in Savings Act (1991)
- 案要求银行更为充分地告知客户,其经营政策和公众储蓄账户的收益率和贷款服务的费用
- Require banks to more fully disclose their service policies and the true rates of return offered on the public's savings and the fees associated with credit services.
- 《多德-弗兰克金融改革法案》Dodd-Frank Regulatory Reform bill(2010)
- 强调要向客户提供更完整易懂的语言来表达其价格信息,避免误导。
- Emphasized providing consumers with more complete and understandable language to convey service prices and avoid misleading information
- 巴塞尔协议Basel I and II, and Basel III
《瑞格尔-尼尔跨州银行和分行效率法案》(1994)The Riegle-Neal Interstate Banking Law
- 为降低多个银行的成本耗费从而使其开展跨州业务
- Repealed previous provisions that prevented full-service interstate banking nationwide
- 主要条款Major provisions of the Riegle-Neal Act included:
- 资本充足、管理优良的银行控股公司可以在美国各地收购银行。
- Adequately capitalized and managed holding companies can acquire banks anywhere in the United States
- 跨州银行控股公司可以将其跨州收购的附属银行整合成其分支行机构,除非所在州禁止这种分支行业务。
- Interstate holding companies may consolidate their affiliated banks acquired across state lines into full-service branch offices
- 任何单个银行不得控制10%以上的美国存款,或者控制的存款超过某一州存款的30%(该州取消后一条限制的除外)。
- No single banking company can control more than 10 percent of nationwide deposits or more than 30 percent of deposits in a single state (unless a state waives this latter restriction)
- 历史上首次从法律上授予一大批银行吸收存款和对客户进行跨州跟踪服务的权利
- For the very first time in U.S. history, American banks could accept deposits and follow their customers across state lines.
《金融服务现代化法案》(1999)The Financial Services Modernization Act (The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
- 20世纪最重要的银行法规之一便是《金融服务现代化法案》,它于1999年11月由克林顿总统签署。该法案推翻了生效多年的《格拉斯-斯蒂格尔法案》和《银行控股公司法案》
- One of the most important U.S. banking statutes signed into law Overturned long-standing provisions of the Glass-Steagall Act and the Bank Holding Company Act
- 允许银行公司以共同所有权与保险和证券公司建立关联关系
- Permitted banking companies to affiliate with insurance and securities firms under common ownership
- 保险和证券公司被允许采取股份公司的形式控制一个或多个银行
- Securities and insurance companies could form financial holding companies that control one or more banks
- 银行也被允许销售保险,只要它遵守该州的保险规章。
- Banks were permitted to sell insurance and security services,provided they conform to state and federal rules
- 《GLB法案》的目的是授予有条件的美国银行和其他金融机构使自己服务多样化的权利,从而减少其商业风险。
- This law's purpose was to allow qualified U.S. financial-service companies to diversify their service offerings and reduce their overall business risk exposure
- 带来一些争议
《爱国者法案》The USA Patriot Act 和《银行保密法案》Bank Secrecy Act:对抗恐怖主义和反洗钱
- 补充了《银行保密法案》
- 《银行保密法案》于1970年因反洗钱而通过
- Made a series of amendments to the Bank Secrecy Act, which was passed originally in 1970 to combat money laundering
- 身份审核
- 在美经营的金融机构需要备案新开户顾客的身份或持有账户的变化
- Requires that financial-service providers establish the identity of customers opening new accounts or holding accounts whose terms are changed
- 通常在最低限度内,是通过要求顾客出示驾驶执照或其他可以接受的附照片身份证明,并获得顾客的社会保障账户号码
- Usually accomplished by asking for a driver's license or other acceptable picture ID and obtaining the social security number of the customer
- 及时报告
- 服务提供者还被要求核对户身份以免其是政府提供的可疑恐怖分子名单或恐怖组织的一员,如果有任何可疑的恐怖分子或客户账户的可疑活动,需要立即报告美国财政部。
- Service providers are required to check the customer's ID against a government-supplied list of terrorist organizations and report any suspicious activity in a customer's account
《萨班斯-奥克斯利法案》(2002)
- 组成了上市公司会计监管委员会以促成会计职业的更高标准并促进审计上市公司(包括银行和其他金融机构)财务报告的准确与客观公正
- The Public Company Accounting Supervision Committee was formed to promote higher standards in the accounting profession and to promote the accuracy and impartiality of auditing the financial reports of listed companies, including banks and other financial institutions
- 公司的高级管理人员要对其公司财务报告的真实性负责
- The company's senior management is responsible for the authenticity of its company's financial reports
21世纪出现的新法律和法规:《多德-弗兰克金融改革法案》《巴塞尔协议》和世界各地的其他规则
未解决的监管问题Unresolved Regulatory Issues
- 我们应该怎样才能建立监管机构的安全网来保护小额存款者不受损失,仅仅依靠通常的政府发起的存款保险吗?
- What should we do about the regulatory safety net set up to protect small depositors from loss, usually through government-sponsored deposit insurance?
- 我们可以较好地训练监管人员以使他们适应新的金融市场环境吗
- Can we train regulators to be as good as they need to be in a more complex financial marketplace?
- 随着金融服务业的兼并与集中,造就了更少但却更大的金融机构,更少的监管机构可行吗?
- With the financial-services industry consolidating and converging into fewer, but bigger, firms, can we get by with fewer regulators?
- 我们可以简化目前的监管机构并且带来更高的效率吗?
- Can we simplify the current regulatory structure and bring greater efficiency to the task?
- 金融机构遍及全球各地,哪个国家或哪些国家应该监管它们的活动
- As financial firms reach their arms around the globe, what nation or nations should regulate their activities?
对与银行竞争的非银行金融机构的监管
信用合作社Credit Unions
- 国家信用合作社管理委员会
- National Credit Union Administration (NCUA)
储蓄协会Savings and Loans and Savings Banks (“Thrifts”)
- 州政府授权的储蓄协会由州政府或委员会监管或审查
- State-chartered associations are supervised and examined by state boards or commissions
- 联邦授权的储蓄贷款机构和储蓄银行由储蓄机构监管办公室(美国财政部的一部分)进行监管。
- Federally chartered savings associations fall under the jurisdiction of the Office of Thrift Supervision
- 《多德-弗兰克金融改革法案》于2010年通过,储蓄机构监理局和货币监理局合并,这样存款机构和国民银行在联邦水平上就有了同样的管理机构。
- The Dodd-Frank Act merged the Office of Thrift Supervision with the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency so that thrift institutions and national banks would have the same regulatory agency at the federal level
货币市场基金Money Market Funds
- 证券交易委员会
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
人寿和财产/灾害保险公司Life and Property/Casualty Insurance Companies
- 州保险委员
- State insurance commissions
- 联邦政府似乎更多参与了保险公司的监管
- Recently the federal government has become somewhat more involved in insurance
- 当保险公司组成金融控股公司并兼并银行和其他受联邦监管的金融公司时,它们就可能处于联邦储备系统的监管之下。
- When insurers form holding companies to acquire commercial and investment banks or other federally regulated financial businesses, they may come under the Federal Reserve's review
- 根据《多德-弗兰克金融改革法案》,建立新的联邦保险办公室(FIO)以帮助减少系统风险以及阻止破坏性的保险损失。这些系统风险通常是由大型保险公司(例如AIG)所从事的创新性和高风险性活动引起的。
- Under the Dodd-Frank Act, a new federal insurance office was set up to help reduce the systemic risk caused by innovative, but sometimes highly risky, activities of the largest insurers (such as AIG) and prevent disruptive insurance failures
财务公司Finance Companies
- 被联邦政府监管多达几十年
- Regulated at the state government level for many decades
- 州政府的监管力度在各州有所差别
- The depth of state regulation varies across the United States
- 大多数州的监管集中在以下几个方面:向公众提供的贷款协议的内容和类型、贷款利率的规定(一些州规定了利率最高限制)以及当借款人无法还款时收回贷款的措施。
- Most states focus upon the types and contents of loan agreements they offer the public, the interest rates they charge (with some states setting maximum loan rates), and the methods they use to repossess property or to recover funds from delinquent borrowers
- 最近,由于监管程度低导致一些小贷款公司大量出现
- Relatively light state regulation has led to a recent explosion in the number of small-loan companies
- 2010年的《多德-弗兰克金融改革法案》对小额贷款产生了重要影响,限制小额贷款未来成长以及导致许多机构倒闭
- The passage of the Dodd-Frank Act in 2010 caused many to close as the maximum interest rates that these entities could charge was drastically reduced
共同基金Mutual Funds
- 美国证券交易委员会要求这些公司在该委员会注册、定期提供财务报告,并向投资者提供相关说明书,披露其财务状况、近期表现以及每个基金的管理目标。
- The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) requires these businesses to register with that agency, submit periodic financial reports, and provide investors with a prospectus that reveals the financial condition, recent performance, and objectives of each fund
