Capital investment
Basics of Capital Allocation
Types of capital investments 投资类型
- Business maintenance维持业务
- Going concern or maintenance持续经营项目:machine replacement, infrastructure improvement
- Regulatory/compliance法律规定项目 (如给外卖员买保险、污水处理)
- Business growth促进增长
- Expansion扩张已有项目
- Other开辟新项目
Typical steps in the capital allocation process 投资步骤
- Generating ideas
- Investment analysis
- Capital allocation planning
- The process used by a company's management to make capital investment decisions
- Monitoring and post-audit (事后审计)
Principles of capital allocation 投资原则
- Include需要考虑
- Opportunity costs: the foregone return of the resource invests in the next-best project 考虑机会成本
- After-tax incremental cash flows provide a sound basis for capital budgeting. It involves basic principles as follows 考虑税后增量现金流
- Externalities: Synergy (positive effect) 正外部性,与原项目互补, Cannibalization (negative effect) 负外部性,与原项目互斥
- Timing value of cash flows is crucial. 现金流所在时间
- Exclude不需要考虑
- Sunk costs: the cost has already been incurred 沉没成本
- Financing costs: they are considered in discount rate (avoiding double counting problem) 融资成本,利息成本
Cash Flow Patterns 现金流的分类
- Conventional CF: cash flows change signs once 投一次之后稳定收益
- Nonconventional CF: cash flows change signs more than once 多次投资
Investment Decision Criteria
Valuation methods for single project 判断方式
- Net present value (NPV)
- Internal rate of return (IRR)
Net present value
- Net present value(NPV) is the sum of the present value of all the after-tax incremental cash flows of the project, indicates the expected wealth changing for the firmNPV=CF_0+\frac{CF_1}{(1+r)^1}+\dots+\frac{CF_n}{(1+r)^n}
- r= required rate of return for capital suppliers, cost of capital for capital receivers 投资回报率/融资资金成本
- Investment decision criteria (for single/independent project 项目间互斥独立):
- If NPV\gt 0, then accept/invest
- If NPV\lt 0, then reject/not invest
- Advantages
- Directly reflects the expected wealth changing for the firm and its shareholders 直观
- Disadvantages
- Ignore the size of the project
Internal rate of return
- Internal rate of return(IRR) is the discount rate that makes the total present value of all cash flows,the NPV, equal to zeroNPV=0=CF_0+\frac{CF_1}{(1+IRR)^1}+\dots+\frac{CF_n}{(1+IRR)^n}
- IRR is the annualized expected return on the project
- When applying the IRR approach, required rate of return is referred as hurdle rate
- Investment decision criteria (for single/independent project):
- If IRR\gt\text{cost of capital}, then accept/invest
- If IRR\lt\text{cost of capital}, then reject/not invest
- Advantages
- It reflects the profitability
- Disadvantages
- No IRR (NPV无法等于0) or Multiple IRR (nonconventional cash flow 现金流变符号几次就最多有几解)
- Impractical implicit assumption of reinvestment rate (IRR) 再投资回报率不一定也为IRR
Confilct
- Choose the projects with higher NPV IRR大也要再算一遍NPV,NPV是最终依据
- NPV and IRR project rankings may conflict due to:
- Different sizes of CFs 现金流
- Different timing of CFs 时间
- Different reinvestment rate assumptions 再投资利率假设
- IRR assumes CFs can reinvest at project's IRR
- NPV assumes CFs can reinvest at the cost of capital (more conservative/realistic)
Project interaction
- Independent projects (独立项目,无限资金)
- projects are unrelated to each other The firm can raise the funds it wants for all profitable projects, requiring little management effort
- Accept all projects with NPV\gt 0 (IRR\gt\text{cost of capital})
- Mutually exclusive projects(互斥项目,无限资金)
- projects compete directly with each other
- Choose the one with highest NPV
- limited funds(有限资金)
- Resource scarce: firm has limited ability to take on additional projects (e.g., limited funds/skilled IT personnel)
- Capital rationing: the firm has a fixed amount of funds to invest
- Project sequencing: projects should be taken in time order
Corporate Use of Capital Allocation
Return on invested capital (ROIC)
- Measure of the profitability of a company relative to the amount of capital invested by the equity and debtholders
ROIC=\frac{\text{After tax operating profit}}{\text{Average book value of invested capital}}
If ROIC\gt\text{cost of capital/WACC}, firm's value for shareholders increases
If ROIC\lt\text{cost of capital/WACC}, firm's value for shareholders decreases
NPV and Stock prices NPV对股价的影响
- Value of the company's shares will increase by the new investment's positive NPV. 计算每股的NPV,就是增加值
- When an analyst learned news of a project 还受到预期的影响
- If the project's profitability is less than expected, the stock price might drop.
- If the project's profitability is more than expected, the stock price might increase.
Real Options 实物期权
Real options
- Types of real options
- Timing options (delay investment) 早晚都要投,但是可以改变投资时间
- Sizing options (abandonment & growth option) 改变投资规模,可以不投或多投
- Flexibility options (price setting & production-flexibility) 其它的灵活度,如改变价格或产量
- Fundamental options (gold mine & oil well) 买卖标的资产的权利
- Evaluate approaches
- NPV(\text{with option})=NPV(\text{no option})+\text{Value of options}-\text{Cost of option}
- 考虑期权后可能使得NPV大于0
Common Capital Allocation Pitfalls 错误
Common capital allocation pitfalls
- Inertia(惯性) in capital investments through years
- Source of capital bias by management
- Internal funds as "free" 自有资金
- External funds as "expensive" 外部资金,如债务
- Failure to consider investment alternatives 没有考虑其它选项
- Pushing "pet" projects 老板喜欢的项目
- Basing investment decisions on EPS, net income, or ROE 不能基于净利润
- Internal forecasting errors NPV的参数错误
- Incorrect overhead costs
- Incorrect discount rate
- Incorrect treatment of opportunity costs and sunk costs
- Failure to incorporate market responses
Working Capital and Liquidity
Financing Options融资渠道
Internal sources
- After-tax operating cash flows税后经营现金流
- Working capital efficiency
- Account payable
- Account receivable
- Inventory存货
- Marketable securities交易性金融资产
External sources
- Financial intermediaries金融机构,一对一
- Lines of credit信用贷款(uncommitted未承诺的, committed承诺的, revolving额度可循环的,还钱后可以继续借)
- Secured loans抵押贷款(e.g.,assignment of accounts receivable抵押应收账款)
- Factoring保付代理(卖掉应收账款)
- Web-based lenders & non-banklenders网贷
- Capital markets资本市场,一对多
- Short-term commercial paper大公司发布的商票,一般无抵押
- Long-term debt & equity债券、股票
Working Capital & Liquidity管理流动资本
Working capital management style
- Conservative保守: holding larger amount of cash, receivables and inventories for more financial flexibility
- Aggressive激进: holding less amount of cash, receivables and inventories for higher equity returns
- Moderate: between the two approaches above
- Liability-matching approach负债匹配,匹配期限
variable current assets可变流动资产(不是一直保持的) ← short-term financing
permanent current assets永久流动资产(如办公用品) ← long-term financing
- Liability-matching approach负债匹配,匹配期限
Liquidity management变现资产
- Liquidity: company's ability to meet its short-term obligations using cash or assets can be converted into cash quickly快速
- Liquidity management: company's ability to generate cash when needed, at the lowest possible cost折损小
Sources of liquidity流动性的来源
- Primary source of liquidity: cash from day-to-day operations.不影响经营
- Free cash flow
- Ready cash balances
- Short-term funds: trade credit, bank lines of credit, short-
- term investment portfolio
- Cash management
- Secondary sources of liquidity: using a secondary source may deteriorate the company's financial and operating positions损害经营能力
- Negotiating debt contract债务重组,和债券人求情
- Liquidating assets变卖资产
- Filing for bankruptcy protection and reorganization破产保护、破产重组
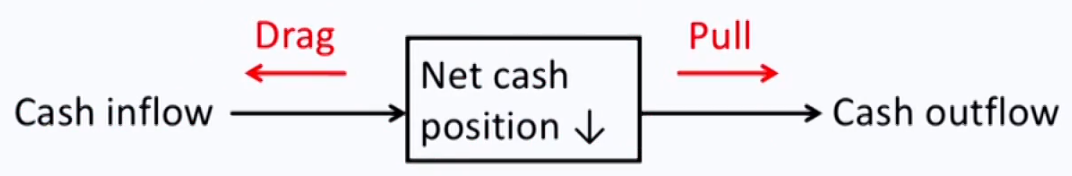
Drags and pulls on liquidity
- Drags收钱慢 on liquidity: delay, reduce cash inflows, or increase borrowing cost
- Uncollected receivables;obsolete inventory; tight credit
- Pulls付钱快 on liquidity: accelerate cash outflows
- Making payment early;reduced trade credit limits or short-term lines of credit
Measuring Liquidity衡量流动性
Liquidity ratios短期偿债能力
Generally, the greater the liquidity ratios, the higher a company's liquidity
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Current ratio流动比率 }=\frac{\text { Current assets }}{\text { Current liabilities }} \\
& \text { Quick ratio速动比率 }=\frac{\text { Cash }+ \text { Short-term securities }+ \text { Receivables }}{\text { Current liabilities }} \\
& \text { Cash ratio现金比率 }=\frac{\text { Cash }+ \text { Short-term securities }}{\text { Current liabilities }}
\end{aligned}
Turnover ratios
Generally, the higher of receivables/inventory turnover, the better working capital is managed. However, the lower of payables turnover, the better working capital is managed
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Receivables turnover应收账款周转率(要快) }=\frac{\text { Credit sales }}{\text { Average receivables }} \\
& \text { Inventory turnover存货周转率(要快) }=\frac{\text { Cost of goods sold }}{\text { Average inventory }} \\
& \text { Payables turnover应付账款周转率(要慢) }=\frac{\text { Credit purchases }}{\text { Average trade payables }}
\end{aligned}
Number of days
Generally, the lower #days of receivables/inventory,the better working capital is managed. However, the higher #days of payable, the better working capital is managed
\begin{aligned}
& \text{Number of days of receivables应收账款周转天数(要小)} =\frac{365}{\text { Receivables turnover }}\\
& \text{Number of days of inventory存货周转天数(要小)} =\frac{365}{\text { Inventory turnover }}\\
& \text{Number of days of payables应付账款周转天数(要大)} =\frac{365}{\text { Payables turnover }}
\end{aligned}
Cycles
- Operating cycle经营周期
- A measure of the time needed to convert raw materials into cash from a sale
Operating cycle = Number of days of receivable + Number of days of inventory
卖出货物的天数+收到钱的天数 - The shorter the operating cycle, the more effective a company manage its working capital
- A measure of the time needed to convert raw materials into cash from a sale
- Cash conversion cycle (Net operating cycle)现金支出天数