证券经纪和交易商Security Brokers and Dealers and Investment Banks
- 一系列联邦和州政府监管适用于这些金融工具的交易者,它们购买销售证券、承销新证券的发行并给公司和政府提供财务建议
- A combination of federal and state supervision applies to these traders in financial instruments who buy and sell securities,underwrite new security issues, and give financial advice
- 其主要监管机构是证券交易委员会
- The chief federal regulator is the SEC
- 要求这些公司定期提供财务报告、限制负债数量并调查内部交易准则
- Requires these firms to submit periodic reports, limits the volume of debt they take on, and investigates insider trading practices
Hedge Funds, Private Equity Funds, and Venture Capital Companies
- 金融机构受监管最少的
- Some of the most lightly regulated of all financial institutions
- 美国证券交易委员会仍会对其在小投资者可进入的公开市场销售证券而向公众提供信息进行广泛的监督。
- The SEC in the United States has broad oversight of the information these firms provide to the public when they choose to sell securities in the open market that are accessible to small investors
- 对该行业的监管实质上还是很少的,一方面因为它还是相对比较新的行业,另一方面是它一般不向小投资者筹集资金
- Regulation in this sector is virtually invisible, in part because it is relatively new and because it normally does not seek out many funds from small investors
- 《多德-弗兰克金融改革法案》提倡商业银行与私人投资的更大分离。
- The Dodd-Frank Act of 2010 calls for greater separation between commercial banks and these riskier private investors
中央银行体系对银行及其他金融机构决策和政策的影响
各国的中央银行
- 美国的中央银行————联邦储备系统
- The central bank of the United States is the Federal Reserve System (the Fed)
- 央行的基本任务是实施货币政策(monetarypolicy),既确保银行业和金融体系运作良好,又要确保该体系创造的货币和信用能促进国家经济目标的实现。通过控制货币和信贷的增长,美联储及其他国家中央银行尽力确保其经济以适当的速度增长,尽量降低失业率、抑制通货膨胀
- A central bank’s primary job is monetary policy
- Involves making sure the supply and cost of money and credit from the financial system contribute to the nation’s economic goals
- By controlling the growth of money and credit, the Fed and other central banks around the globe try to ensure that the economy grows at an adequate rate, unemployment is kept low,and inflation is held down
- 由于美联储不需要政府融资,因此在实现这些目标时相对自由
- The Fed is free to pursue these goals because it does not depend on the government for its funding Passes along most of its earnings to the U.S. Treasury
- 欧盟也有自己的中央银行————欧洲中央银行。它独立于政府,在抑制通货膨胀时具有很大自主权。
- The European Union also have a central bank -the European Central Bank(ECB)
- It is relatively free and independent of governmental control as it pursues its main goal of avoiding inflation
- 相比而言,日本的日本银行(Bank of Japan)、中国的中国人民银行(People’s Bank of China)以及其他亚洲国家的中央银行受到政府较多的控制,其中有些国家近些年正在经历着高通胀、币值剧烈波动和其他重要的经济问题。
- In contrast, the Bank of Japan (BOJ), the People's Bank of China(PBC), and central banks in other parts of Asia appear to be under close control of their governments
- Several of these countries have experienced higher inflation rates,volatile currency prices, and other significant economic problems in recent years
- 虽然仍处于激烈的争论中,旦近年来的研究(如伯拉德和威尔士)表明,越独立的中央银行就越能更好地实现国家的长期经济目标,特别是在抑制通货膨胀方面。
- Recent research suggests that more independent central banks have been able to come closer to their nation's desired level of economic performance (particularly better control of inflation)
美国联邦储备系统的组织结构
- 联储委员会Board of Governors
- 委员会由7名成员组成,委员由总统提名并通过议会确认,委员任期不超过14年。
- This governing body must contain no more than seven persons,each selected by the president of the United States and confirmed by the Senate for terms not exceeding 14 years
- 委员会主席和副主席由总统从这7名委员中选出,任期4年(但是候选人有可能发生变化)
- The board chairman and vice chairman are appointed by the president from among current board members, cach for four year terms (though these appointments may be renewed)
- 委员会管理和监督12个区储备银行及其分支机构的活动,
- The board regulates and supervises the activities of the 12 district Reserve banks and their branch offices
- 规定银行及其他存款机构的准备金比率,批准12家储备银行收取的贴现利率,制定影响利率、货币和银行信贷增长的公开市场政策。
- It sets reserve requirements, approves all changes in the discount (loan) rates posted by the 12 Reserve banks, and takes the lead in the system in determining open market policy
- 联邦公开市场委员会Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
- 大部分投票委员由联储董事会成员担任,
- The Federal Reserve Board members make up a majority of the voting members of the FOMC
- 其他的投票委员由12个联储银行行长中的5人担任,每人担任决策委员的期限是1年(除了纽约联邦储备银行的行长,因为他是常任决策会员)。
- The other voting members are 5 of the 12 Federal Reserve bank presidents, who each serve one year in filling the remaining five official voting seats on the FOMC, except for the president of the New York Federal Reserve Bank, who is a permanent voting member
- FOMC的具体任务是制定指导公开市场操作(open market operations,OMO)的决策,即由联邦银行买卖证券
- Primary task is to set policies that guide the conduct of open market operations, the buying and selling of securities by the Federal Reserve banks
- 联储体系分为12个区,每个区域设立一个联邦储备银行(FederalReserve Bank)监督会员银行,同时也为它们服务。联邦储备银行向本区域存款机构提供的主要业务有:在银行和其他存款机构之间电汇资金;确保银行及其顾客持有的证券的安全;发行美国财政部和其他联邦机构的新证券;由每个联邦银行的“贴现窗口”向银行及其存款机构发放短期贷款;保持和供给货币;清算和托收流动的支票和其他现金款项;向金融机构及公众发布影响其利益变化的信息。
- There are 12 districts contained in the Federal Reserve System, with a Federal Reserve Bank chartered in each district
- Key services that the Federal Reserve banks offer to depository institutions in their districts:
Issuing wire transfers of funds between depository institutions
Safe-keeping securities owned by depository institutions and their customers
Issuing new securities from the U.S. Treasury and selected other federal agencies
Making loans to qualified depository institutions through the "Discount Window"
Dispensing supplies of currency and coin
Clearing and collecting checks and other cash items
Providing information to keep financial-firm managers and the public informed about developments affecting the welfare of their institutions
- 货币监理署授权成立的所有银行(国民银行)及那些愿意接受联储监督和监管的银行被称为会员银行(member banks)。会员银行必须在联邦银行区域内买卖股票(占其支付资本和盈余的6%),并且接受美联储工作人员的综合检查
- All banks chartered by the Comptroller of the Currency (national banks) and those few state banks willing to conform to the Fed's supervision and regulation are designated member banks
- Member institutions must purchase stock (up to 6 percent of their paid-in capital and surplus) in the district Reserve bank and submit to comprehensive examinations
中央银行的主要任务:制定和实施货币政策
- 中央银行的主要任务是制定并实施货币及信贷政策,促进经济的持续增长,避免高通货膨胀。
- A central bank's principal function is to conduct money and credit policy to promote sustainable growth in the economy and avoid severe inflation
- 为了实现这些目标,大多数央行采用各种手段影响银行体系的法定准备金、金融体系中的贷款利率、全球外汇市场上的汇率。
- To pursue these important objectives, most central banks use a variety of tools to affect the legal reserves of the banking system,the interest rates charged on loans made in the financial system, and relative currency values in the global foreign exchange markets
- 中央银行主要通过以下三个工具来影响法定准备金、利率和货币价值:公开市场操作、贴现率、各种银行负债的法定准备金。
- To influence the behavior of legal reserves, interest rates, and currency values, central banks usually employ one or more of three main tools: open market operations, the discount rate on loans to qualified financial institutions, and legal reserve requirements on various bank liabilities
中央银行的公开市场工具
- 目前在许多重要的国家,公开市场操作成为中央银行货币政策的主要工具。例如,美国联邦储备系统中的代表性政策工具是公开市场账户(SOMA)经理在纽约联邦储备银行的交易席位,由此购买和销售美国国库券、债券、票据以及其他可用的证券
- Open market operations (OMO) have become the principal tool of central bank monctary policy. In the United States, OMO involves the buying and selling of U.S.Treasury bills, bonds, and notes and selected federal agency securities
- 这些交易在联储交易席位和符合联储要求的初级交易商之间进行。