- A measure of the time from paying suppliers for materials to collecting cash from the subsequent sale of goods
Cash conversion cycle = Number of days of receivable + Number of days of inventory - Number of days of payable
考虑赊购原材料 - The shorter the cash conversion cycle, the more effective a company manage its working capital
- A measure of the time from paying suppliers for materials to collecting cash from the subsequent sale of goods
Evaluating Short-Term Financing Choices短期融资的评估
Major objectives of short-term borrowing目标
- Ensure sufficient capacity exists to handle peak cash needs满足突发需求
- Maintain sufficient sources of credit to be able to fund ongoing cash needs满足持续需求
- Ensure that rates obtained are cost-effective and do not substantially exceed market averages成本不能大大超过市场平均
- Ensure both implicit(如可转债) and explicit(如利息) financing costs are considered要考虑到隐性与显性成本
Factors influence short-term borrowing strategy
- Company size and creditworthiness规模与信誉
- Asset nature for secured loans资产量
- Legal and regulatory constraints监管限制
- Flexibility of financing options灵活性
Passive & active borrowing strategies
- Passive strategies: tend to be passive in response to urgent needs for liquidity, characterized by a steady, regular rollover of the same amount of money each time
- Active strategies: usually more flexible and can reflect plans, reliable forecasts, and comparative pricing
Cost of Capital-Foundational Topics
Weighted Average Cost of Capital
Cost of Capital
- Cost of capital资本成本
- The required rate of return for capital suppliers要求回报率
- The opportunity cost of funds for capital suppliers Alternative to raise capital机会成本
- A company can raise capital from:
- Debt债权人
- Preferred stock优先股股东
- Common equity普通股股东
- Cost of capital of a company
- The required rate of return that investors demand for the average-risk investment of a company
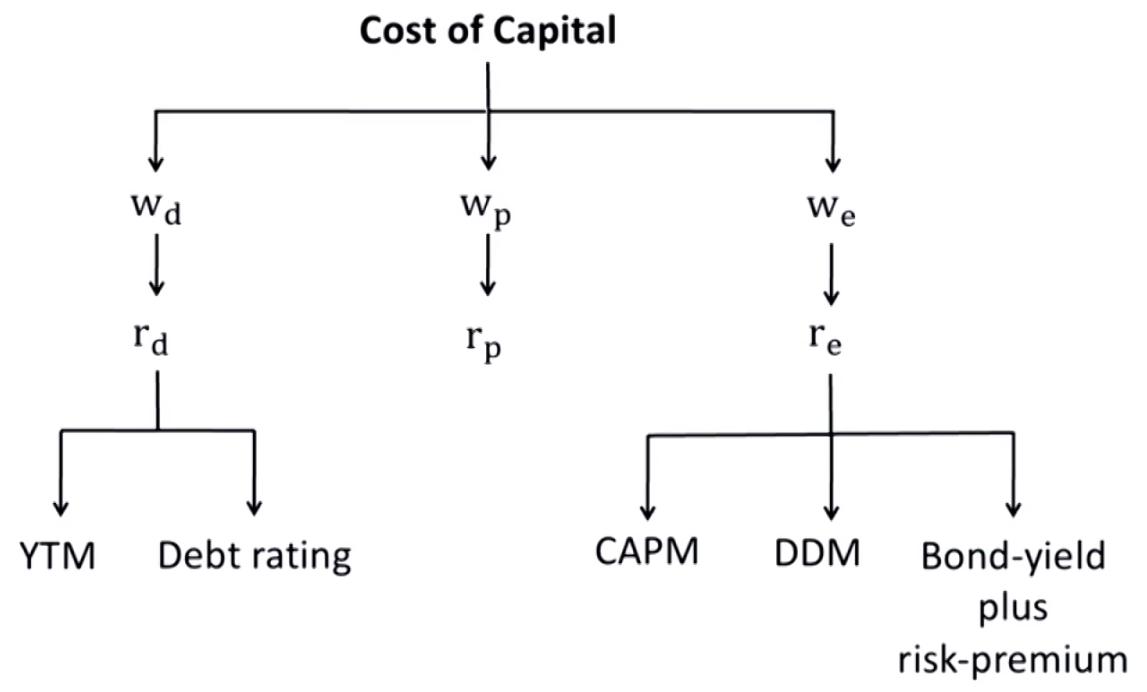
- The most common way to estimate the cost of capital of a company is weighted average cost of capital (加权平均资本成本WACC), which is to calculate the margin costs of each sources of capital and then calculate a weighted average of these costs. WACC also refers to marginal cost of capital (MCC)
Weighted average cost of capital (WACC)
- 公司的资本成本,可以用来折现公司未来的现金流
\text { WACC }=w_d \times r_d \times(1-t)+w_p \times r_p+w_e \times r_e- \mathrm{w}= company's target capital structure,not the current capital structure
- r_d= the before-tax marginal cost of debt债权人要求的回报率
- r_p= the marginal cost of preferred stock普通股股东要求的回报率
- \mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{e}}= the marginal cost of common equity优先股股东要求的回报率
- \mathrm{t}= the company's marginal多借一块钱收的税 tax rate税盾
- 使用market value
- r_d\lt r_p\lt r_e
Weights in WACC
- Use this target capital structure if it is available
- If target capital structure is not available, estimate weights using one of the several approaches:
- The company's current capital structure
- Infer the target capital structure by trends in the company's capital structure or statements by management
- Use averages of comparable companies'capital structures
Cost of the Various Sources of Capital
Cost of debt
- YTM approach根据债券的公允市场价格反推YTM
- Yield to maturity (YTM) is the annual return that an investor earns on a bond if the investor purchases the bond today and holds it until maturity
\mathrm{P}_0=\frac{\mathrm{PMT}}{(1+\mathrm{YTM})^1}+\frac{\mathrm{PMT}}{(1+\mathrm{YTM})^2}+\cdots+\frac{\mathrm{PMT}+\mathrm{FV}}{(1+\mathrm{YTM})^{\mathrm{n}}} - After-tax cost is the true effective cost of debt to the company since interest payments are generally tax-deductible
- After tax cost of debt =YTM × (1-tax rate)
- Yield to maturity (YTM) is the annual return that an investor earns on a bond if the investor purchases the bond today and holds it until maturity
- Debt-rating approach用类似公司的债券的YTM代替
- When a reliable current market price for a company's debt is not available, the debt-rating approach can be used to estimate the before-tax cost of debt
- Using the yield(r_d)on comparably rated评级 bonds for maturities期限 that closely match that of the company's existing debt相似的评级和期限
- After tax cost of debt =r_d × (1-tax rate)
Cost of preferred stoek
- For nonconvertible, non-callable preferred stockthat has a fixed dividend rate and no maturity date, we can use the formula for the cost of a preferred stock:
\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{p}}=\frac{\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{p}}}{\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{p}}} \longrightarrow \mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{p}}=\frac{\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{p}}}{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{p}}}
D_p=the preferred stock dividend per share优先股股利
P_p=the current preferred stock price per share优先股股价
Cost of common equity
- CAPM approach
\begin{aligned} & \qquad r_e=R_f+\beta\left[E\left(R_m\right)-R_f\right] \\ & R_f=\text { risk-free rate } \\ & \beta=\text { beta (systematic risk) of firm's stock } \\ & E\left(R_m\right)=\text { expected market return } \\ & E\left(R_m\right)-R_f=\text { expected market risk premium } \end{aligned}- 无风险收益率优先选择长期国债
- DDM approach
\begin{aligned} & \qquad P_0=\frac{D_1}{r_e-g} \longrightarrow r_e=\frac{D_1}{P_0}+g \\ & D_1=D_0\times(1+g)=\text { the expected dividends next period } \\ & P_0=\text { current stock price } \\ & g=\text { firm's expected constant growth rate }=(1-\text {payout ratio})\times ROE \end{aligned} - Bond yield plus risk premium approach
\begin{align} &r_e = r_d +\text { risk premium} \\ & r_d = \text {before-tax cost of debt} \\ & \text {risk premium} = \text {historical spread between stock return and debt return} \end{align}- Risk premium is the compensation return for the additional risk of equity compared with debt In developed country, risk premium ranges from 3% to 5%
Issues in Cost of Capital
Cost of capital for a public company上市公司的\beta
- When estimating the cost of equity with CAPM approach,equity beta must be estimate
- For publicly traded company, an unadjusted or “raw” historial beta can be estimated by an ordinary least square regression
- A future beta tends to regress to the mean value of 1
- Adjusted beta =(2/3)(Unadjusted beta)+(1/3)(1.0)
Cost of capital for a nonpublic company非上市公司的\beta
- For a thinly traded or non-publicly traded company,estimation of the equity beta is challenging用类似公司的\beta来估计
- using a publicly traded comparable company's equity beta(g) and adjusting it for financial leverage differences
- Comparable company:a company with similar business risk经营风险一样,财务风险可以不一样
- Pure-play method: un-lever & re-lever
- Un-lever:去除财务风险
\beta_A=\beta_E \times\left[\frac{1}{1+(1-\mathrm{t}) \times\frac{\mathrm{D}}{\mathrm{E}}}\right] - Re-lever:调整为自己的财务风险
\beta_E^{\prime}=\beta_A \times\left[1+\left(1-\mathrm{t}^{\prime}\right) \times \frac{\mathrm{D}^{\prime}}{\mathrm{E}^{\prime}}\right]
D/E: debt-to-equity ratio
- Un-lever:去除财务风险
- higher leverage and lower liquidity contribute to higher β
Flotation Cost存在发行成本时
- Flotation cost is relatively high in stock issuance
- There are two ways to incorporate the flotation cost
- Incorporate into the cost of capital (DDM)
- Incorporate into the cash flows in NPV computation(Preferred)
- Incorporate flotation cost
Incorporate into the cost of capital (DDM)
r_e=\frac{D_1}{P_0-F}+g \quad \text { or } \quad r_e=\frac{D_1}{P_0(1-f)}+g
\mathrm{f}=flotation cost in percentage amount
F=flotation cost in monetary amount - Incorporate into the cash flows in NPV computation
NPV(\text{witout flotation cost})-F=NPV(\text{with floation cost})
F=after-tax flotation cost in monetary amount
Capital Structure资本结构
Factors Affecting Capital Structure Decision
Internal factors
- Business model characteristics商业模式
- revenue, earnings, and cash flow sensitivity业务稳定性
- asset type有形资产、无形资产
- asset ownership所有权,如外包资产
- Existing leverage杠杆高,再融资成本高
- Corporate tax rate
- Capital structure policies, guidelines
- Third-party debt rating
External factors
- Market conditions/business cycle
- Regulatory constraints
- Industry/peer firm leverage
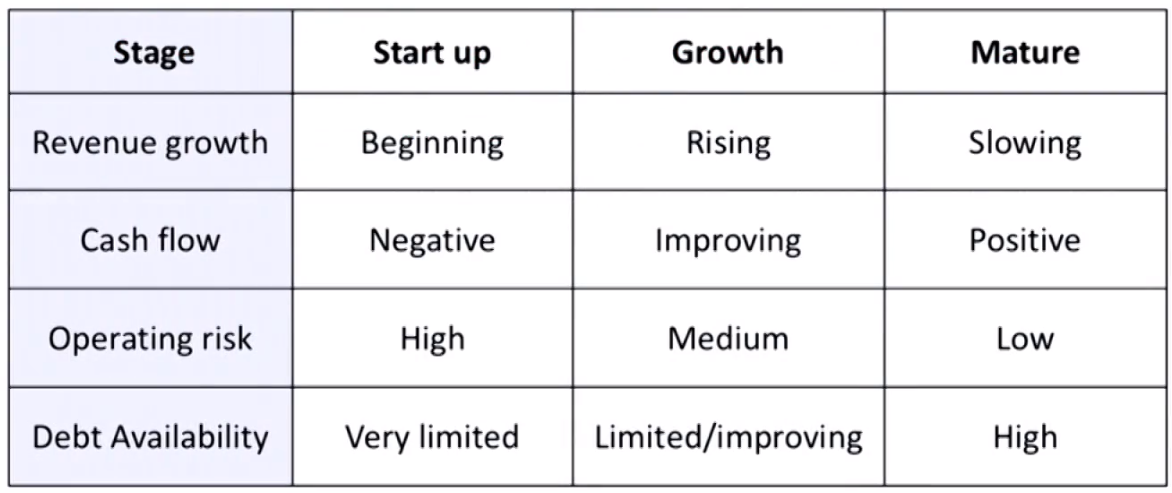
Capital Structure and Company Life Cycle
Unique situations
- Capital intensive businesses with marketable assets
- Real estate, utilities, shipping, and airlines
- tend to have higher leverage
- Capital-light businesses
- Software-based technology businesses
- tend to have lower leverage
Modigliani-Miller Propositions
Modiglianjand-Miller assumption
- Homogeneous expected cash flows同质化预期
- Perfect capital markets完美资本市场
- no transactions costs
- no taxes
- no bankruptcy costs
- and symmetric information
- Investors can borrow and lend at the risk-free rate无风险利率借贷
- No agency costs没有代理成本
- Independent financing decision & investment decision投融资决策互不干扰
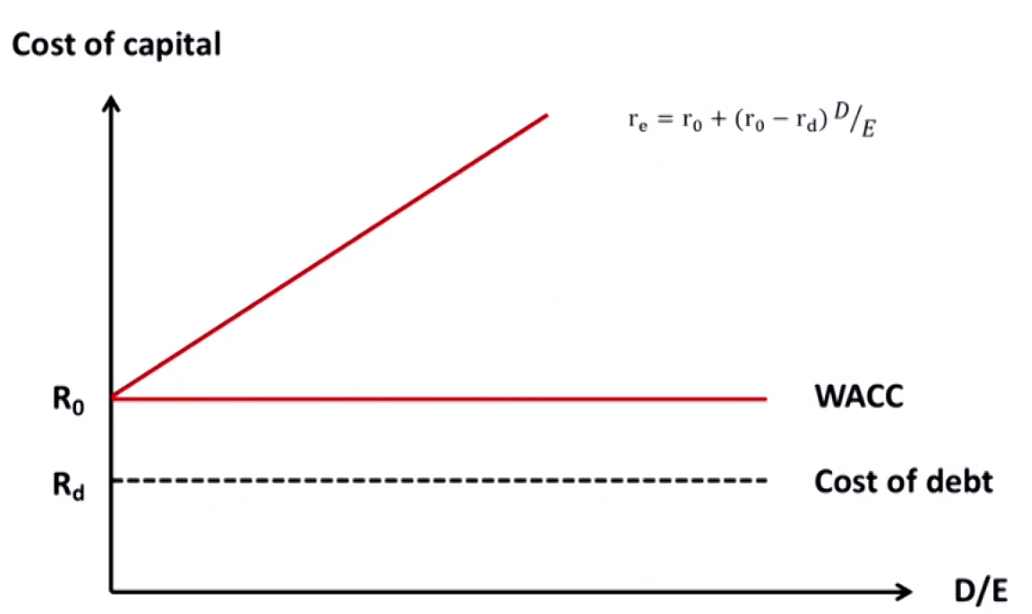
Modigliani and Miller Theory(without taxes)
- MM Proposition I:
- Capital structure irrelevance资本结构无所谓
V_{Levered} = V_{Unlevered} - MM Proposition II:
r_e=r_0+(r_0-r_d)\times\frac{D}{E}- r_0=cost of capital for all-equity company
- The cost of equity is a linear function of the company's debt/equity ratio
- WACC不随权重改变,恒为r_0
Modigliani and Miller Theory(with taxes)
- MM Proposition I:
V_{Levered} = V_{Unlevered} + t\times Debt- t=marginal tax rate, t\times Debt=debt tax shield
- A firm's optimal capital structure is all debt最优资本结构是全负债(因为税盾)
- MM Proposition II:
r_e=r_0+(r_0-r_d)(1-t)\times\frac{D}{E}- r_{WACC}\lt r_0
- WACC for the company with debt must be lower than that for the all-equity company
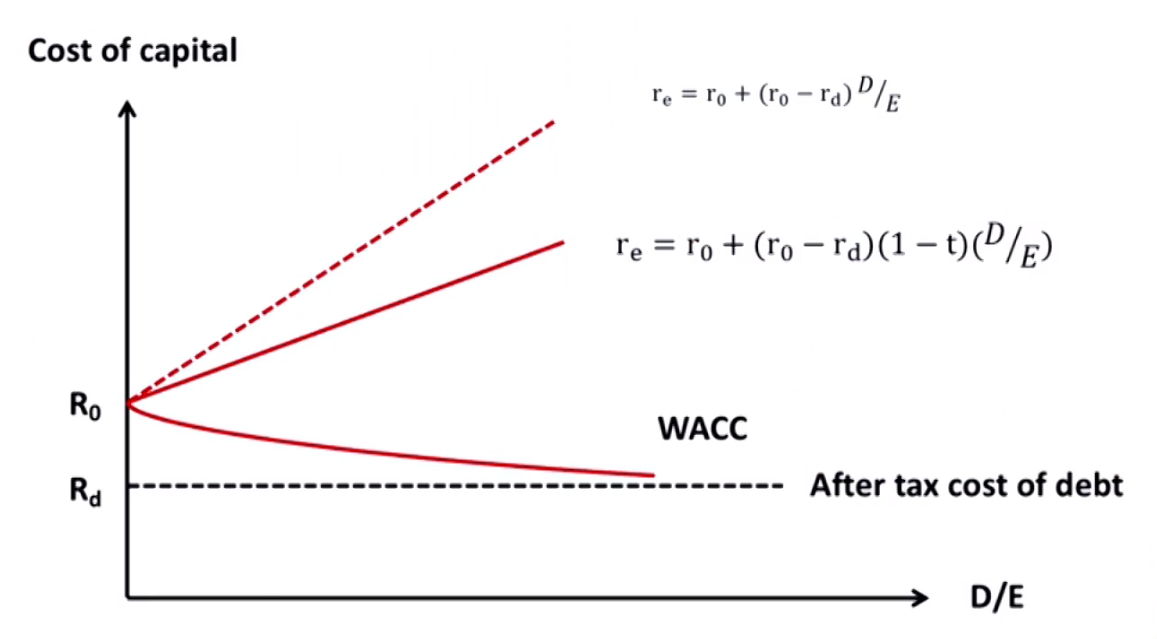
Other Factors Affecting Capital Structure Decision
Costs of financial distress负债高的坏处
- Direct costs: actual cash expenses associated with the bankruptcy process
- legal and administrative fees
- Indirect costs
- forgone失去 investment opportunities, impaired ability to conduct business, etc.