- These transactions are conducted between the Fed’s trading desk and selected primary dealers who meet the Fed's qualifications
- OMO被认为是美联储最为重要的政策工具,主要是因为这种工具可以每天使用(有时一天不止一次),而且如果联储政策失误,该工具可以通过买卖交易的抵消迅速纠正。
- OMO is considered to be the most important policy tool for many central banks because it can be used every day and, if a mistake is made or conditions change, its effects can be quickly reversed
- 中央银行出售证券将降低金融系统中的存款和贷款增长率。利率倾向于增加。
- Central bank sales of securities tend to decrease the growth of deposits and loans within the financial system. Interest rates tend to rise
- 相反地,中央银行将购买较多的证券将增加金融系统中的存款和贷款增长率,利率倾向于减少。
- In contrast, central bank purchases of securities tend to increase the growth of deposits and loans. Interest rates tend to fall
- 美联储的联邦公开市场委员会将存款机构间隔夜准备金贷款的联邦基金率作为盯住目标,希望联邦基金利率的变化能影响到经济中的其他相关利率。
- The FOMC targets the federal funds rate attached to overnight loans of reserves between depository institutions in order to achieve the Fed's monetary policy goals, hoping that changes in the federal funds rate will spread to other interest rates in the economy
其他的中央银行政策工具
- 许多中央银行是银行及其他存款机构短期资金的重要来源
- Many central banks are an important source of short-term loans for depository institutions
- 当联储向借款银行发放准备金贷款时,法定准备金的供给暂时增加,可能会导致银行贷款和存款增加
- When the Fed loans reserves, the supply of legal reserves expands temporarily, which may cause loans and deposits to expand
- 当借款银行偿还贴现窗口贷款时,银行的准备金减少,其存款和贷款也不得不减少。
- When these discount window loans are repaid, the borrowing institutions lose reserves and may be forced to curtail the growth of their deposits and loans
- 联储收取的贷款利率-贴现率由每个区联储银行的股东大会决定并经联储委员会批准。
- The loan rate charged by the Fed, the discount rate, is set by each Reserve bank's board of directors and must be approved by the Federal Reserve Board
- 中央银行偶尔也使用变动准备金率作为货币政策工具。
- Central banks also occasionally use changes in reserve requirements as a monetary policy tool
- 出售交易存款(如支票账户)的银行和其他存款机构必须提取存款的小部分作为准备金,或者以库存现金形式和以在中央银行的存款作为准备金
- Institutions must place a small percentage of each dollar of deposits in reserve, either in the form of vault cash or in a deposit at thecentral bank
- 提高准备金比率,即银行必须保留存款中的更大比例作为准备金,用于放贷的资金就减少。
- Raising reserve requirements means that financial firms must set aside more of each incoming dollar of deposits into required reserves, and less money is available to support making new loans
- 降低准备金利率,则准备金的一部分转化为银行可以借出的资金
- On the other hand, lowering reserve requirements releases reserves for additional lending
- 中央银行通常并不使用准备金率作为政策工具,因为其影响过大且不容易反向操作,而且存款也并不像过去那样是银行唯一的资金来源。
- Central banks rarely change reserve requirements. Powerful impact, cannot easily be reversed and because banks are less dependent on deposits as a source of funds
- 另一个重要的政策工具是道义劝告。利用该政策,央行希望通过向个人及机构施加心理压力以使其遵守央行的政策
- One other important policy tool————moral suasion. Through this policy tool, the central bank tries to bring psychological pressure to bear on individuals and institutions to conform to its policies
习题
What key roles does the Federal Reserve System perform in the banking and financial system?
- Supervising and regulating banks to ensure safety of the nation's banking and protect consumers
What is the principal job performed by the FDIC?
- Insures deposits, examines and supervises financial institutions for soundness
What is the Glass-Steagall Act, and why was it important in banking history?
- Separated commercial banking from investment banking and created the FDIC
- Protects depositor's money
How have bank failures influenced recent legislation?
- Recent bank failures have caused huge losses to federal insurance reserves and damaged public confidence in the banking system.
How and why was the Dodd-Frank Regulatory Reform Act crafted to reduce systemic risk in the financial system, promote fair lending, protect consumers, and separate banks from key nonbank firms in an effort to restore public confidence?
- Created due to the 2008 recession and was created to prevent future financial crisis
- Lax regulations led to extremely risky lending practices
Compare the rules of Basel I II III. Why are they important in Global financial market?
What is monetary policy?
- Policies that control the supply of money, the price of money, and the availability of credit.
What services does the Federal Reserve provide to depository institutions?
- Provide financial services to depository institutions including banks and credit unions, much like those that banks provide for their customers. These services include collecting checks, electronically transferring funds, and distributing and receiving cash and coin.
第3章 银行及金融服务业的组织与结构
引言
- 第1章探讨了现代银行和许多金融服务竞争者所担当的行为角色及提供的服务
- Chapter 1 explored many of the roles and services of the modern bank and competitors of banks.
- 多年来,为开展这些业务和满足客户要求,银行发展了多种组织形式
- Over the years, bankers and the managers of competing financial institutions have evolved into different organizational forms.
- 金融机构的规模并不是其组织构建和出色运营的唯一决定因素,
- A financial institution’s size are not the only determinant of how it is organized or how well it performs.
- 在本章中,我们将会看到公众流动性及其对金融服务要求的变化,金融服务客户资源潜在竞争者的出现和不断变化的政府监管明显地改变了银行和金融服务业的主要结构、规模和组织类型。
- In this chapter, we will discuss the causes that have dramatically changed the structure, size, and types of organizations dominating the financial-services industry today.
商业银行业的内部组织与结构
不断增加的规模和资产的集中
- 商业银行是家庭贷款、支票存款和借记卡的主要提供者。按世界标准而言,大多数美国银行规模较,然而,这些最小的金融机构,尽管数量很多,却仅持有整个行业资产的1%多一点。
- Commercial banking is the dominant supplier of credit and payments services to businesses and households
- On one hand, many banks in the United States are small by global standards.
- These smallest financial institutions, numerous as they are, held little more than one percent of total industry assets.
- 与之对比,美国银行业也不乏一些全球数一数二的大型机构。花旗银行和摩根大通银行,以及位于北卡罗来纳夏洛特的美国银行,它们所持资产(大约6万亿美元之上)。
- In contrast, the American banking industry also contains some of the largest financial service organizations on the planet.
- Citigroup, JP Morgan Chase, and the Bank of America hold about 6 trillion dollars combined
总结
- Banking continues to be increasingly concentrated in the smallest and the very largest of all financial firms.
- Both small and medium-size banks have lost substantial market share to the biggest banks.
Internal Organization of the Banking Firm
- The great differences in size across the industry that have appeared in recent years.
- It has led to market differences in the way banks and other service providers are organized internally and in the variety of financial services each institution sells in the markets it chooses to serve.
社区银行和其他以社区为中心的金融机构Community Banks and Other Community-Oriented Financial Firms
- 致力于吸引小规模的、以消费者为导向的存款和对消费者及小型企业提供贷款业务,将诸如此类的银行称为零售银行
- Devoted principally to the markets for smaller locally based deposits and loan sand are often referred to as a retail bank.
- 与此形成鲜明对比的是批发银行
- Financial firms of this type stand in sharp contrast to wholesale banks.
- 高级经理人和经理人之间、经理人和部门员工之间都紧密联系。
- Close contact between top management and management and staff of each division is common.
- 社区银行还会受到当地经济状况和法律法规的影响
- Community banks areusually significantly impacted by changes in the health of the local economy and keeping up with new regulations
- 这些机构的势力范围却在减少,无论是机构的数量还是市场份额
- These institutions have been losing ground, both in numbers of institutions and in industry shares Around 14,000 community banks in 1985 and about6,000 in 2010.