- Leverage increases → Probability of bankruptcy increases
Optimal capital structure
- Static trade-off theory of capital structure
\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{L}}=\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{U}}+\mathrm{t} \times \mathrm{Debt}-\mathrm{PV}\text{(costs of financial distress)}- Debt can be a significant portion because of tax-deductibility
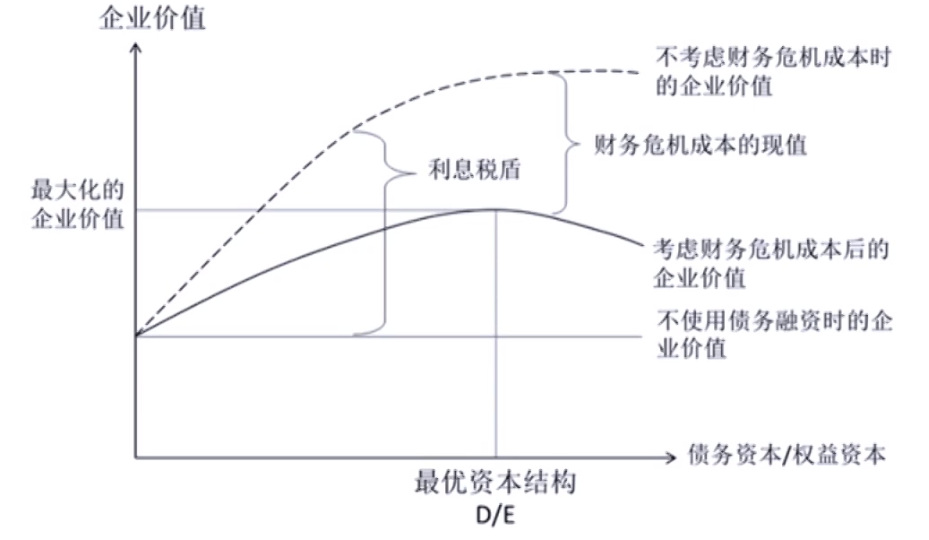
- Debt can be a significant portion because of tax-deductibility
Information asymmetric信息不对称成本
- The higher information asymmetric信息不对称, the higher returns demanded by both debt and equity capital suppliers信息不对称使得要求回报率高
- Pecking order theory(signaling model)
- Internal capital> Debt > External equity
Agency costs代理成本
- Agency theory predicts that an increase in use of debt results in a reduction in agency costs
- Monitoring costs are the costs borne by owners to monitor the management of the company监控代理人的成本
- Bonding costs are the costs borne by owners to assure that managements are working in the owner's best interest绑定利益的成本
- Michael Jensen's free cash flow hypothesis
- Higher debt levels discipline managers by reducing the company's free cash flow and thus management's opportunities to misuse cash
Leverage
Definition of Leverage
- A given change in one variable leads to a greater change in other variable because of fixed cost
- Operating leverage: created by fixed operating cost(e.g.depreciation and rent)
- Financial leverage: created by fixed financial cost(e.g. interest)
- Leverage increases the volatility of a company's earnings and cash flows (both up and down), as well as increases the risk of creditors or shareholders of a company.
- 股利不会带来杠杆
Measures of Leverage
Risk decomposition
- Business risk: the risk associated with operating earning, and is the combination of sales risk and operating risk
- Sales risk: uncertainty with respect to the price and quantity of goods and services
- Operating risk: risk attributed to the use of fixed cost in operation(e.g. rent, depreciation)
- Financial risk: the risk associated with how a company finances its operations
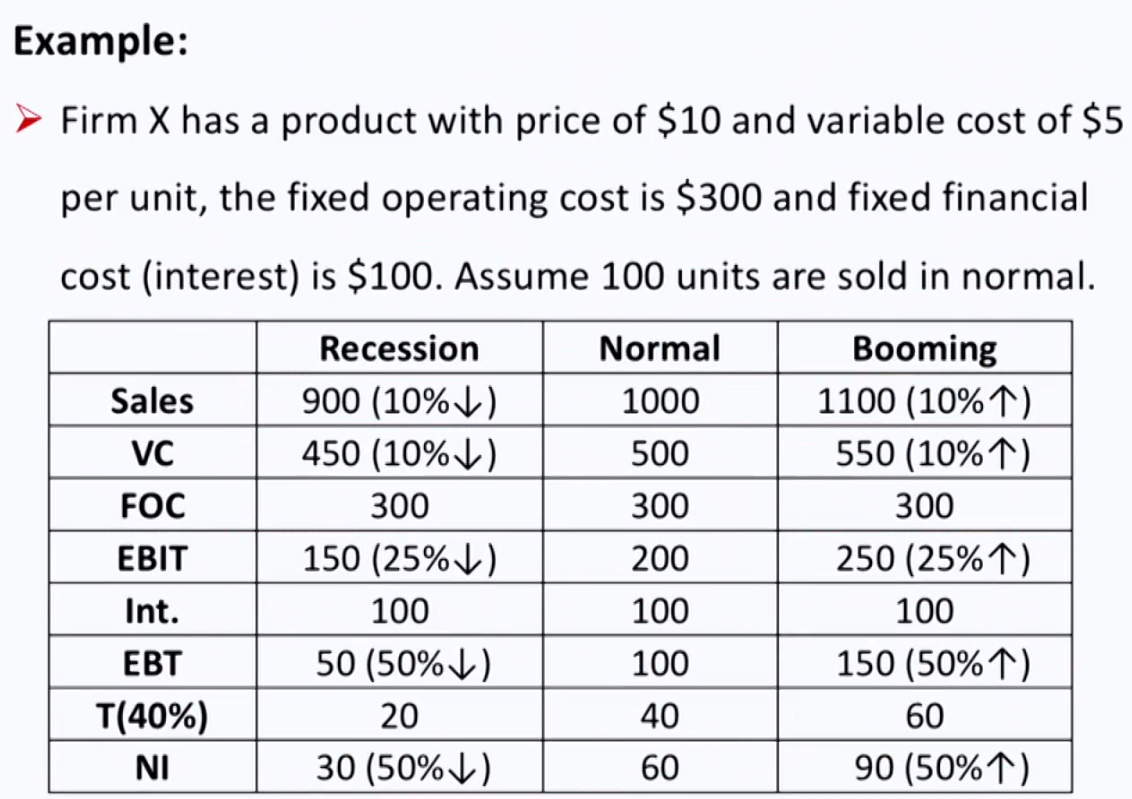
Degree of operating leverage (DOL 经营杠杆)
- DOL is a quantitative measure of the sensitivity of operating income to changes in revenues
\begin{aligned} & \mathrm{DOL}=\frac{\text { Percentage change in EBIT }}{\text { Percentage change in sales }}=\frac{\frac{\Delta \mathrm{EBIT}}{\mathrm{EBIT}}}{\frac{\Delta \mathrm{Q}}{\mathrm{Q}}} \\ & \mathrm{DOL}=\frac{\mathrm{Q}(\mathrm{P}-\mathrm{V})}{\mathrm{Q}(\mathrm{P}-\mathrm{V})-\mathrm{F}}=\frac{\text { Contribution margin }}{\text { Contribution margin }-\mathrm{F}}=\frac{\mathrm{EBIT}+\mathrm{F}}{\mathrm{EBIT}} \end{aligned}- If EBlT is positive and fixed operating cost is greater than 0,DOL is greater than 1
Degree of financial leverage(DFL 财务杠杆)
- DFL is a quantitative measure of the sensitivity of net income to changes in operating income.
\mathrm{DFL}=\frac{\text { Percentage change in NI }}{\text { Percentage change in EBIT }}=\frac{\frac{\Delta \mathrm{NI}}{\mathrm{NI}}}{\frac{\Delta \mathrm{EBIT}}{\text { EBIT }}}=\frac{\mathrm{EBIT}}{\text { EBIT }- \text { Int. }}- If interest is greater than 0, DFL is greater than 1.
- DFL is no affected by the tax rate because tax is not fixed cost.
Degree of total leverage (DTL)
- Measure of the sensitivity of net income to changes in the number of units produced and sold
- A combination of DOL and DFL
\begin{aligned} & \text { DTL }=\frac{\frac{\Delta \mathrm{NI}}{\mathrm{NI}}}{\frac{\Delta \text { Sales }}{\text { Sales }}}=\frac{\frac{\Delta \mathrm{EBIT}}{\text { EBIT }}}{\frac{\Delta \text { Sales }}{\text { Sales }}} \times \frac{\frac{\Delta \mathrm{NI}}{\mathrm{NI}}}{\frac{\Delta \mathrm{EBIT}}{\text { EBIT }}}=\mathrm{DOL} \times \mathrm{DFL} \\ & \mathrm{DTL}=\frac{\mathrm{Q}(\mathrm{P}-\mathrm{V})}{\mathrm{Q}(\mathrm{P}-\mathrm{V})-\mathrm{F}-\mathrm{Int} .}=\frac{\mathrm{EBIT}+\mathrm{F}}{\text { EBIT }- \text { Int. }} \end{aligned}
Breakeven point
- Breakeven point (Q_{BE}):quantity of sales at which the company's net income is zero
\mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{BE}}=\frac{\text { Fixed cost }}{\text { Unit contribution margin }}=\frac{\mathrm{F}+\text { Int. }}{\mathrm{P}-\mathrm{V}} - Operating breakeven point (Q_{OBE}):quantity of sales at which the company's operating income is zero
\mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{OBE}}=\frac{\text { Fixed operating cost }}{\text { Unit contribution margin }}=\frac{\mathrm{F}}{\mathrm{P}-\mathrm{V}}
Corporate Structures and Ownership & Business Models
Corporate Structures商业结构 and Owners所有人
Classification of business structure
企业大于公司
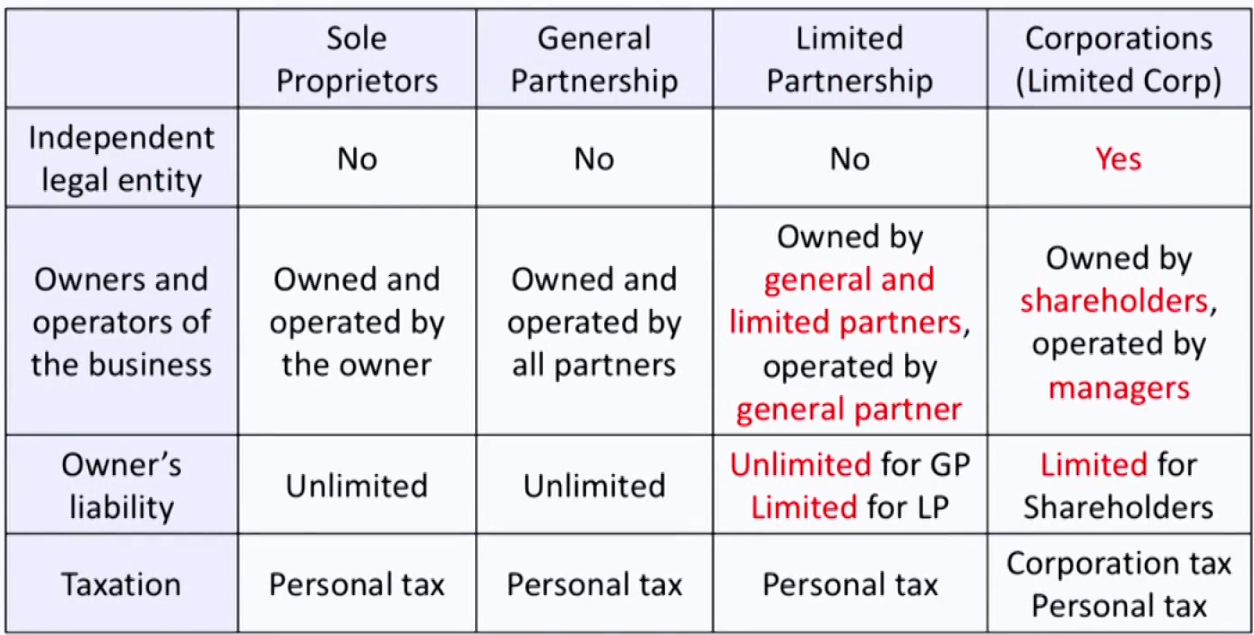
- 独资企业
- 普通合伙企业(只有一种合伙人GP出资)
- 有限合伙企业(还有有限合伙人LP出资)
- 有限责任公司
Classification of corporation
- Nonprofits非营利性公司: might generate profits, but profits cannot be paid out as dividends没有股东,利润免税,只能再投资
- For-Profits: profit seeking business entity
- Private非上市
- Public上市: exchange listed company,or the number of its shareholder is greater than certain amount
Difference between private and public company
- Exchange listing and share ownership transfer
- Private: not trade on exchange, difficult to transfer shares
- Public: trade on exchange, easy to transfer shares
- Registration and disclosure requirements
- Private: meets registration requirements
- Public: meets registration, mandated disclosure and exchange listing requirements
- Share issuance
- Private: issue shares through private placement私下配售 with a legal document “Private Placement Memorandum(PPM 私下配售备忘录)" to accredited investors合格投资者
- Public: issue shares in the capital market公开增发 with much larger size capital raised
Public and private company conversion
- Private to Public
- Initial Public Offering (IPO首次公开募股发行)
- Direct Listing (DL直接上市):
No investment bank involved不需要投行,速度快成本低
No new capital is raised没有发行新股 - Acquisition并购
Acquired by a public company 被已上市公司并购
Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC)
- Public to Private私有化
- Leveraged Buyout (LBO杠杆收购)
- Management Buyout (MBO管理层收购)
Trends in public and private companies
- Emerging markets: number of public companies increases
- Developed markets: number of public companies declines
- Mergers and acquisitions
- LBOs and MBOs
- Private companies remain private
Easy to access capital in private markets