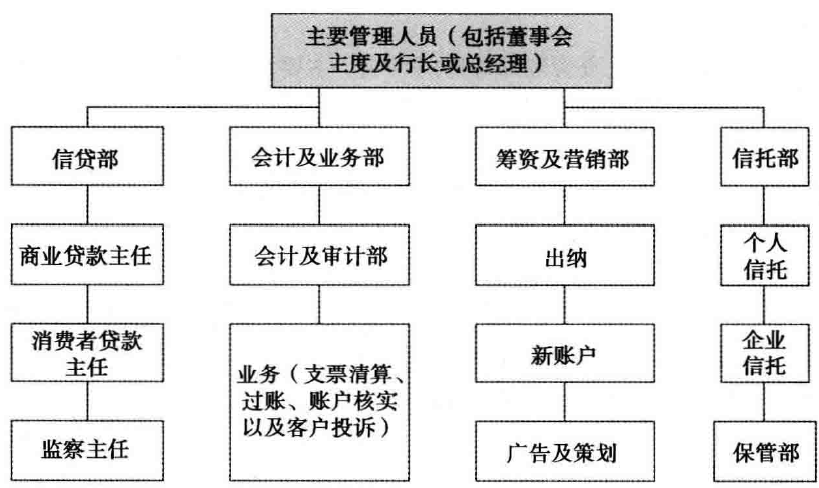
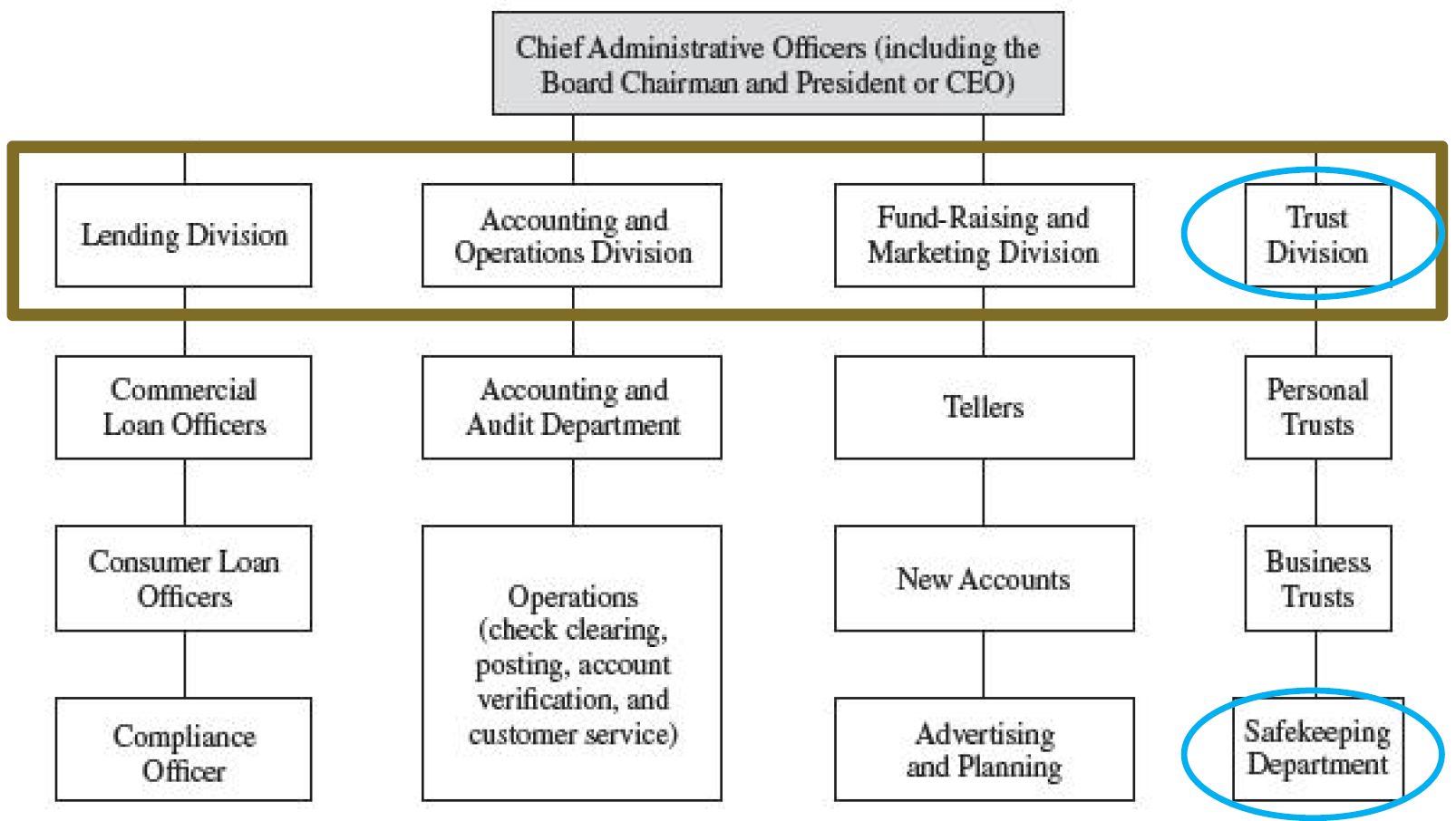
- These institutions have been losing ground, both in numbers of institutions and in industry shares Around 14,000 community banks in 1985 and about6,000 in 2010.
大型银行:货币中心、批发和零售Larger Banks – Money Center, Wholesale and Retail
- 大型(数十亿美元)货币中心银行(位于大城市,且主要业务为批发金融或批发和零售金融结合)的组织结构图比小型社区或零售银行要复杂得多
- A large money center bank is usually located in a large city and has a focus towards wholesale or wholesale plus retail
- 众多大型银行朝着利润中心型靠拢
- Some of the largest banks have moved toward the profit-centered or performance approach
- 银行的主要部门都致力于最大限度地获取利润并密切监督自身的运营行为。
- Each major department strives to maximize its contribution to profitability or to some other performance indicator
- 大型货币中心银行较小型、以社区为中心的银行拥有更多优势,它们有更强的多样化经营能力,具有更强的抵御起伏不定的经济风险的能力,拥有能以相对较低的成本筹集金融资本的重要优势,
- The largest money-center banks possess some important advantages over community oriented institutions
- Better diversified - both geographically and by product line
- Can better withstand the risks of a fluctuating economy
- Able to raise huge amounts of financial capital at relatively low cost
- Can attract top managerial talent
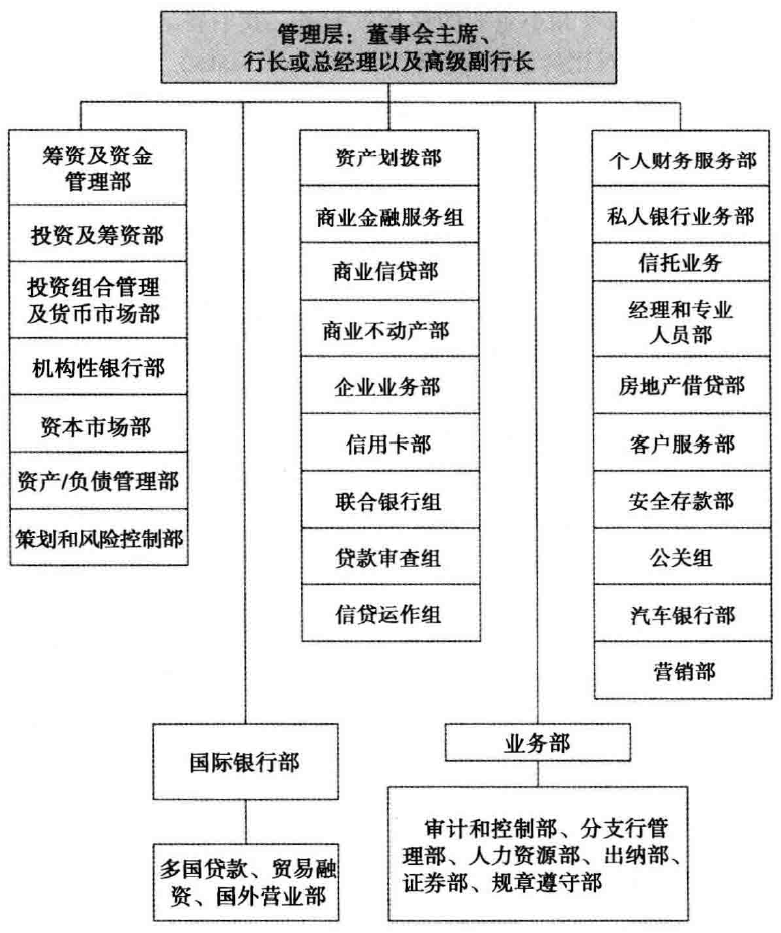
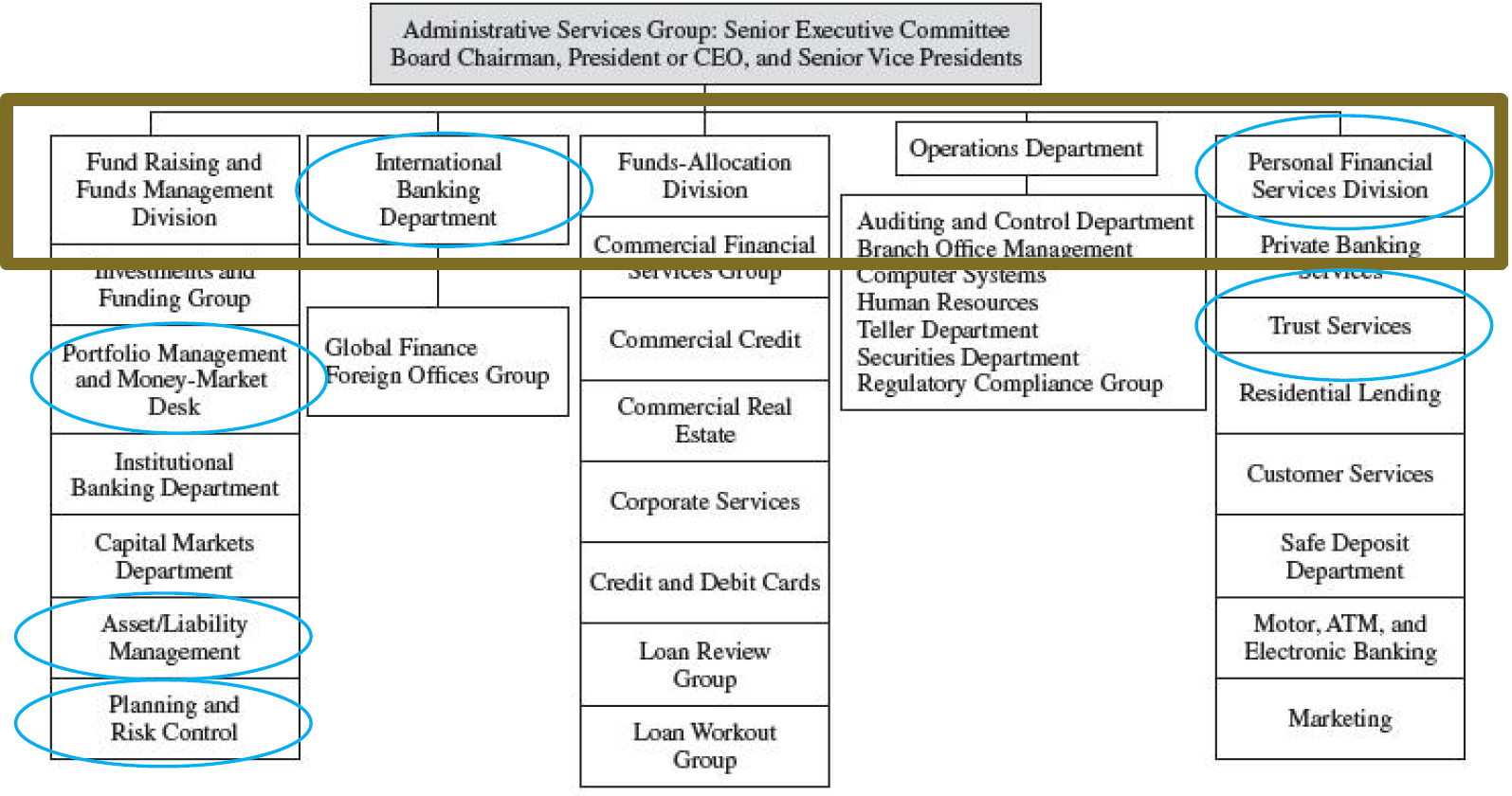
银行组织的发展趋势与银行业的类型
银行组织的发展趋势
- 大多数银行机构有越来越复杂的趋势
- The tendency in recent years has been for most financial institutions to become more complex organizations over time
- 当金融机构开始发展时,往往是从开发新的服务项目和添置新设施开始
- When a financial firm begins to grow, it usually adds new services and new facilities
- 影响银行组织形式的另一方面是:银行管理者必须掌握对组织结构进行变动的技能,越来越多的银行逐渐采取以市场和销售为导向的策略
- Another significant factor influencing financial organizations today is the changing makeup of the skills financial-service providers need to function effectively (cash inflow-oriented vs.profit-oriented)
- 银行需要更多的具备计算机知识的雇员和更多的可供这些雇员使用的电子设备
- Financial firms have needed growing numbers of people with computer skills
- Call centers have grown in the industry to sell profitable services and respond to customer problems
- 自动簿记技术减少了管理人员用于日常业务的时间
- Automated book keeping has reduced the time managers spend in routine operations
银行业组织结构和类型概览
- Member banks vs. Insured banks;National banks vs. State chartered banks;Affiliated banks vs. Independent banks(Acquired by holding companies or not)
单元制银行组织结构
- 单元制银行作为银行业最古老的一种组织结构Unit banks, one of the oldest kinds, offer all of their services from one office(“一行一店”)