Avoid the regulatory burdens
Avoid public investors' short-term focus
Greater decision-making flexibility
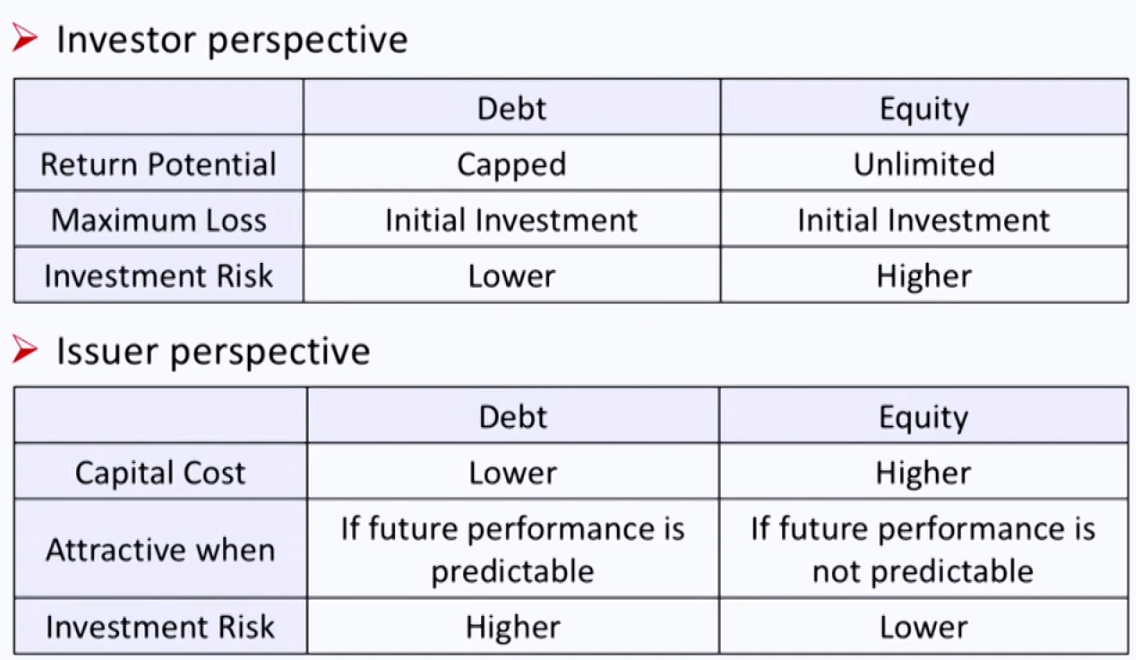
Differences between lenders and owners
- Lenders (debtholders) have
- Priority claims over principal and interest
- No voting power
- Legal standing to force bankruptcy and liquidation
破产保护,期间债权人必须等着
破产清算,砸锅卖铁还债
破产重组,原股东扫地出门,债权人变成新股东
- Owners (shareholders) have
- Residual claims over net asset and dividend
- Voting power
Business Models & Risks
Business Model Features
- Value proposition价值主张
- Customers客户与市场(who)
- Firm offering企业提供的产品和服务(what)
- Channels渠道(where)
Direct sales strategy直销: disintermediate没有中间商,cost-effective
Agency代销: drop shipping
Omnichannel strategy全渠道,线上+线下 - Pricing定价(how much)
Premium, parity, discount
Price setter价格制定者, price taker
A company with little differentiation in products and high price sensitivity is a price taker and it's not appropriate to take premium pricing.
- Value chain价值链条: 单个企业本身如何为客户创造价值
- Supply chain供应链: 企业内外部生产产品或提供服务的整个过程。在外部,可能涉及多个企业
- 盈利水平(profitability)
- 利润率(profit margin)
- 单位收益与单位成本(unit economics)
- 盈亏平衡点(break-even points)
Pricing定价策略
- Pricing and revenue models定价模型
- Value-based pricing基于客户获得的价值进行定价
- Cost-based pricing基于发生的成本进行定价
- Price discrimination价格歧视
- Auction/reverse auction models根据人
- Tiered pricing分级定价。如批发
- Dynamic pricing动态定价。根据时间
- Auction/Reverse auction models拍卖/逆向拍卖
- Pricing for multiple products多产品定价
- Bundling捆绑销售
- Razors-and-blades pricing“剃刀-刀片"定价。本体便宜而配套消耗品高定价
- Optional product pricing可选商品定价。加购同类或配套产品有优惠
- Pricing for rapid growth追求高速增长的定价
- Penetration pricing渗透定价。低价抢占份额
- Freemium pricing免费模式。提供免费版和付费版,如游戏氪金
- Hidden revenue business models隐性收入模式。表面免费,如微信抖音等传媒业
- Alternatives to ownership购买的替代
- Recurring revenue/subscription pricing订阅。如会员模式
- Fractionalization分解。碎片化出租服务,空间上(如写字楼)和时间上(如共享单车)
- Leasing租赁
- Licensing授权。无形资产提供,如版权专利
- Franchising特许经营。比授权更全面,不仅包括无形资产
Profitability and unit economics
- Operating profit/margin经营利润率
- Unit economics
- Revenues and costs in per-unit basis
- Break-even point盈亏平衡销量
Business Model Types
- Business model variations商业模式的变动
- Private label or “contract” manufacturers自有品牌
- Licensing arrangements贴牌加工
- Value added resellers增值销售。提供附加服务,如4s店
- Franchise models特许经营
- E-Commerce business models电子商务的商业模式
- Affiliate marketing: performance marketing联盟营销。如微信选择优质伙伴,提供流量然后收取利益
- Marketplace businesses: without ownership of products交易平台。如淘宝,不参与经营
- Aggregators: re-markets products and services聚合模式。交易平台的升级,有自有品牌,如京东自营,参与经营
- Network effects网络效应 and platform business models
- increasing value of a network to its users as more users join.具有正外部性
- One-sided同质如微信 network effects
- Two-sided异质如淘宝 or multi-sided network effects
- Crowdsourcing business models众包业务模式。买方参与卖方的产品通过,如UGC
- Hybrid business models混合模式
Financial lmplication影响融资
- External factors
- Economic conditions宏观环境
- Demographic trends人口趋势
- Sector demand characteristics vary by industry行业需求特征,如刚需
- Industry cost characteristics行业成本,资本密集型或轻资产
- Political, legal, and regulatory environment法律监管因素
- Social and political trends社会趋势
- Firm-specific factors
- Stage of development of the business所处阶段,如初创
- Competitive position竞争地位,如品牌优势
- Business model商业模式
Asset-light business models轻资产
Lean startups精益创业,外包一切
Pay-in-advance预收款,下游预售+上游赊购
Risks
-
Marco risk宏观风险
- Impact all businesses
- Industries that are more sensitive to economic activities have a higher level of macro risk.