- 其中有少量业务(如吸收存款和支票兑现)通过专门性服务设施来提供,如便利窗口、自动柜员机(ATM)以及银行的网站
- Some services (such as taking deposits, cashing checks,or paying bills) may be offered from limited-service facilities, such as drive-up windows and automated teller machines (ATMs) that are linked to the bank's computer system.
- 全美1/3约1600家商业银行没有全业务分支机构
- About one-third U.S. banks today operate just one full service office.
- These organizations are stil common today
- 单元制银行数量如此之多的原因之一在于,即使电子银行业和银行业巨头在大规模兼并,新开业银行的数量却仍在快速增长,大约有15%的社区银行成立时间不到10年
- One reason for the large numbers of unit banks is the continuing formation of new banks (about 15p of all community banks are less than 10 years old)
- 众多客户似乎仍钟情于小型银行,因为这类小型银行更了解客户,并为其提供个性化服务
- Many customers still seem to prefer smaller banks,which often seem to know their customers better than larger banks (pros and cons)
- 如果经济疲软,人们倾向于其他市场领域时
- Surrounding economy weakens;People and business move away to other market areas.
- 大多数银行渴望开展多种服务 However, many new banks start out as unit organizations
- 只有当其不断发展吸引到更多的资源和专业人才时,才可能突破这种组织形式
- Because their capital, management and staff are severely limited until the financial firms can grow and attract additional resources and professional staff.
分支行制组织结构
- 随着规模的扩大,单元制银行通常会决定建立一个分支银行As a unit financial firm grows larger in size it usually decides at some point to establish a branching organization.
- When?
- 当银行所在地处于经济快速发展阶段时
- It serves a rapidly growing region.
- 在进人新地区时遵循其企业及家庭客户的特点和需求
- It finds itself under pressure to follow its business and household customers as they move into new locations.
- 将市场拱手让给地理位置更为优越的竞争者
- It loses them to more conveniently located financial-service competitors.
- 银行通过一些营业点提供服务,包括一个主营业部门,还有一个或多个全业务型分支行部门They offer the full range of services from several locations, including a head office and one or more full-service branch offices.
- 通过一个支持性网络来提供有限的服务,包括便利窗口、自动取款机...
- Junior Level: Likely to offer limited services through a supporting network of drive-in windows,ATMs, computers network, point-of-sale terminals in stores and shopping centers, the Internet...
- 分支行制银行的高层管理人员通常是在总行办公,但是每个全业务分支行也有其领导班子,这些管理人员在批准客户的贷款申请和其他日常业务的运作上有一定的决策权力
- Senior Level: Management of a branching organization is usually located at the home office, though each full-service branch has its own management team with limited authority to make decisions.
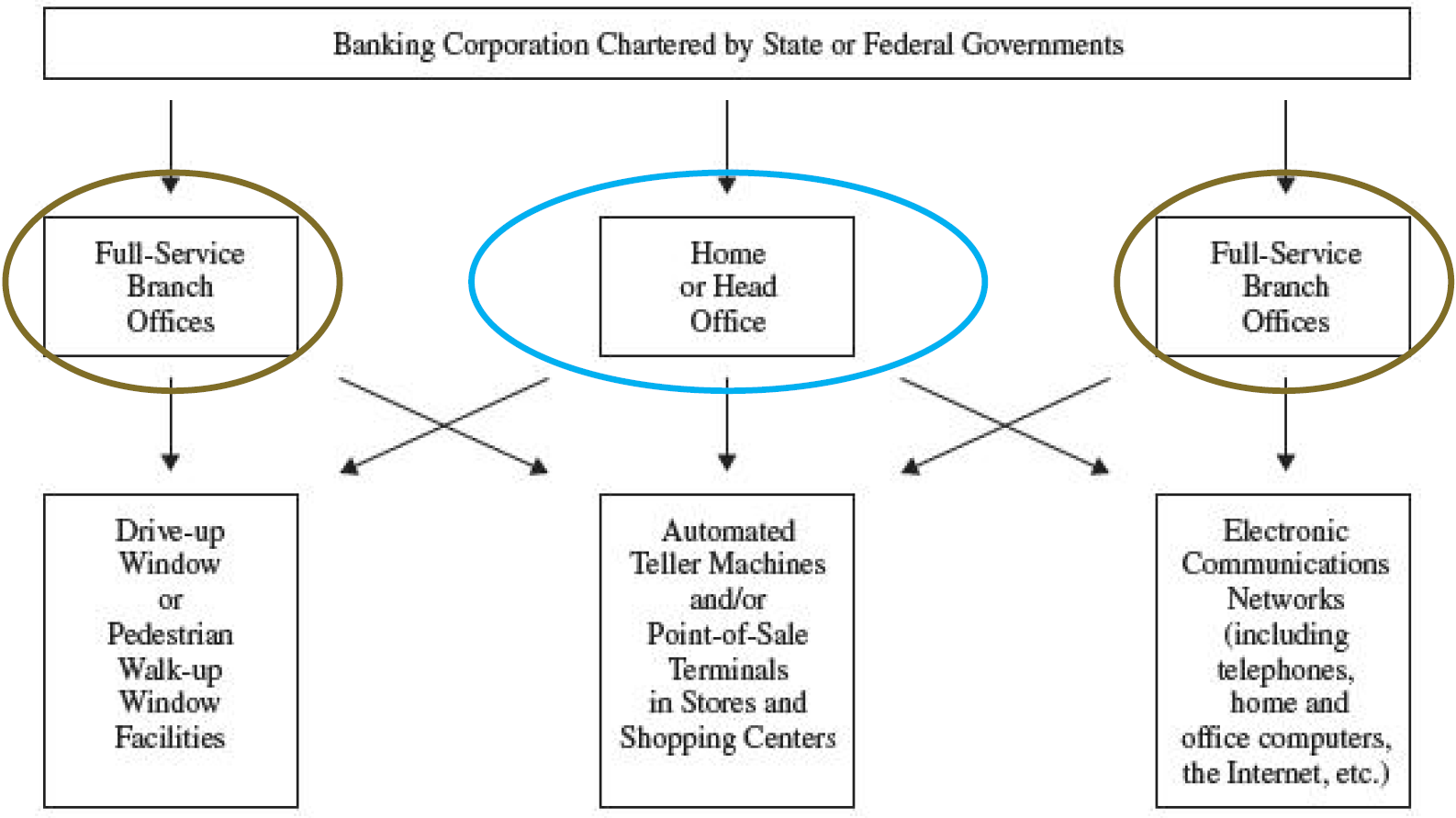
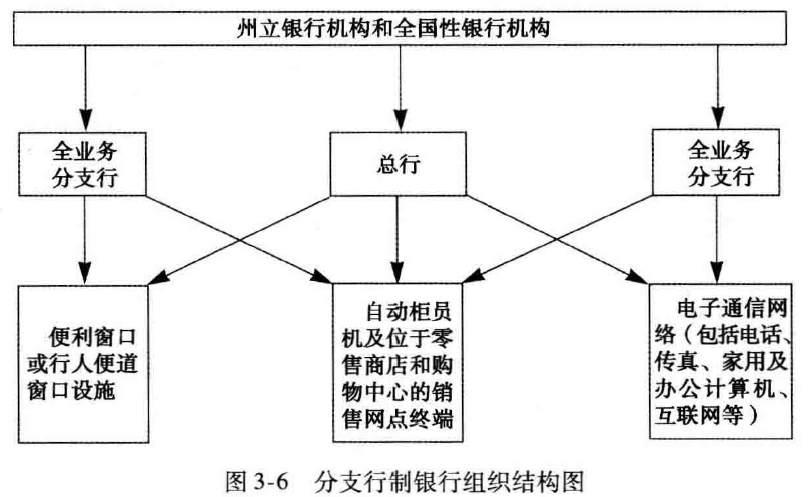
分支行的增长
- 在20世纪30年代大萧条时期,美国平均只有1/5 的银行设有全业务支行
- During the Great Depression of the 1930s, only one in five American banks operated a full-service branch office
- 在21世纪初,平均每家银行都经营着差不多12家全业务支行
- By the beginning of the 21st century, the average U.S. bank operated close to 12 full-service branch offices.
- 原因之一就是在过去数十年中,大量人口由城市流向郊区
- One contributing factor has been the exodus of population from cities to suburban communities
- 《瑞格尔-尼尔跨州银行和分行效率法案》为全国范围内银行新分支机构的扩张提供了法律基础(如跨州银行)
- The passage of the Riegle-Neal Interstate Banking and Branching Efficiency Act in 1994 provided the basis for expansion
- 近年来,银行新分支机构的扩张速度似乎在减缓
- However, in recent years new bank branch office expansion appears to have slowed somewhat.
网站和电子网络:传统分支行的替代还是补充
- Electronic branches
- Internet banking services
- Automated teller machines (ATMs)Point-of-sale (POS) terminals
- Personal computers
- Call-center systems
- Virtual banks
虚拟银行
- 网络为基础的银行从传统银行
- Definition: Provide their services exclusively through the Web.
- 收取较低的服务费
- Advantage: significantly lower transaction cost.
- 尽管网络银行可以很大地削减成本,但是并没有显示出持续的盈利能力
- However, despite significantly lower transaction costs, virtual banking firms have not yet demonstrated they can be consist profitable.
- Net Bank公司,拥有25亿美元资产,却因问题贷款和不能维系良好的银行-消费者关系而于2007年破产。
- One typical example: Net Bank Inc., the first Internet-only savings and loan association, launched during the 1990s, failed in 2007 with assets of$2.5 billion due to troubled loans and inability to offer strong bank-customer relationships.
- 一个注册地。无实体网点。业务链条完整。
银行控股公司的组织结构
- 银行控股公司是持有至少一家银行的股份(权益股)而获得特许经营的公司,通常也兼具其他业务。
- A bank holding company is simply a corporation chartered for the purpose of holding the stock of at least one bank, often along with other businesses
- 大多数控股公司仅仅是持有一家或多家银行的权益股份的很小一部分由此绕过政府监管。
- Many holding companies hold only a small minority of the outstanding shares of one or more banks, why?Escaping government regulation.
- 一家控股公司试图控制一家美国银行,就必须获得联邦储备委员会的许可,定期上报由联邦储备委员会所做的稽核记录
- If a holding company seeks to control a U.S. bank, it must be approval from the Feds and submit to periodic examinations by Feds. (Bank Holding Company Act)
- 近年来,银行控股公司发展迅速The growth of holding companies has been rapid in recent decades
- 更容易利用资本市场筹资
- Access to capital markets in raising funds
- 更能运用杠杆(相对权益资本更多的债务)
- Ability to use higher leverage (more debt capital relative to equity capital)
- 具有用内部一部分业务的利润补偿公司其他部分业务损失的税收优势
- Tax advantages (offset profits from one business with losses generated by other firms part of the same company)
- 能够向银行业务以外的其他业务扩张。
- Ability to expand into businesses outside banking
- 美国大多数注册的银行控股公司都是单一银行控股公司Most registered bank holding companies in the United States are one-bank companies
- 然而,这些单一银行控股公司通常还拥有和经营着一家或多家非银行企业
- However, these one-bank companies frequently control one or more nonbank businesses as well.