-
Business risk业务风险
- Industry risks行业风险
Cyclicality行业周期
Industry structure行业结构
Competitive intensity行业集中度
Competitive dynamics within the value chain波特五力
Long-term growth and demand outlook前景 - Company-specific risks公司风险
Execution risk: management执行风险
Capital investment risk:sub-optimal investment投资不有效
ESG risk: governance risk环保社会公司治理
Operating leverage经营杠杆
Product market risk产品上市风险
Competitive risk竞争风险Cost advantages规模效应
Product or service differentiation差异化
Network effects正反馈
Switching barriers转化障碍
- Industry risks行业风险
-
Financial risk财务风险
- Financial leverage
- Total leverage
Corporate Govenance and ESG
Stakeholder Groups
Definition of corporate governance
- Corporate governance is the system of internal controls and procedures by which individual companies are managed
- Shareholder theory takes the view that the most important responsibility of a company's managers is to maximize shareholder's profits
- Stakeholder theory focuses on the interest of all stakeholder groups, and try to minimize and manage the conflicting interests between stakeholders
Stakeholder groups
- Shareholders
- Board of directors
- Some companies have staggered boards交错改选,每次只允许更换一部分董事
- Managers and employees
- Creditors
- Suppliers
- Customers
- Government
Corporate governance theories
- Shareholder theory: the most important responsibility of a company's managers to maximize shareholder value
- Stakeholder theory: consider the interests of not only its shareholders, but also its customers, suppliers, employees,and others who have an interest in the company
Relationships Between Stakeholders
Principal-agent relationship委托代理关系
- Shareholder vs. Management/Board of directors
- Conflicts of interest
Entrenchment极度的保守
Excessive risk taking激进 (if giving management too many stock grants and options)
Empire building盲目扩张 - Agency costs
- Conflicts of interest
Other relationships
- Controlling控股股东 vs. Minority shareholder少数股东
- Voting rights(e.g., takeover transactions收购交易)
- Manager vs. Board
- Information asymmetries信息不透明
- Shareholders vs.Creditor(Debtholder)
- Different structure of risks and returns风险承受能力不同
Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management
- Involves identifying, understanding, and prioritizing the interests of stakeholder groups, then managing the company's relationships with these groups
- Need to reflect legal, contractual, organizational, and governmental infrastructure that defines the rights,responsibilities, and powers of each group
Mechanisms of stakeholder management
- Shareholder mechanisms
- Board of director and management mechanisms
- Employee mechanisms
- Creditor mechanisms
- Customer and supplier mechanisms
- Government mechanisms
Shareholder mechanisms
- Shareholder meetings股东大会
- Annual general meeting(AGM,年度股东大会)
- Extraordinary general meeting(EGM,临时股东大会)
公司章程修订、兼并收购、变卖重大资产业务
需要更多投票 - Proxy voting: authorize another to vote代理投票
- Voting process:Straight voting vs. Cumulative voting利于中小股东
- Unequal voting rights: Dual-share classes同股不同权
- Corporate reporting and transparency披露财报
- Shareholder activism (e.g., hedge funds)股东参与管理
- Shareholder derivative lawsuits股东诉讼
- Corporate takeovers企业收购
- Tender offers要约收购
- Proxy fight代理权争夺战
- Hostile takeover恶意收购 & anti-takeover measures反收购
Board of director mechanisms - committees
- Audit committee审计委员会: oversee the audit and control systems at the company and ensure their effectiveness. Supervising the internal audit function, recommending external auditors.
- Composed of independent directors only.
- Remuneration/Compensation committee薪酬委员会: develops and proposes remuneration policies for the directors and key executives, with shareholders' say on pay股东对高管薪酬有话语权.
- Majority of members should be independent.
- Governance committee治理委员会: ensure that the company adopts good corporate governance practices.
- Nomination committee提名委员会: nominate candidates as directors and senior executives, for election by shareholders.
- Risk committee风险管理委员会: assists the board in determining the risk policy, profile, and appetite of the company.
- Investment committee投资委员会: reviews material investment opportunities and considers their viability
Creditor mechanisms
- Bond indenture(e.g., covenants条款, collaterals抵押品)
- Corporate reporting and transparency
- Creditor committees
Government Mechanisms
- Laws & regulations
- Common law(better protection for equity & debtholders)
- Civil law
- Corporate governance codes as guiding principles
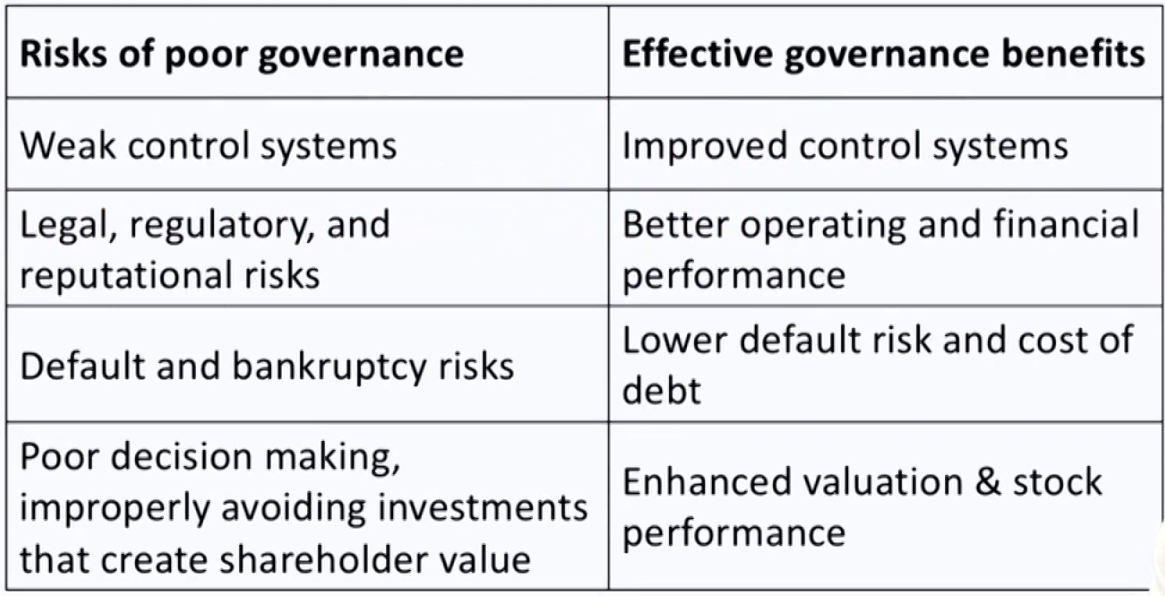
Corporate Governance Risks & Benefits
Other ESG Considerations
ESG integration/ESG investing
- The practice of considering environmental, social, and governance factors in the investment process
- Also referred to as:
- Sustainable Investing (SI)
- Responsible Investing(RI)
- Social Responsible Investing(SRI)
ESG implementation methods
- Negative screening: exclude certain sectors companies that violate accepted standards in ESG concerns不投黑名单
- Positive screening/best-in-class approaches: focus on investments with favorable ESG aspects, aims to identify companies that embrace solid ESG-related principles in their operations and strategies投白名单
- Full integration into individual stock valuation is the explicit inclusion of ESG factors into traditional financial analysis of individual stocks (e.g., as inputs into cash flow forecasts and/or cost-of-capital estimates)将ESG融入投资决策中
- Thematic investing主题投资:is investment in themes or assets specifically related to ESG factors, such as clean energy, green technology, or sustainable agriculture围绕符合ESG主题的公司投资
- Engagement/active ownership: Uses shareholder power to influence corporate behavior收购股份然后要求公司做ESG
- Impact investing影响投资: Seeks to achieve targeted social or environmental objectives along with measurable financial returns投资需要达到自己设定的ESG目的