- 这些非银行企业必须提供有利于“公众利益”的“与银行业密切相关的业务”,比如,提高金融服务能力或降低服务费用。
- These nonbank business must offer services “closely related to banking” that also yield “public benefit’such as improved availability of financial services or lower service price.
- 银行控股公司进人非银行业的重要优势是可以使收人和利润来源多元化同时降低风险敞口的预期
- The principal advantage for holding companies entering nonbank lines of business is the prospect of diversifying sources of revenue and profits and reducing risk exposure
- 少数银行控股公司的组织形式是多银行控股公司A minority of bank holding company organizations are multibank holding companies
- 多银行控股公司约把持着全美银行总资产额的70%
- Multibank companies control more than 70p of the total assets of all U.S. banking organizations
- 在《瑞格尔-尼尔跨州银行和分行效率法》(1994)生效之前,这种银行组织形式对某些银行股东和管理层具有很大吸引力
- Prior to the RN Act (1994), this form is an alternative to operate interstate banking business.
- 控股公司扩张和并购的一个显著后果是大幅度减少了独立的银行组织的数目。
- One dramatic effect of holding company expansion has been a sharp decline in the number of independently owned banking organizations.
- 人们谴责银行控股公司吞并原来独立的银行而削弱了竞争。与此相反,银行控股公司的支持者则声称这类组织通过扩大银行企业的规模和加入业内竞争进一步提高了银行业的效率,为客户提供了更多的服务,银行破产的可能性降低,利润更高且平稳。
- Holding company banking has been blamed for reducing competition by critics
- Supporters of the holding company movement claim greater efficiency, more services, lower probability of organizational failure, and higher and more stable profits
- 控股公司作为一个整体较之不采用控股公司组织的获利更为丰厚
- The holding company as a whole tends to be more profitable than banking organizations that do not form holding companies
- 破产概率也要低于规模相当的独立银行
- Moreover, the failure rate for holding company banks appears to be below that of comparable-size independent banks
- 然而,至少有历史证据证明多银行控股公司可能将有些社区的稀缺资本抽干并且弱化了规模较小的城镇和乡村地区
- However, there is evidence that multibank holding companies may drain scarce capital from some communities and weaken smaller towns and rural areas
跨州银行业以及1994年《瑞格尔-尼尔跨州银行和分行效率法案》
金融控股公司Financial Holding Companies (FHCs)
- 《瑞格尔-尼尔跨州银行和分行效率法案》允许美国的银行控股公司在无须任何州许可的情况下收购银行
- Riegle-Neal allows holding companies to acquire banks throughout the United States without needing any state's permission to do so and to establish branch offices across state lines
- 为什么通过联邦政府法案并得到各州的支持呢Why did the federal government eventually enact and the states support interstate banking laws?
- 需要新的资本振兴苦苦挣扎中的地区经济;
- The need to bring in new capital to revive struggling local economies
- 非银行业金融机构在全国扩张金融业务范围时面临较少的限制
- The expansion of financial-service offerings by nonbank financial institutions that faced few restrictions on their ability to expand nationwide
- 多样化经营和开拓更多的市场机遇是一些大金融公司的强烈要求
- A strong desire on the part of the largest financial firms to geographically diversify their operations and open up new marketing opportunities
- 管理者和许多银行家认为大金融公司效率更高、更不容易破产
- The belief among regulators that larger financial firms may be more efficient and less prone to failure
- 金融业务信息传递技术的进步允许银行为更广阔地区的顾客服务
- Advances in the technology of financial-services delivery, permitting service to customers over broader geographic areas
- 依据《金融服务现代化法案》,金融控股公司(FHC)被定义为一种特殊的控股公司并可以提供极广泛的金融服务,包括证券交易和包销以及保险业务Under the terms of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley (GLB) Act,financial holding companies (FHCs) are defined as a special type of holding company that may offer the broadest range of financial services, including dealing in and underwriting securities and selling and underwriting insurance
- 在FHC组织结构下,每一个控股金融公司都有自己的资金和管理,它们的盈利和亏损与FHC 的其他控股公司分离。这样,FHC就建立了防止公司全面亏损的保护措施。
- With the FHCs, each affiliated financial firm has its own Capital, Management, Profits or losses separate from the profits or losses of other affiliates of the FHC, Some protection against companywide losses
- 将美国的银行体系推向一种更大规模的合并
- Led to consolidation and convergence within the industry
兼并和收购正在重塑金融服务部门的组织结构
- 分支银行、银行控股公司和最新的金融控股公司的出现是由多种原因造成的
- The rise of branching, bank holding companies, and financial holding companies has been fueled by multiple factors
- 另一个促成这些组织形式产生的强有力因素是其进行兼并和收购的能力
- Another powerful factor spurring these organizational types forward is their ability to carry out mergers and acquisitions
- 大公司一直在追逐小的金融机构并大量购买它们的资产
- Bigger companies have pursued smaller financial-service providers and purchased their assets in great numbers
- Since 1980 more than 12,000 bank mergers have occurred in the United States
- 财务协同效应
- Synergy is the concept that the combined value and performance of two companies will be greater than the sum of the separate individual parts. Synergy is a term that is most commonly used in the context of mergers and acquisitions (M&A)
银行主要竞争者组织结构的变化
- 银行的主要竞争者(信用合作社、储蓄协会、金融公司、保险公司、证券交易商和金融集团)
- Banking’s principal competitors -credit unions, savings associations, finance companies, insurance firms, security dealers, hedge funds, and other financial firms
- 银行所有的主要竞争者都像银行所经历的变化一样也正处于变化之中
- All are affected by powerful forces such as rising operating costs and rapidly changing technology
- 到目前为止一个显著的特例是对冲基金
- A notable exception until very recently has been hedge funds.
- 所有的金融机构变得更加相似,特别是在提供服务上
- All financial firms are starting to look alike, especially in the menu of services offered
- 之前讨论的这些重要的结构和组织变化也溢出到了其他金融部门
- Great structural and organizational changes have “spilled over" into one financial-service industry after another
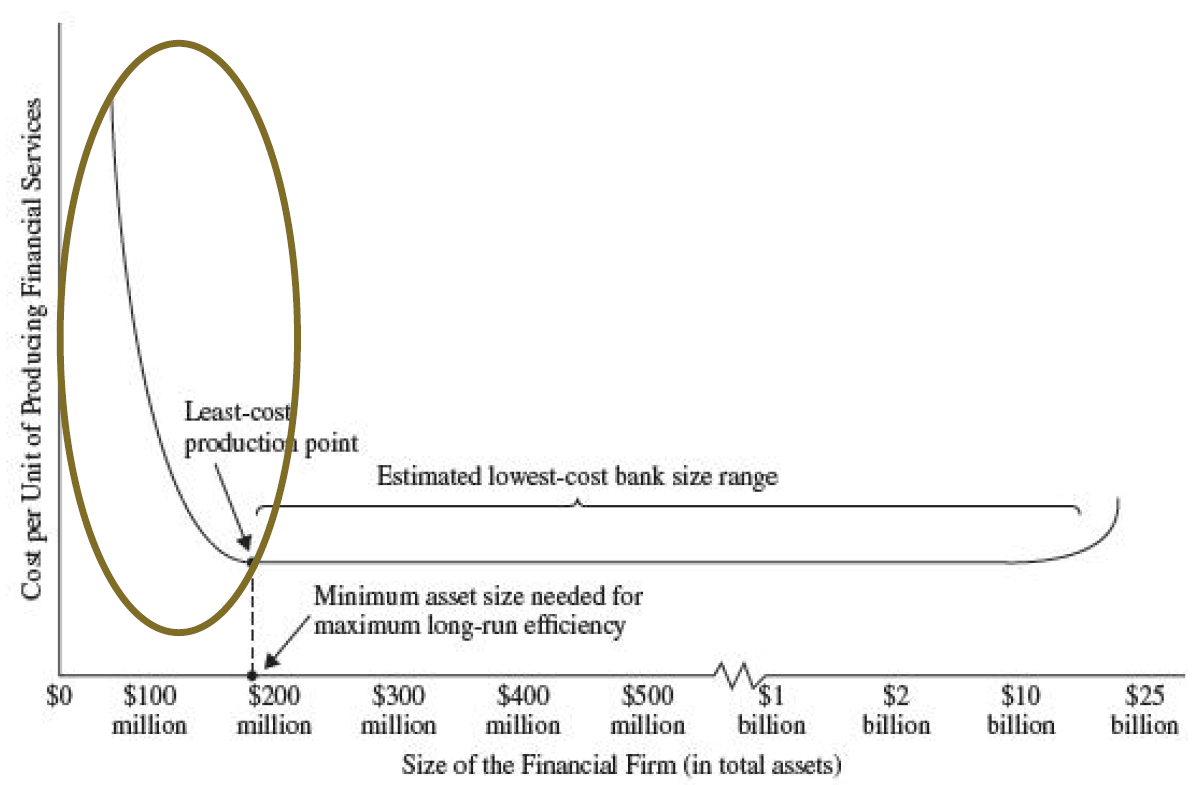
规模与效率:大型金融机构能以更低的成本经营吗
- 如果不是,那么为什么一些金融机构(如花旗银行和德意志银行)变成了地球上最大的公司之一?
- If not, then why have some financial institutions become some of the largest businesses on the planet?
- 金融机构规模的增大可能在两个方面减少了成本:规模经济、范围经济
- Two possible sources of cost savings:Economies of scale; Economies of scope
- 对于金融公司来说,有证据表明银行业至少存在中等规模经济,尽管大多数研究发现范围经济的证据很弱或根本没有。For financial firms, there is evidence for at least moderate economies of scale in banking, though most studies find only weak evidence or none at all for economies of scope
- 也有许多对非银行机构(特别是信用合作社、储蓄协会和保险公司)成本的研究,在大多数情况下,其结论与银行的研究结论相似。
- Studies of selected nonbank financial firms often reach conclusions that roughly parallel the results for banking firms
金融机构的目标及其对经营成本、效率和业绩的影响
- 支出偏好行为Expense-Preference Behavior
- 福利、豪华的办公室、高额的旅游支出比追求股东的最大受益更重要
- When the management of a financial firm decides that benefits for managers (and not the stockholders or the public) should be the primary objective of the company
- 损害股东的利益↵
- Opposite of cost control and eficiency
- 代理理论Agency Theory
- 分析公司所有者(股东)和经理(在法律上是所有者的代理人)之间的关系
- Analyzes relationships between a firm’s owners (stockholders) and its managers, who legally are agents for the owners
- 研究一个机构中是否存在某种机制,可以迫使经理人努力实现公司所有者的利益最大化
- Explores whether mechanisms exist in a given situation for managers to maximize the welfare of their firm’s owners
- 中降低代理成本的方法是建立更完善的系统以监督管理层
- Lower agency costs and better company performance depend upon the effectiveness of corporate governance
习题
What trends are affecting the way banks and their competitors are organized today?
- in general banks are becoming larger/more complex organizations with more departments/services/greater specialization. deregulation and service innovation have accelerated this trend as intense competition at home and abroad has encouraged banks to become larger organizations to serve broader and more diversified market areas.
What trend in branch banking has been prominent in the United States in recent years?
- great majority of states now offer statewide branching
- there was an increase in the 60s, 70s, 80s as the population went from cities to suburban areas
- in the 21st century, there was 5,200 branch banking organizations with 80,000 full service branch office facilities
- though the number of us commercial banks has declined the number of full service branch offices has soared.
- in recent years, growth in full-service has slowed bc of sky rocketing costs of land/building office facilities
- ATMs and electronic networks haven taken over much of the routine banking transactions... not much need for full service branches
What is a bank holding company?
- a corporate that holds an ownership interest in at least one bank. it is also allowed to own nonbank businesses as long as they are related to banking
Are there any significant advantages or disadvantages for holding companies or the public if these companies acquire banks or nonbank business ventures?
- advantages: the ability of holding companies to acquire nonbank business has given them the capacity to cross state lines even where laws have prevented them; allows a holding company to diversify across many different product lines to help stabilize the company's net earnings
- disadvantages: can stretch holding company management too far and make it ineffective causing damage to the performance of banks belonging to the holding company
- the public gains if holding companies are less subject to failure than other finance firms and more effective to operate
- the public losses if the concentration of services in bank holding companies causes the prices of those services to rise or if resources are drained away from local communities causing slower growth of those communities
Can you see any advantages to allowing interstate banking?What about potential disadvantages?
- disadvantages: increase the concentration of banking resources in the US which could possibly lead to higher prices/less services if antitrust laws are not fully enforced
- advantages: generate positive abnormal returns of bank stock. these banks are not tied to one local economic area and appear to be less subject to failure. may also bring greater stability by allowing individual banking organizations to further diversify their operations across different markets, offsetting losses
What relationship appears to exist between bank size, efficiency,and operating costs per unit of service produced and delivered?
- banks and nonbank financial services: economies of scale and economies of scope (more different services provided, the operating cost reduces bc resources are more efficiently used in jointly producing multiple services instead of just one) can lead to significant savings in operating costs with increases in service output
第5章 银行及其主要竞争者的财务报表
习题
balance sheet/report of condition
the balance sheet sheet lists the assets, liabilities, and equity capital held by or invested by a bank. Assets = Liabilities + Stockholder Equity
What are the principal accounts that appear on a bank's balance sheet (Report of Condition)?
cash and deposits (C), private interest bearing securities (S), loans and lease financing's made available to customers (L), and misc. assets (M)
major liabilities held on balance sheet
deposits made by customers (D), non deposit borrowings (NDB), equity capital (EC)
report of income/income statement
reports the amount received and expenses incurred during the period
income statement equation
net income = total revenue-total expenses
problems with book value accounting
as opposed to accrual accounting, book value accounting records the cost or expenses the day they are received or posted.
Which accounts are most important and which are least important on the asset side of a bank's balance sheet?
assets:
- cash
- investment securities
- loans
- Misc. assets
What accounts are most important on the liability side of a balance sheet?
liabilities:
- deposits
- nondeposit borrowings (federal funds/repo agreements)
- equity capital
- misc. liabilities
What are primary reserves and secondary reserves, and what are they supposed to do?
Primary reserves consist of cash, including a bank's vault cash and checkable deposits held with other banks or any other funds such as reserves with the Federal Reserve that are accessible immediately to meet demands for liquidity made against the bank.
Secondary reserves consist of assets that pay some interest (though usually pay returns that are much lower than earned on other assets, such as loans) but their principal feature is ready marketability.
what accounts make up the report of income?
Interest Income (Loans, Securities, Other)
Interest Expenses (Deposits, Nondeposit Borrowings, Other)
Net Interest Income
Provision for Loan Losses
Noninterest Income (Service Charges on Deposits, Fiduciary Activities Fees, Investment Banking and Brokerage Fees, Other)
Noninterest Expenses (Employee Expenses, Occupancy Expenses, Outside Processing Expenses, Other)
Security Gains or Losses (may not be recurring); Security Gains/Losses may be included in noninterest income/expenses or separated since it may not be recurring.
Income before extraordinary items
+/- Extraordinary Items (should not be recurring)
Income after extraordinary items
Applicable Taxes
Net Income After Taxes
What is the relationship between the provision for loan losses on a bank's Report of Income and the allowance for loan losses on its Report of Condition?
- Gross loans equal the total of all loans currently outstanding that are recorded on the bank's books.
- The allowance for loan losses is built up gradually over time by an annual noncash expense item that is charged against the bank's current income, known as the Provision for Loan Losses.
- The dollar amount of the annual loan-loss provision plus the amount of recovered funds from any loans previously declared worthless (charged off) less any loans charged off as worthless in the current period is added to the allowance-for-loan-losses account. If current charge-offs of worthless loans exceed the annual loan-loss provision plus any recoveries on previously charged-off loans the annual net figure becomes negative and is subtracted from the allowance-for-loan-losses account.
What are the key features or characteristics of the financial statements of banks and similar financial firms?
- The main similarities can be found on the asset side of their balance sheets. All of the above rely on loans and securities, although they normally label them differently. The main difference is the source of funds. None of the aforementioned competitors can draw upon deposits and has to rely on money market, other borrowings and equity. These differences are rooted in the nature of their line of business and underlying regulations. Fee income may also be a much larger percentage of their income
allowance for loan losses
- a reserve allowance built up over time for future loan loses (bad debt). ALL is a contract asset account. this means that new loan losses will not affect net income. when the loan is deemed uncollectible, it will be charged (written off the books) by reducing the ALL account and decreasing the (gross) loan account.
provision for loan losses
- annual estimated losses from uncollectible loans are credited to the PLL account from a gross loan account. it is a noncash expense